Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Apr;73(4):239-241. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.4.239.
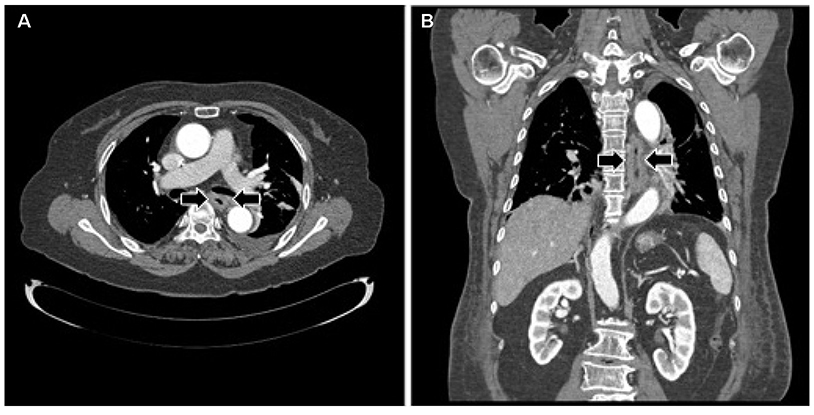
Acute Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. sunjinboo@jejunu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2443639
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.4.239
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huang YC, Cheng CY, Liao CY, Hsueh C, Tyan YS, Ho SY. A rare case of acute phlegmonous esophagogastritis complicated with hypopharyngeal abscess and esophageal perforation. Am J Case Rep. 2017; 18:125–130.
Article2. Kim GY, Ward J, Henessey B, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:168–174.
Article3. Hsu CY, Liu JS, Chen DF, Shih CC. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: report of a survived case. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996; 43:1347–1352.4. Jung C, Choi YW, Jeon SC, Chung WS. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: radiologic diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:862–863.
Article5. Kim HS, Hwang JH, Hong SS, et al. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1532–1535.
Article6. Yun CH, Cheng SM, Sheu CI, Huang JK. Acute phlegmonous esophagitis: an unusual case (2005: 8b). Eur Radiol. 2005; 15:2380–2381.
Article7. Woo WG, Do YW, Lee GD, Lee SS. Phlegmonous esophagitis treated with internal drainage and feeding jejunostomy. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017; 50:453–455.
Article8. Hu DC, McGrath KM, Jowell PS, Killenberg PG. Phlegmonous gastritis: successful treatment with antibiotics and resolution documented by EUS. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 52:793–795.
Article9. Kim NY, Park JS, Lee KJ, Yun HK, Kim JS. A case of acute phlegmonous gastritis causing gastroparesis and cured with medical treatment alone. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:309–314.
Article10. Chang PC, Wang WL, Hwang TZ, Cheng YJ. Intramural dissection with mucosal rupture alleviating phlegmonous esophagitis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012; 41:442–444.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Diffuse Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis: A Case Report
- Treatment of phlegmonous esophagitis in various patients: a case series
- Two Cases of Phlegmonous Esophagogastritis in New Onset Type 2 Diabetes
- Two Cases of Acute Phlegmonous Gastritis
- Acute Phlegmonous Esophagitis with Mediastinitis Complicated by an Esophageal Perforation: A Case Report