Adolescent Build Plotting on Body Composition Chart and the Type of Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. scchung@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2157951
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1385
Abstract
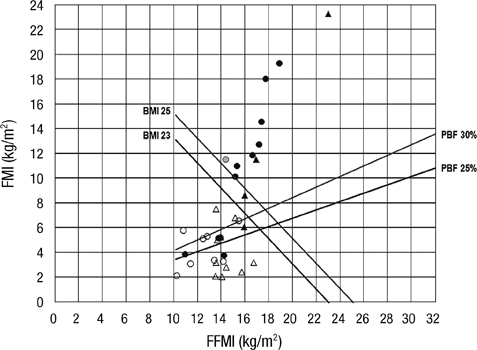
- Although the prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing, there are cases difficult to categorize into certain type in pediatric diabetic patients. The aims of this study were to detect and choose a proper treatment modality for atypical cases of diabetes mellitus, using the body composition chart. We conducted a retrospective study from August 2005 to 2012 with patients who visited Konkuk University Medical Center, and were diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. The medical records were reviewed for the anthropometric data and indices of body composition. The subjects were grouped by the type of diabetes and gender. We constructed a body composition chart plotting fat free mass index and fat mass index (FMI). Body mass index and all body composition indices were higher in type 2 diabetes, in each gender in analysis with Mann-Whitney test. Significant determinant of diabetes type was revealed as FMI and contributing factors on FMI were analyzed with regression analysis. Six atypical cases were identified by a body composition chart including non-obese type 2 diabetes showing suboptimal growth with lower BMI related to relatively lower insulin secretion and type 1 diabetes with insulin resistance resulted from obesity. Body composition chart analysis might be useful in characterization of diabetes type and detection of atypical cases and early adjustment of diabetes management strategy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Reference Values of Body Composition Indices: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Hye Won Park, Ha Yeong Yoo, Chul-Hyun Kim, Hyeoijin Kim, Byung Ok Kwak, Kyo Sun Kim, Sochung Chung
Yonsei Med J. 2015;56(1):95-102. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.95.Therapeutic approaches to obesity and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents
Sochung Chung
J Korean Med Assoc. 2018;61(10):599-606. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2018.61.10.599.Body mass index and body composition scaling to height in children and adolescent
Sochung Chung
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2015;20(3):125-129. doi: 10.6065/apem.2015.20.3.125.Application of body composition zones in boys with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Minhye Choi, Seonhwa Lee, Sun Hwan Bae, Sochung Chung
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019;24(4):243-247. doi: 10.6065/apem.2019.24.4.243.
Reference
-
1. Macaluso CJ, Bauer UE, Deeb LC, Malone JI, Chaudhari M, Silverstein J, Eidson M, Goldberg RB, Gaughan-Bailey B, Brooks RG, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus among Florida children and adolescents, 1994 through 1998. Public Health Rep. 2002. 117:373–379.2. Rosenbloom AL, Joe JR, Young RS, Winter WE. Emerging epidemic of type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:345–354.3. Hathout EH, Thomas W, El-Shahawy M, Nahab F, Mace JW. Diabetic autoimmune markers in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Pediatrics. 2001. 107:e102.4. Jones KL. Role of obesity in complicating and confusing the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes in children. Pediatrics. 2008. 121:361–368.5. Drake AJ, Smith A, Betts PR, Crowne EC, Shield JP. Type 2 diabetes in obese white children. Arch Dis Child. 2002. 86:207–208.6. Keller N, Bhatia S, Braden JN, Gildengorin G, Johnson J, Yedlin R, Tseng T, Knapp J, Glaser N, Jossan P, et al. Distinguishing type 2 diabetes from type 1 diabetes in african American and Hispanic American pediatric patients. PLoS ONE. 2012. 7:e32773.7. Kang HW, Kim DJ, Lee MS, Kim KW, Lee MK. Pathophysiologic heterogeneity in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korean subjects. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2005. 69:180–187.8. Lee BW, Kim SY, Kim JY, Cho KY, Chung YJ, Min YK, Chung JH, Lee MK, Lee MS, Kim KW. Heterogeneity of early-onset and ketosis-resistant diabetes in Korean subjects--is it possible to determine cut-off age of early-onset type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2005. 70:38–45.9. Hannon TS, Janosky J, Arslanian SA. Longitudinal study of physiologic insulin resistance and metabolic changes of puberty. Pediatr Res. 2006. 60:759–763.10. Kyle UG, Schutz Y, Dupertuis YM, Pichard C. Body composition interpretation: contributions of the fat-free mass index and the body fat mass index. Nutrition. 2003. 19:597–604.11. World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and managing the global epidemic. 2000. Geneva: World Health Organization.12. Okorodudu DO, Jumean MF, Montori VM, Romero-Corral A, Somers VK, Erwin PJ, Lopez-Jimenez F. Diagnostic performance of body mass index to identify obesity as defined by body adiposity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010. 34:791–799.13. Heymsfield SB, Heo M, Thomas D, Pietrobelli A. Scaling of body composition to height: relevance to height-normalized indexes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011. 93:736–740.14. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2010. Diabetes Care. 2010. 33:S11–S61.15. Diabetes mellitus. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1985. 727:1–113.16. Yoo EG, Shin HJ, Kim DH. The clinical types and characteristics of diabetes mellitus in Korean Children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2000. 43:1591–1598.17. Lee SY, Gallagher D. Assessment methods in human body composition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008. 11:566–572.18. Keys A, Fidanza F, Karvonen MJ, Kimura N, Taylor HL. Indices of relative weight and obesity. J Chronic Dis. 1972. 25:329–343.19. Wang Z, Zhang J, Ying Z, Heymsfield SB. New insights into scaling of fat-free mass to height across children and adults. Am J Hum Biol. 2012. 24:648–653.20. Hattori K, Tatsumi N, Tanaka S. Assessment of body composition by using a new chart method. Am J Human Biol. 1997. 9:573–578.21. Naylor R, Philipson LH. Who should have genetic testing for maturity-onset diabetes of the young? Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2011. 75:422–426.22. Forbes GB. The companionship of lean and fat. Basic Life Sci. 1993. 60:1–14.23. Maynard LM, Wisemandle W, Roche AF, Chumlea WC, Guo SS, Siervogel RM. Childhood body composition in relation to body mass index. Pediatrics. 2001. 107:344–350.24. Reaven GM. Banting Lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. 1988. Nutrition. 1997. 13:65.25. Schooling CM, Jiang C, Zhang W, Lam TH, Cheng KK, Leung GM. Adolescent Build and Diabetes: The Guangzhou Biobank Cohort Study. Ann Epidemiol. 2011. 21:61–66.26. Rosenthal M, Haskell WL, Solomon R, Widstrom A, Reaven GM. Demonstration of a relationship between level of physical training and insulin-stimulated glucose utilization in normal humans. Diabetes. 1983. 32:408–411.27. Jumpertz R, Thearle MS, Bunt JC, Krakoff J. Assessment of non-insulin-mediated glucose uptake: association with body fat and glycemic status. Metabolism. 2010. 59:1396–1401.28. Moran A, Jacobs DR, Steinberger J, Hong CP, Prineas R, Luepker R, Sinaiko AR. Insulin resistance during puberty: results from clamp studies in 357 children. Diabetes. 1999. 48:2039–2044.29. Wolff-McDonagh P, Kaufmann J, Foreman S, Wisotsky S, Wisotsky JA, Wexler C. Using insulin pump therapy in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2010. 36:657–665.30. Conway B, Miller RG, Costacou T, Fried L, Kelsey S, Evans RW, Orchard TJ. Temporal patterns in overweight and obesity in type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2010. 27:398–404.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Body Composition Analysis in Newly Diagnosed Diabetic Adolescent Girls
- Body Composition and Obesity in Korean Adolescents and its Impact on Diabetes Mellitus
- Body Composition and Diabetes
- Pharmacothearpy of Adolescents with Diabetes
- Therapeutic approaches to obesity and metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents