J Korean Soc Radiol.
2018 Jul;79(1):45-49. 10.3348/jksr.2018.79.1.45.
Acute Phlegmonous Esophagitis with Mediastinitis Complicated by an Esophageal Perforation: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. haneul88@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2416405
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.1.45
Abstract
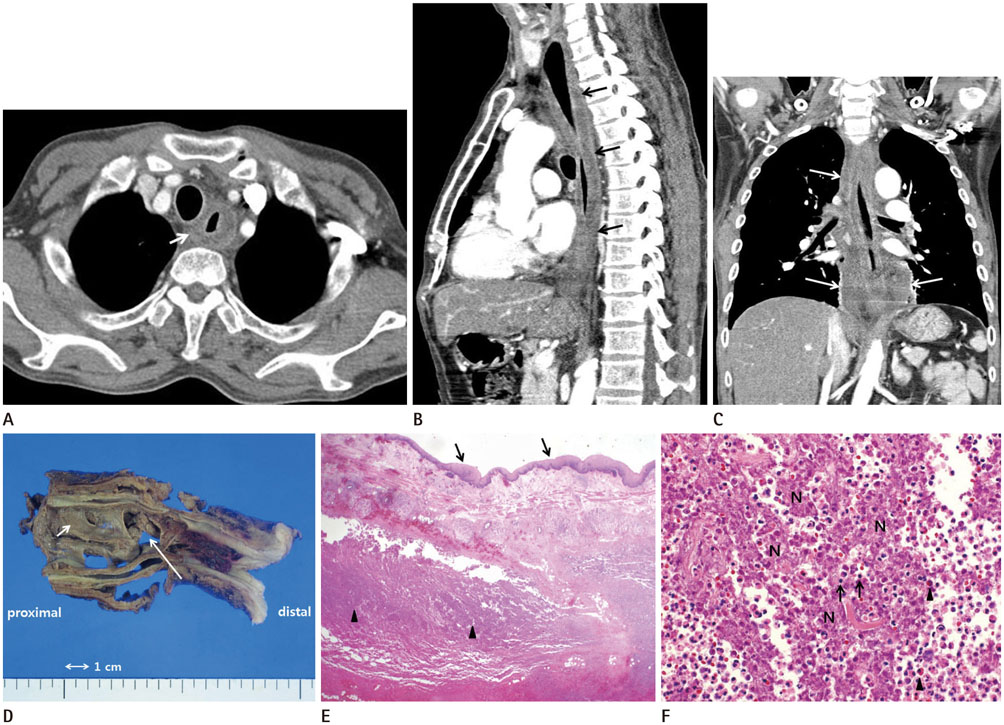
- Phlegmonous esophagitis, a rare and life-threatening disorder, is characterized by bacterial infection of the submucosal and muscularis layers of the esophagus. Herein we report a case of acute phlegmonous esophagitis with mediastinitis complicated by an esophageal perforation in a patient with diabetes mellitus and alcoholic liver cirrhosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huang YC, Cheng CY, Liao CY, Hsueh C, Tyan YS, Ho SY. A rare case of acute phlegmonous esophagogastritis complicated with hypopharyngeal abscess and esophageal perforation. Am J Case Rep. 2017; 18:125–130.
Article2. Wakayama T, Watanabe H, Ishizaki Y, Okuyama T, Ogata H, Tanigawa K, et al. A case of phlegmonous esophagitis associated with diffuse phlegmonous gastritis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994; 89:804–806.3. Hsu CY, Liu JS, Chen DF, Shih CC. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: report of a survived case. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996; 43:1347–1352.4. Yun CH, Cheng SM, Sheu CI, Huang JK. Acute phlegmonous esophagitis: an unusual case (2005: 8b). Eur Radiol. 2005; 15:2380–2381.
Article5. Jung C, Choi YW, Jeon SC, Chung WS. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: radiologic diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:862–863.
Article6. Karimata H, Nishimaki T, Oshita A, Nagahama M, Shimoji H, Inamine M, et al. Acute phlegmonous esophagitis as a rare but threatening complication of chemoradiotherapy: report of a case. Surg Today. 2014; 44:1147–1151.
Article7. Kim GY, Ward J, Henessey B, Peji J, Godell C, Desta H, et al. Phlegmonous gastritis: case report and review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:168–174.
Article8. Kim HS, Hwang JH, Hong SS, Chang WH, Kim HJ, Chang YW, et al. Acute diffuse phlegmonous esophagogastritis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1532–1535.
Article9. Lee CR, Lee JH, Choi SJ, Lee DS, Kim WS, Han SR, et al. [A case of acute phlegmonous esophagitis]. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 20:119–122.10. Isik A, Firat D, Peker K, Sayar I, Idiz O, Soytürk M. A case report of esophageal perforation: complication of nasogastric tube placement. Am J Case Rep. 2014; 15:168–171.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Phlegmonous Esophagitis Combined with Mediastinitis
- Treatment of phlegmonous esophagitis in various patients: a case series
- Mediastinitis and Pneumomediastinum in a Preterm Infant with Iatrogenic Esophageal Perforation: A Case Report
- Esophageal Stricture after Endoscopic Drainage of Esophageal Abscess as a Complication of Acute Phlegmonous Esophagitis: A Case Report
- Phlegmonous Esophagitis Treated with Internal Drainage and Feeding Jejunostomy