J Rheum Dis.
2021 Jul;28(3):119-125. 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.3.119.
Clinical Study Using Healthcare Claims Database
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- KMID: 2516947
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2021.28.3.119
Abstract
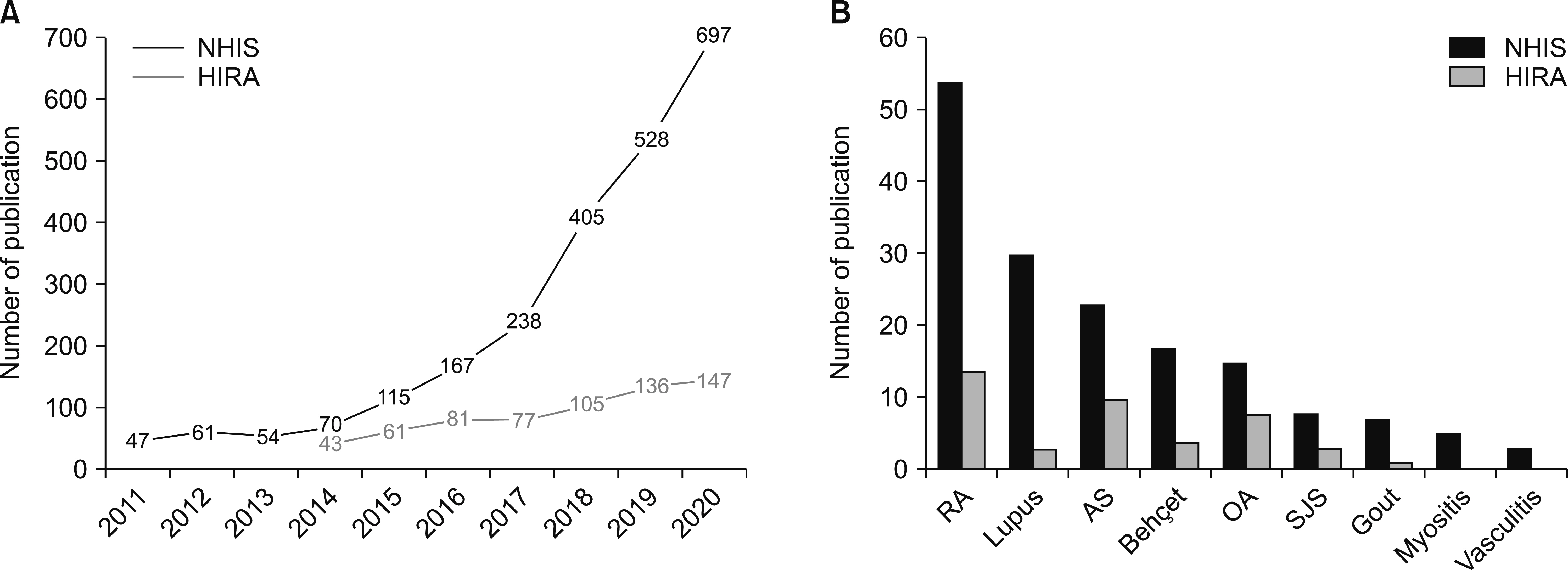
- The healthcare claims database is a database created using claims data accumulated while operating the government’s health insurance system. The National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) provides benefits for health promotion, prevention, diagnosis, and disease and injury treatment, as well as for rehabilitation, birth, and death. Ninety-seven percent of the total population is enrolled in the NHIS; individuals pay a monthly insurance contribution to the system, and the NHIS pays a portion of the cost of reimbursement items to the medical institution when the subscriber receives medical services. In this process, the NHIS and Health Insurance Review Agency (HIRA) decide on payment, and claims data are documented items that medical institutions claim to these government agencies. The NHIS and HIRA have established a database to support policy and academic research, and they provide this database to researchers. Health claims data are representative of the nation, reflecting the actual medical environment. They also shorten the time and cost required for research and have several advantages as research data. However, studies should be conducted with an understanding of the limitations of claims data, a sufficient understanding of the characteristics of the Korean insurance system, and criteria for providing reimbursed services. Moreover, validating the healthcare claims database will facilitate more useful and reliable research.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Pregnancy Outcomes Associated With Biologic Agent Exposure in Patients With Several Rheumatic Diseases and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Soo Min Ahn, Young Bin Joo, Yun Jin Kim, So-Young Bang, Hye-Soon Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(22):e172. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e172.Part 1. Current Status of Hearing Loss Patients in Korea Using National Data: National Health Insurance Service-Database, 2010 to 2020
Junhun Lee, Chul Young Yoon, Jiwon Kim, In-Ki Jin, Michelle J. Suh, Wan-Ho Cho, Hyo-Jeong Lee, Seong Jun Choi, Dongchul Cha, Kyung Ho Park, Soo Hee Oh, Young Joon Seo, Tae Hoon Kong
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2025;68(1):7-18. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2024.00157.
Reference
-
1. Ng B, Chu A. 2014; Factors associated with methotrexate dosing and therapeutic decisions in veterans with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 33:21–30. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-013-2353-9. PMID: 23934386.
Article2. Hsing AW, Ioannidis JP. 2015; Nationwide population science: lessons from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database. JAMA Intern Med. 175:1527–9. DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.3540. PMID: 26192815.3. Lin LY, Warren-Gash C, Smeeth L, Chen PC. 2018; Data resource profile: the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). Epidemiol Health. 40:e2018062. DOI: 10.4178/epih.e2018062. PMID: 30727703. PMCID: PMC6367203.
Article4. National Health Insurance Service Korea. History of the NHIS [Internet]. National Health Insurance Service Korea;Wonju: Available from: https://www.nhis.or.kr/english/wbheaa01300m01.do. cited 2021 May.5. Song SO, Jung CH, Song YD, Park CY, Kwon HS, Cha BS, et al. 2014; Background and data configuration process of a nationwide population-based study using the Korean national health insurance system. Diabetes Metab J. 38:395–403. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2014.38.5.395. PMID: 25349827. PMCID: PMC4209354.
Article6. National Health Insurance Service Korea. Population coverage [Internet]. National Health Insurance Service Korea;Wonju: Available from: https://www.nhis.or.kr/nhis/policy/wbhada01700m01.do. cited 2021 May.7. National Health Insurance Service Korea. Contributions [Internet]. National Health Insurance Service Korea;Wonju: Available from: https://www.nhis.or.kr/english/wbheaa02500m01.do. cited 2021 May.8. Seong SC, Kim YY, Khang YH, Park JH, Kang HJ, Lee H, et al. 2017; Data resource profile: the National Health Information Database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 46:799–800. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyw253. PMID: 27794523. PMCID: PMC5837262.9. Lee CH, Sung NY. 2011; The prevalence and features of Korean gout patients using the National Health Insurance Corporation database. J Rheum Dis. 18:94–100. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2011.18.2.94.
Article10. Kim JA, Yoon S, Kim LY, Kim DS. 2017; Towards actualizing the value potential of Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) data as a resource for health research: strengths, limitations, applications, and strategies for optimal use of HIRA data. J Korean Med Sci. 32:718–28. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.5.718. PMID: 28378543. PMCID: PMC5383602.
Article11. Lee J, Lee JS, Park SH, Shin SA, Kim K. 2017; Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int J Epidemiol. 46:e15. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyv319. PMID: 26822938.
Article12. Kim YI, Kim YY, Yoon JL, Won CW, Ha S, Cho KD, et al. 2019; Cohort Profile: National health insurance service-senior (NHIS-senior) cohort in Korea. BMJ Open. 9:e024344. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-024344. PMID: 31289051. PMCID: PMC6615810.
Article13. Seong SC, Kim YY, Park SK, Khang YH, Kim HC, Park JH, et al. 2017; Cohort profile: the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) in Korea. BMJ Open. 7:e016640. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016640. PMID: 28947447. PMCID: PMC5623538.
Article14. Kim YY, Hong HY, Cho KD, Park JH. 2019; Family tree database of the National Health Information Database in Korea. Epidemiol Health. 41:e2019040. DOI: 10.4178/epih.e2019040. PMID: 31679329. PMCID: PMC6928464.
Article15. Lee CH, Sung NY, Lee J, Bae SC. 2013; Factors associated with gout in South Koreans: analysis using the National Health Insurance Corporation and the National Health Screening Exam databases. Clin Rheumatol. 32:829–37. DOI: 10.1007/s10067-013-2183-9. PMID: 23397143.
Article16. Kwak SG, Park SH, Kim JY. 2021; Incidence and prevalence of juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus in Korea: data from the 2017 National Health Claims Database. J Rheumatol. 48:258–61. DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.191186. PMID: 32358155.
Article17. Chung MK, Park JS, Lim H, Lee CH, Lee J. 2021; Incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus among Korean women in childbearing years: a nationwide population-based study. Lupus. 30:674–9. DOI: 10.1177/0961203320984845. PMID: 33460342.
Article18. Hong M, Moon DS, Chang H, Lee SY, Cho SW, Lee KS, et al. 2018; Incidence and comorbidity of reactive attachment disorder: based on National Health Insurance claims data, 2010-2012 in Korea. Psychiatry Investig. 15:118–23. DOI: 10.30773/pi.2017.11.01. PMID: 29475227. PMCID: PMC5900398.19. Won S, Cho SK, Kim D, Han M, Lee J, Jang EJ, et al. 2018; Update on the prevalence and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in Korea and an analysis of medical care and drug utilization. Rheumatol Int. 38:649–56. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-017-3925-9. PMID: 29302803.
Article20. Kang EH, Choi HK, Shin A, Lee YJ, Lee EB, Song YW, et al. 2019; Comparative cardiovascular risk of allopurinol versus febuxostat in patients with gout: a nation-wide cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 58:2122–9. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kez189. PMID: 31098635.
Article21. Nam JH, Lee C, Kim N, Park KY, Ha J, Yun J, et al. 2019; Impact of continuous care on health outcomes and cost for type 2 diabetes mellitus: analysis using National Health Insurance cohort database. Diabetes Metab J. 43:776–84. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0189. PMID: 31701688. PMCID: PMC6943271.
Article22. Choi J, Kim HJ, Lee J, Cho S, Ko MJ, Lim YS. 2019; Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients treated with entecavir vs tenofovir for chronic hepatitis B: a Korean nationwide cohort study. JAMA Oncol. 5:30–6. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4070. PMID: 30267080. PMCID: PMC6439769.23. Cho WK, Lee NY, Han K, Suh BK, Park YG. 2020; The population prevalence, associations of congenital heart defect and mortality risk for Down's syndrome in South Korea based on National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) data. Clin Epidemiol. 12:519–25. DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S251637. PMID: 32547243. PMCID: PMC7266305.24. Gavrielov-Yusim N, Friger M. 2014; Use of administrative medical databases in population-based research. J Epidemiol Community Health. 68:283–7. DOI: 10.1136/jech-2013-202744. PMID: 24248997.25. Kimm H, Yun JE, Lee SH, Jang Y, Jee SH. 2012; Validity of the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in Korean national medical health insurance claims data: the Korean heart study (1). Korean Circ J. 42:10–5. DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.1.10. PMID: 22363378. PMCID: PMC3283749.
Article26. Park JS, Kang M, Song JS, Lim HS, Lee CH. 2020; Trends of gout prevalence in South Korea based on medical utilization: a National Health Insurance Service Database (2002∼2015). J Rheum Dis. 27:174–81. DOI: 10.4078/jrd.2020.27.3.174.
Article27. Kim JW, Kwak SG, Lee H, Kim SK, Choe JY, Park SH. 2017; Prevalence and incidence of gout in Korea: data from the national health claims database 2007-2015. Rheumatol Int. 37:1499–506. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-017-3768-4. PMID: 28676911.
Article28. Kestle JR. 2015; Administrative database research. J Neurosurg. 122:Sentinel Initiative;441–2. DOI: 10.3171/2014.4.JNS14689. PMID: 25415073.29. Sentinel Initiative. Health outcomes of interest [Internet]. Available from: https://www.sentinelinitiative.org/methods-data-tools/health-outcomes-interest. cited 2021 May.30. Kim JW, Kwak SG, Park SH. 2018; Prescription pattern of urate-lowering therapy in Korean gout patients: data from the national health claims database. Korean J Intern Med. 33:228–9. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2016.429. PMID: 28823114. PMCID: PMC5768547.
Article31. Fetter RB, Freeman JL. 1986; Diagnosis related groups: product line management within hospitals. Acad Manage Rev. 11:41–54. DOI: 10.5465/amr.1986.4282622. PMID: 10311457.
Article32. Seo HY, Yoon SJ, Kim EJ, Oh IH, Lee YH, Kim YA. 2013; The economic burden of rheumatic heart disease in South Korea. Rheumatol Int. 33:1505–10. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-012-2554-6. PMID: 23239034.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Conducting and Reporting a Clinical Research Using Korean Healthcare Claims Database
- Introduction to the Medical Research Using National Health Insurance Claims Database
- Cardiovascular Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Treatment Patterns of Osteoporosis and Factors Affecting the Prescribing of Bone-forming Agents: From a National Health Insurance Claims Database
- A guide for the utilization of Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service National Patient Samples