J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Oct;25(10):1506-1512. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.10.1506.
Toll-like Receptors and Antimicrobial Peptides Expressions of Psoriasis: Correlation with Serum Vitamin D Level
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. esl@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2157857
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.10.1506
Abstract
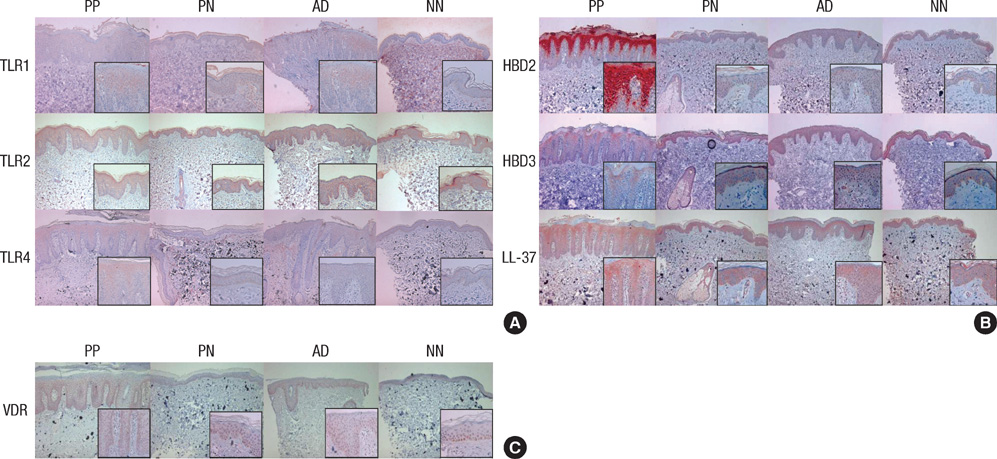
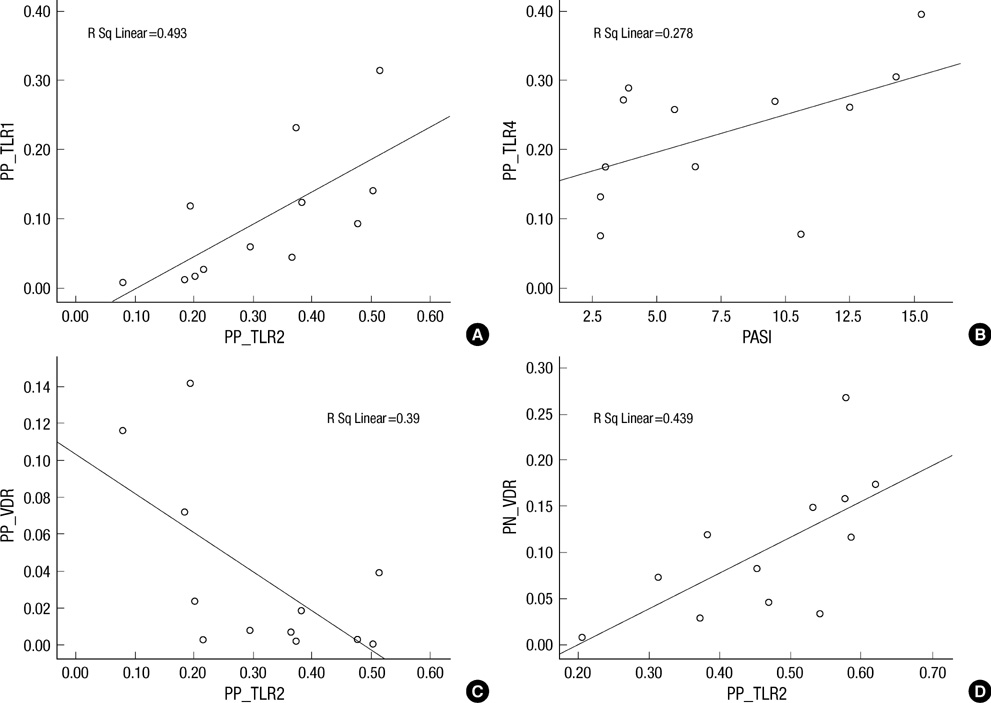
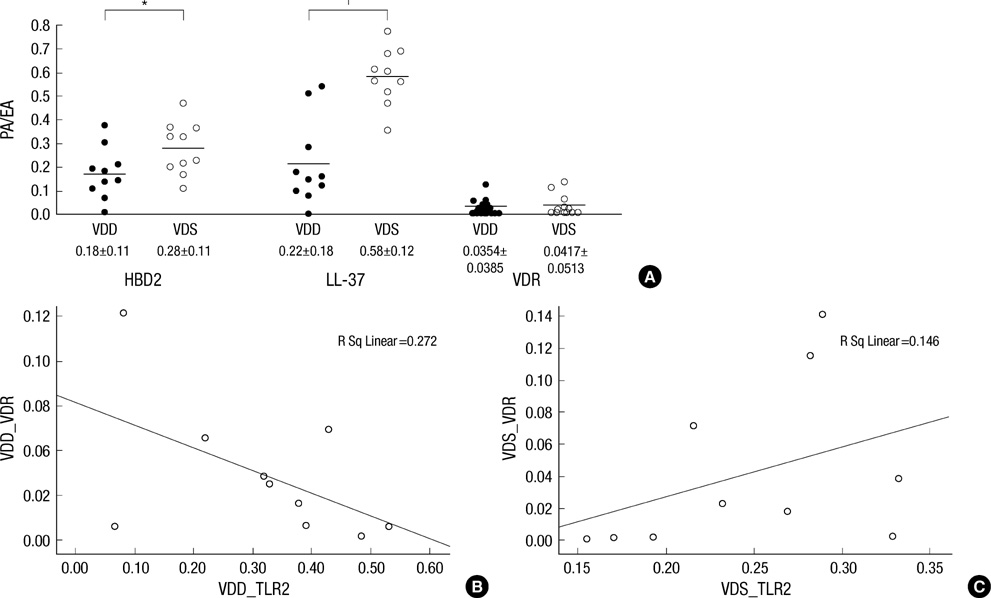
- To evaluate the association of Toll-like receptors (TLRs), antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and vitamin D receptors (VDRs) in psoriasis, lesional (PP) and perilesional skin (PN) from psoriasis, atopic dermatitis (AD) patients and healthy controls (NN) were studied by immunohistochemistry. Compared with PN, AD and NN skin, dysregulated expression of TLRs, AMPs and VDR was detected in PP skin. Noteworthy, our results showed altered correlation between TLR2 and VDR expression in PP and PN skin. Human beta defensin 2 (HBD2) and cathelicidin (LL-37) expressions in the PP skin were higher in serum vitamin D sufficient (VDS) groups than serum vitamin D deficient (VDD) groups. Negative correlation was found between TLR2 and VDR expression in the PP skin of VDD groups. However, positive correlation was noted in the PP skin of VDS groups. Based on the present results, therapies targeting the activity of TLRs, AMPs and vitamin D, including modulation of the TLR-VDR pathways, might provide new therapeutic approaches to the psoriasis and other inflammatory skin diseases.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cathelicidin LL-37: An Antimicrobial Peptide with a Role in Inflammatory Skin Disease
Markus Reinholz, Thomas Ruzicka, Jürgen Schauber
Ann Dermatol. 2012;24(2):126-135. doi: 10.5021/ad.2012.24.2.126.
Reference
-
1. Buchau AS, Gallo RL. Innate immunity and antimicrobial defense systems in psoriasis. Clin Dermatol. 2007. 25:616–624.2. Baker BS, Ovigne JM, Powles AV, Corcoran S, Fry L. Normal keratinocytes express Toll-like receptors (TLRs) 1, 2 and 5: modulation of TLR expression in chronic plaque psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2003. 148:670–679.
Article3. Schauber J, Dorschner RA, Coda AB, Buchau AS, Liu PT, Kiken D, Helfrich YR, Kang S, Elalieh HZ, Steinmeyer A, Zugel U, Bikle DD, Modlin RL, Gallo RL. Injury enhances TLR2 function and antimicrobial peptide expression through a vitamin D-dependent mechanism. J Clin Invest. 2007. 117:803–811.
Article4. Nomura I, Goleva E, Howell MD, Hamid QA, Ong PY, Hall CF, Darst MA, Gao B, Boguniewicz M, Travers JB, Leung DY. Cytokine milieu of atopic dermatitis, as compared to psoriasis, skin prevents induction of innate immune response genes. J Immunol. 2003. 171:3262–3269.
Article5. Sumikawa Y, Asada H, Hoshino K, Azukizawa H, Katayama I, Akira S, Itami S. Induction of beta-defensin 3 in keratinocytes stimulated by bacterial lipopeptides through toll-like receptor 2. Microbes Infect. 2006. 8:1513–1521.6. Schauber J, Gallo RL. Antimicrobial peptides and the skin immune defense system. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 122:261–266.
Article7. Ong PY, Ohtake T, Brandt C, Strickland I, Boguniewicz M, Ganz T, Gallo RL, Leung DY. Endogenous antimicrobial peptides and skin infections in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:1151–1160.
Article8. Saeki H, Asano N, Tsunemi Y, Takekoshi T, Kishimoto M, Mitsui H, Tada Y, Torii H, Komine M, Asahina A, Tamaki K. Polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor gene in Japanese patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Dermatol Sci. 2002. 30:167–171.
Article9. Barnes PF, Modlin RL, Bikle DD, Adams JS. Transpleural gradient of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in tuberculous pleuritis. J Clin Invest. 1989. 83:1527–1532.
Article10. Mathieu C, Adorini L. The coming of age of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) analogs as immunomodulatory agents. Trends Mol Med. 2002. 8:174–179.
Article11. Liu PT, Stenger S, Li H, Wenzel L, Tan BH, Krutzik SR, Ochoa MT, Schauber J, Wu K, Meinken C, Kamen DL, Wagner M, Bals R, Steinmeyer A, Zugel U, Gallo RL, Eisenberg D, Hewison M, Hollis BW, Adams JS, Bloom BR, Modlin RL. Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science. 2006. 311:1770–1773.
Article12. Morimoto S, Yoshikawa K, Fukuo K, Shiraishi T, Koh E, Imanaka S, Kitano S, Ogihara T. Inverse relation between severity of psoriasis and serum 1,25-dihydroxy-vitamin D level. J Dermatol Sci. 1990. 1:277–282.
Article13. Shi SR, Liu C, Taylor CR. Standardization of immunohistochemistry for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections based on the antigen-retrieval technique: from experiments to hypothesis. J Histochem Cytochem. 2007. 55:105–109.
Article14. Kim SK, Kang HY, Lee ES, Kim YC. Clinical and histopathologic characteristics of nevus depigmentosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:423–428.
Article15. Kim YC, Kim YJ, Kang HY, Sohn S, Lee ES. Histopathologic features in vitiligo. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008. 30:112–116.
Article16. Kim YJ, Han JH, Kang HY, Lee ES, Kim YC. Androgen receptor overexpression in Becker nevus: histopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis. J Cutan Pathol. 2008. 35:1121–1126.
Article17. Holme SA, Anstey AV, Badminton MN, Elder GH. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in erythropoietic protoporphyria. Br J Dermatol. 2008. 159:211–213.
Article18. Lim HJ, Kim JI. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status in wintertime in premenopausal working women. Korean J Nutr. 2006. 39:649–660.19. Krutzik SR, Hewison M, Liu PT, Robles JA, Stenger S, Adams JS, Modlin RL. IL-15 links TLR2/1-induced macrophage differentiation to the vitamin D-dependent antimicrobial pathway. J Immunol. 2008. 181:7115–7120.
Article20. Liu PT, Krutzik SR, Modlin RL. Therapeutic implications of the TLR and VDR partnership. Trends Mol Med. 2007. 13:117–124.
Article21. Liu PT, Schenk M, Walker VP, Dempsey PW, Kanchanapoomi M, Wheelwright M, Vazirnia A, Zhang X, Steinmeyer A, Zugel U, Hollis BW, Cheng G, Modlin RL. Convergence of IL-1beta and VDR activation pathways in human TLR2/1-induced antimicrobial responses. PLoS One. 2009. 4:e5810.22. De Rycke L, Vandooren B, Kruithof E, De Keyser F, Veys EM, Baeten D. Tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade treatment down-modulates the increased systemic and local expression of Toll-like receptor 2 and Toll-like receptor 4 in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:2146–2158.23. Seung NR, Park EJ, Kim CW, Kim KH, Kim KJ, Cho HJ, Park HR. Comparison of expression of heat-shock protein 60, Toll-like receptors 2 and 4, and T-cell receptor gammadelta in plaque and guttate psoriasis. J Cutan Pathol. 2007. 34:903–911.24. Wu C, Luan Q, Li C, Zheng Z. Effects of antikeratin 16 antibodies on the expression of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in keratinocytes. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009. 34:236–239.
Article25. de Jongh GJ, Zeeuwen PL, Kucharekova M, Pfundt R, van der Valk PG, Blokx W, Dogan A, Hiemstra PS, van de Kerkhof PC, Schalkwijk J. High expression levels of keratinocyte antimicrobial proteins in psoriasis compared with atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2005. 125:1163–1173.
Article26. Pingel LC, Kohlgraf KG, Hansen CJ, Eastman CG, Dietrich DE, Burnell KK, Srikantha RN, Xiao X, Belanger M, Progulske-Fox A, Cavanaugh JE, Guthmiller JM, Johnson GK, Joly S, Kurago ZB, Dawson DV, Brogden KA. Human beta-defensin 3 binds to hemagglutinin B (rHagB), a non-fimbrial adhesin from Porphyromonas gingivalis, and attenuates a pro-inflammatory cytokine response. Immunol Cell Biol. 2008. 86:643–649.27. Milde P, Hauser U, Simon T, Mall G, Ernst V, Haussler MR, Frosch P, Rauterberg EW. Expression of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in normal and psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1991. 97:230–239.
Article28. Reichrath J, Muller SM, Kerber A, Baum HP, Bahmer FA. Biologic effects of topical calcipotriol (MC 903) treatment in psoriatic skin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997. 36:19–28.
Article29. Wang TT, Nestel FP, Bourdeau V, Nagai Y, Wang Q, Liao J, Tavera-Mendoza L, Lin R, Hanrahan JW, Mader S, White JH. Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J Immunol. 2004. 173:2909–2912.
Article30. Buchau AS, Schauber J, Hultsch T, Stuetz A, Gallo RL. Pimecrolimus enhances TLR2/6-induced expression of antimicrobial peptides in keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. 128:2646–2654.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between the Severity of Atopic Dermatitis and Serum Vitamin D Levels
- Cathelicidin LL-37: An Antimicrobial Peptide with a Role in Inflammatory Skin Disease
- Calcitriol May Down-Regulate mRNA Over-Expression of Toll-Like Receptor-2 and -4, LL-37 and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Cultured Human Keratinocytes
- Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides according to Changes of Transepidermal Water Loss Levels in Patients with Atopic Dermatits
- Do Toll-like Receptors Play a New Role as a Biomarker of Irritable Bowel Syndrome?