Korean J Crit Care Med.
2015 Nov;30(4):249-257. 10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.4.249.
Sepsis in Patients Receiving Immunosuppressive Drugs in Korea: Analysis of the National Insurance Database from 2009 to 2013
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of General Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Anesthesiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hogeol@gmail.com
- 4Department of Information Statistics, Andong National University, Andong, Korea.
- KMID: 2156177
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.4.249
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The aim of this study is to evaluate the influence of immunosuppressants on in-hospital mortality from sepsis.
METHODS
Using data of the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service, we collected data from patients who were admitted to the hospital due to sepsis from 2009 to 2013. Based on drugs commonly used for immunosuppression caused by various diseases, patients were divided into three groups; immunosuppressant group, steroid-only group, and control group. Patients with no history of immunosuppressants or steroids were assigned to the control group. To identify risk factors of in-hospital mortality in sepsis, we compared differences in patient characteristics, comorbidities, intensive care unit (ICU) care requirements, and immunodeficiency profiles. Subgroup analysis according to age was also performed.
RESULTS
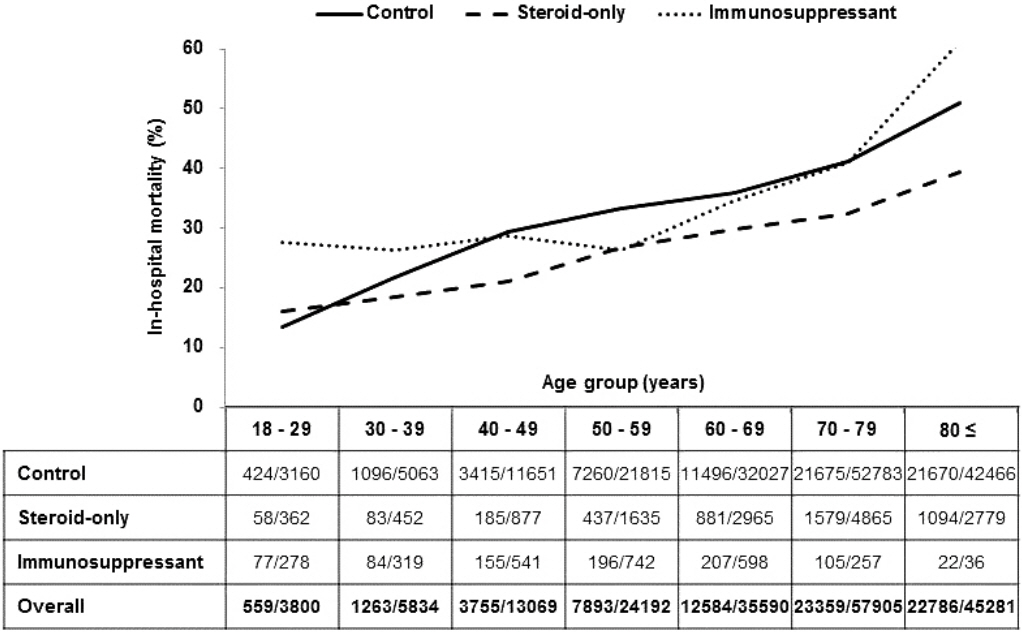
Of the 185,671 included patients, 13,935 (7.5%) were in the steroid-only group and 2,771 patients (1.5%) were in the immunosuppressant group. The overall in-hospital mortality was 38.9% and showed an increasing trend with age. The steroid-only group showed the lowest in-hospital mortality among the three groups except the patients younger than 30 years. The steroid-only group and immunosuppressant group received ICU treatment more frequently (p < 0.001), stayed longer in the hospital (p < 0.001), and showed higher medical expenditure (p < 0.001) compared to the normal group. Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that age, male gender, comorbidities (especially malignancy), and ICU treatment had a significant effect on in-hospital mortality.
CONCLUSIONS
Despite longer hospital length of stay and more frequent need for ICU care, the in-hospital mortality was lower in patients taking immunosuppressive drugs than in patients not taking immunosuppressive drugs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Sepsis in Immunocompromised Patients: Current Status in Korea
Kwangha Lee
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2015;30(4):239-240. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.4.239.Should Very Old Patients Be Admitted to the Intensive Care Units?
Jun Kwon Cha, In-Ae Song
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2017;32(4):376-377. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2017.00521.Critical Care Research Using “Big Data”: A Reality in the Near Future
Kwangha Lee
Acute Crit Care. 2018;33(4):269-270. doi: 10.4266/acc.2018.00346.
Reference
-
References
1. Castellanos-Ortega A, Suberviola B, García-Astudillo LA, Holanda MS, Ortiz F, Llorca J, et al. Impact of the Surviving Sepsis Campaign protocols on hospital length of stay and mortality in septic shock patients: results of a three-year follow-up quasi-experimental study. Crit Care Med. 2010; 38:1036–43.
Article2. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care Med. 2013; 39:165–228.
Article3. Shiramizo SC, Marra AR, Durão MS, Paes ÂT, Edmond MB, Pavão dos Santos OF. Decreasing mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock patients by implementing a sepsis bundle in a hospital setting. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e26790.
Article4. Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008; 36:296–327.
Article5. Leentjens J, Kox M, van der Hoeven JG, Netea MG, Pickkers P. Immunotherapy for the adjunctive treatment of sepsis: from immunosuppression to immunostimulation. Time for a paradigm change? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 187:1287–93.6. Galbois A, Aegerter P, Martel-Samb P, Housset C, Thabut D, Offenstadt G, et al. Improved prognosis of septic shock in patients with cirrhosis: a multicenter study*. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42:1666–75.7. Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Carlet J, Dellamonica P, Gouin F, Lepoutre A, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults. A multicenter prospective study in intensive care units. French ICU Group for Severe Sepsis. JAMA. 1995; 274:968–74.
Article8. Linden PK. Approach to the immunocompromised host with infection in the intensive care unit. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2009; 23:535–56.
Article9. Weiss SL, Fitzgerald JC, Balamuth F, Alpern ER, Lavelle J, Chilutti M, et al. Delayed antimicrobial therapy increases mortality and organ dysfunction duration in pediatric sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42:2409–17.
Article10. Kroschinsky F, Weise M, Illmer T, Haenel M, Born-haeuser M, Hoeffken G, et al. Outcome and prognostic features of intensive care unit treatment in patients with hematological malignancies. Intensive Care Med. 2002; 28:1294–300.
Article11. Japiassú AM, Amâncio RT, Mesquita EC, Medeiros DM, Bernal HB, Nunes EP, et al. Sepsis is a major determinant of outcome in critically ill HIV/AIDS patients. Crit Care. 2010; 14:R152.
Article12. Choi NK, Chang Y, Choi YK, Hahn S, Park BJ. Signal detection of rosuvastatin compared to other statins: data-mining study using national health insurance claims database. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010; 19:238–46.
Article13. Koo BK, Lee CH, Yang BR, Hwang SS, Choi NK. The incidence and prevalence of diabetes mellitus and related atherosclerotic complications in Korea: a National Health Insurance Database Study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e110650.
Article14. Shen HN, Lu CL, Yang HH. Epidemiologic trend of severe sepsis in Taiwan from 1997 through 2006. Chest. 2010; 138:298–304.
Article15. Kumar G, Kumar N, Taneja A, Kaleekal T, Tarima S, McGinley E, et al. Nationwide trends of severe sepsis in the 21st century (2000-2007). Chest. 2011; 140:1223–31.
Article16. Kübler A, Adamik B, Durek G, Mayzner-Zawadzka E, Gaszyński W, Karpel E, et al. Results of the severe sepsis registry in intensive care units in Poland from 2003-2009. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2015; 47:7–13.17. Bouza E, Loeches B, Muñoz P. Fever of unknown origin in solid organ transplant recipients. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2007; 21:1033–54. .
Article18. Kieslichova E, Rocen M, Merta D, Kudla M, Splichal I, Cap J, et al. The effect of immunosuppression on manifestations of sepsis in an animal model of cecal ligation and puncture. Transplant Proc. 2013; 45:770–7.
Article19. Tolsma V, Schwebel C, Azoulay E, Darmon M, Souweine B, Vesin A, et al. Sepsis severe or septic shock: outcome according to immune status and immunodeficiency profile. Chest. 2014; 146:1205–13.20. Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002; 96:21–43.21. Buttgereit F, Burmester GR, Lipworth BJ. Optimised glucocorticoid therapy: the sharpening of an old spear. Lancet. 2005; 365:801–3.
Article22. Senderovitz T, Viskum K. Corticosteroids and tuberculosis. Respir Med. 1994; 88:561–5.
Article23. Cline JC, Davis SM. Risks of infection or reactivation of tuberculosis associated with chronic corticosteroid therapy. Ann Pharmacother. 1997; 31:775–6.24. Kennedy WA, Laurier C, Gautrin D, Ghezzo H, Paré M, Malo JL, et al. Occurrence and risk factors of oral candidiasis treated with oral antifungals in seniors using inhaled steroids. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000; 53:696–701.
Article25. Girardin E, Grau GE, Dayer JM, Roux-Lombard P, Lambert PH. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988; 319:397–400.26. Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:138–50.
Article27. Ferrer R, Martin-Loeches I, Phillips G, Osborn TM, Townsend S, Dellinger RP, et al. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med. 2014; 42:1749–55.28. Yokota PK, Marra AR, Martino MD, Victor ES, Durão MS, Edmond MB, et al. Impact of appropriate antimicrobial therapy for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock--a quality improvement study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e104475.29. Poutsiaka DD, Davidson LE, Kahn KL, Bates DW, Snydman DR, Hibberd PL. Risk factors for death after sepsis in patients immunosuppressed before the onset of sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis. 2009; 41:469–79.
Article30. Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J, Paz HL. Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: a trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Crit Care Med. 2007; 35:1244–50.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of Patients with Acute Toxic Exposure between 2009 and 2013: Data from the Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service and the National Emergency Department Information System
- Introducing big data analysis using data from National Health Insurance Service
- Baseline use of hydroxychloroquine or immunosuppressive drugs and the risk of coronavirus disease 2019
- Strongyloides stercoralis and other intestinal parasites in patients receiving immunosuppressive drugs in northern Iran: a closer look at risk factors
- Clinical Study Using Healthcare Claims Database