Acute Diffuse Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jhhwang@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Thoracic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2157863
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.10.1532
Abstract
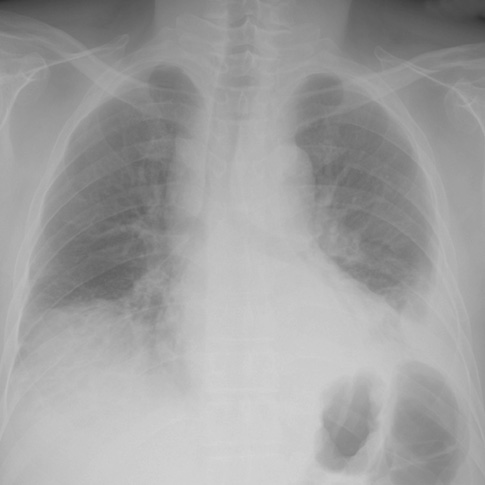
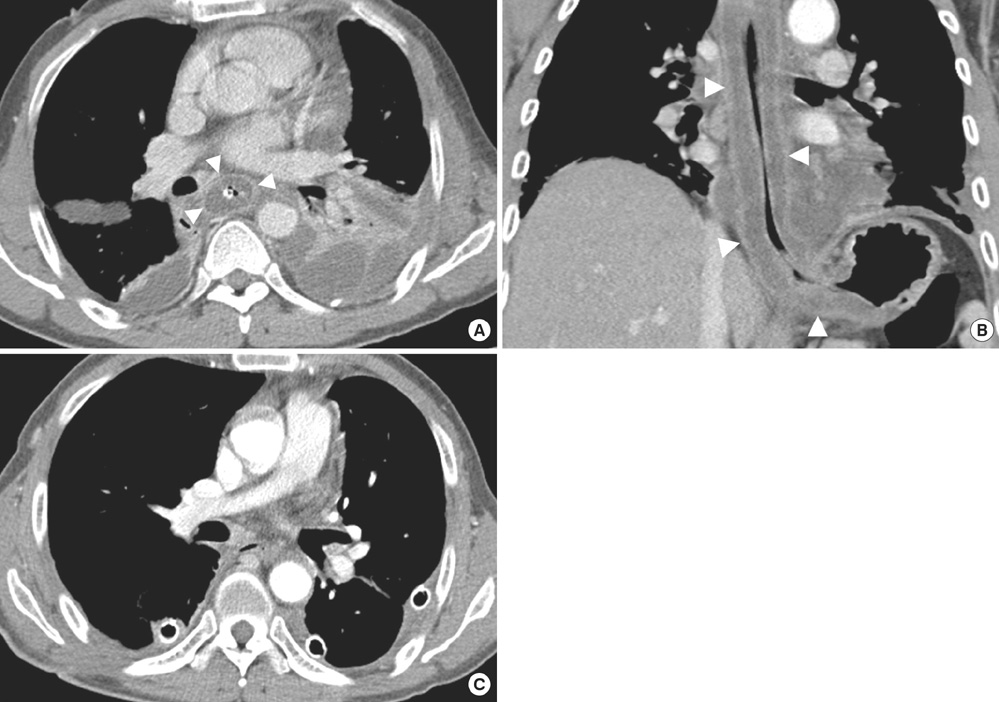
- Acute phlegmonous infection of the gastrointestinal tract is characterized by purulent inflammation of the submucosa and muscular layer with sparing of the mucosa. The authors report a rare case of acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis, which was well diagnosed based on the typical chest computed tomographic (CT) findings and was successfully treated. A 48-yr-old man presented with left chest pain and dyspnea for three days. Chest radiograph on admission showed mediastinal widening and bilateral pleural effusion. The patient became febrile and the amount of left pleural effusion is increased on follow-up chest radiograph. Left closed thoracostomy was performed with pus drainage. A CT diagnosis of acute phlegmonous esophagogastritis was suggested and a surgery was decided due to worsening of clinical condition of the patient and radiologic findings. Esophageal myotomies were performed and the submucosal layer was filled with thick, cheesy materials. The patient was successfully discharged with no postoperative complication.
MeSH Terms
-
Acute Disease
Cellulitis/complications/*diagnosis/radiography
Drainage
Esophagitis/complications/*diagnosis/surgery
Gastritis/complications/*diagnosis/surgery
Humans
Klebsiella Infections/diagnosis
Klebsiella pneumoniae/isolation & purification
Male
Middle Aged
Pleural Effusion/etiology/radiography
Thoracostomy
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Acute Phlegmonous Esophagitis with Mediastinitis Complicated by an Esophageal Perforation: A Case Report
Hye Soo Shin, Song Soo Kim, Jin Hwan Kim
J Korean Soc Radiol. 2018;79(1):45-49. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2018.79.1.45.Acute Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis
Taehoon Kim, Yeon Namgung, Sun Young Jeong, Sun-Jin Boo
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2019;73(4):239-241. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.4.239.Two Cases of Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis in New Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jae Woong Yoon, Chei Won Kim, Min Ju Kim, Hae Yoon Kwon, Shin Il Kim, Si Nae Lee, Seongbin Hong, Kyung-Hee Lee, Ju Young Han, So Hun Kim, Moonsuk Nam, Yong Seong Kim
J Korean Diabetes. 2015;16(2):153-159. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2015.16.2.153.급성 봉소염성 식도염의 합병증으로 발생한 식도 내 농양의 내시경적 배액술 후 발생한 식도내강의 협착: 증례 보고
Min Ji Kim, Dae Gon Ryu, Su Bum Park, Cheol Woong Choi, Hyung Wook Kim, Su Jin Kim
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2022;80(6):262-266. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2022.098.Treatment of phlegmonous esophagitis in various patients: a case series
Han Sol Lee, Chul Ho Lee, Yun-Ho Jeon
J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2023;40(4):442-447. doi: 10.12701/jyms.2023.00136.
Reference
-
1. Hsu CY, Liu JS, Chen DF, Shih CC. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: report of a survived case. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996. 43:1347–1352.2. Wakayama T, Watanabe H, Ishizaki Y, Okuyama T, Ogata H, Tanigawa K, Kawahara Y. A case of phlegmonous esophagitis associated with diffuse phlegmonous gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994. 89:804–806.3. Lee CR, Lee JH, Choi SJ, Lee DS, Kim WS, Han SR, Chung NW, Park HS, Choi SH. A case of acute phlegmonous esophagitis. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2000. 20:119–123.4. Yun CH, Cheng SM, Sheu CI, Huang JK. Acute phlegmonous esophagitis: an unusual case (2005: 8b). Eur Radiol. 2005. 15:2380–2381.
Article5. Jung C, Choi YW, Jeon SC, Chung WS. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: radiologic diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:862–863.
Article6. Kim GY, Ward J, Henessey B, Peji J, Godell C, Desta H, Arlin S, Tzagournis J, Thomas F. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005. 61:168–174.
Article7. Jung JH, Choi HJ, Yoo J, Kang SJ, Lee KY. Emphysematous gastritis associated with invasive gastric mucormycosis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:923–927.
Article8. Mann NS, Borkar BB, Mann SK. Phlegmonous esophagitis associated with epiphrenic diverticulum. Am J Gastroenterol. 1978. 70:510–513.9. I H, Park CS, Kim YD. Treatment of phlegmonous esophagitis combined with mediastinitis. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007. 40:711–714.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of phlegmonous esophagitis in various patients: a case series
- Two Cases of Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis in New Onset Type 2 Diabetes
- Acute Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis
- Acute Phlegmonous Esophagitis with Mediastinitis Complicated by an Esophageal Perforation: A Case Report
- Phlegmonous Esophagitis Treated with Internal Drainage and Feeding Jejunostomy