Korean J Neurotrauma.
2014 Apr;10(1):31-34. 10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.1.31.
Central Pontine and Extrapontine Myelinolysis in a Patient with Traumatic Brain Injury Following Not Rapid Correction of Hyponatremia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. 72ysh@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2156095
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.1.31
Abstract
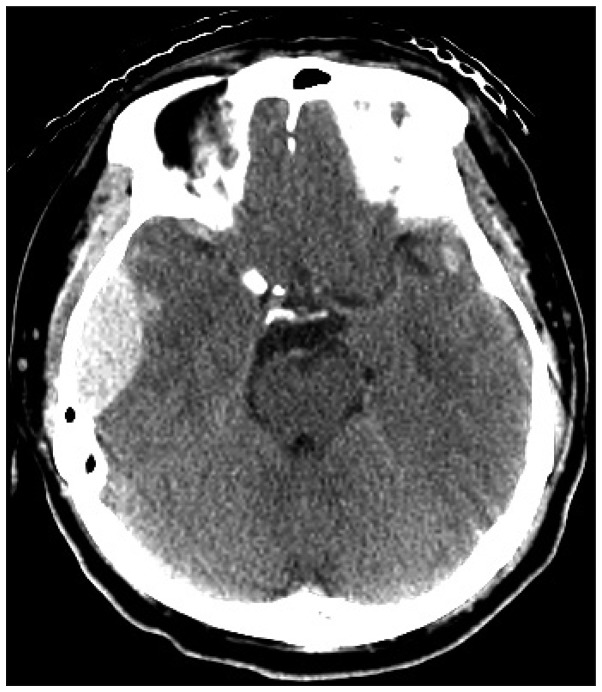
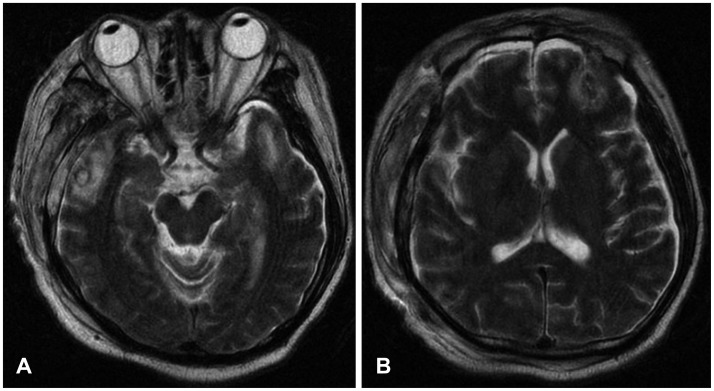
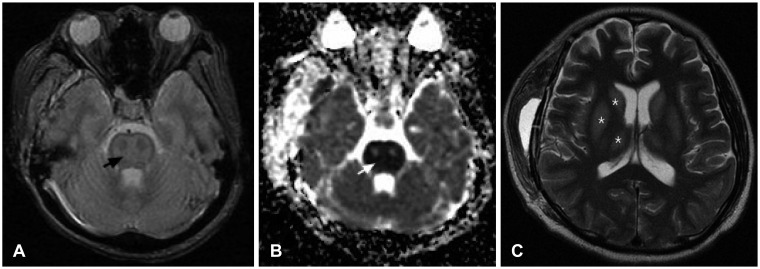
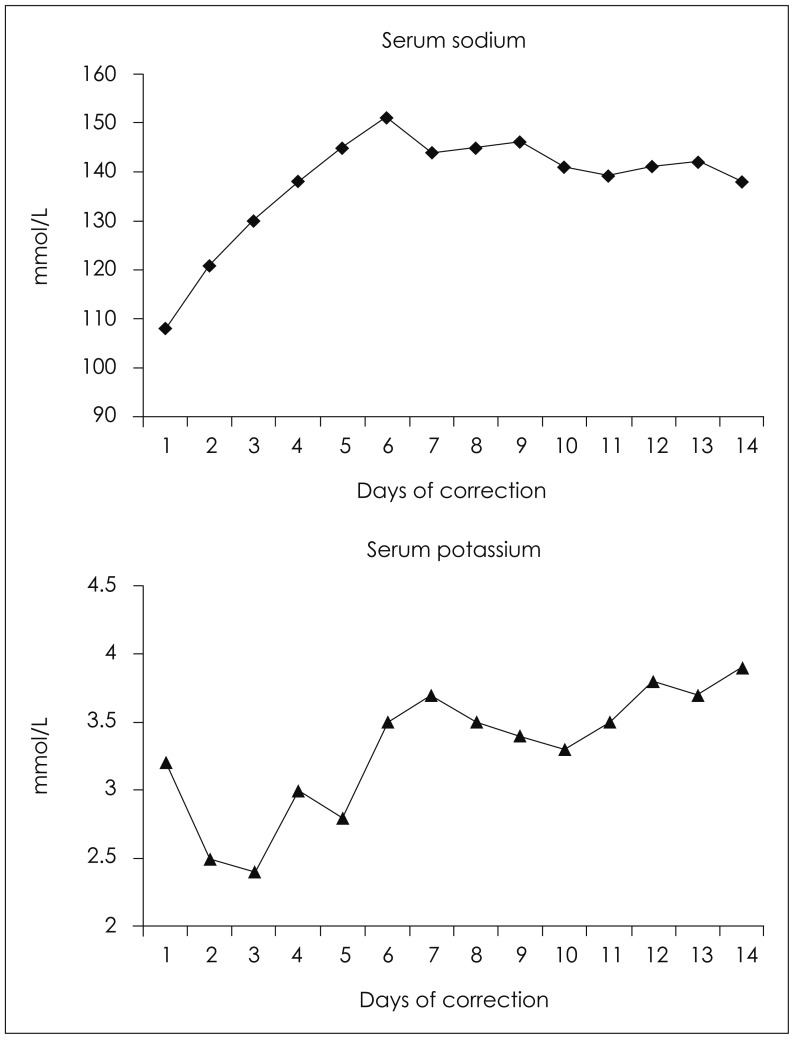
- Central pontine myelinolysis occurs inconsistently as a complication of severe and prolonged hyponatremia, particularly when corrected too rapidly. This condition is a concentrated, frequently symmetric, noninflammatory demyelination within the central basis pontis. We describe a head injury patient who developed central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis following a gradual correction of hyponatremia. More attention should be paid to correcting hyponatremia combined with hypokalemia in patients who have a history of alcoholism.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abbott R, Silber E, Felber J, Ekpo E. Osmotic demyelination syndrome. BMJ. 2005; 331:829–830. PMID: 16210283.
Article2. de Souza A. Akinetic-rigid syndrome due to extrapontine and pontine myelinolysis following appropriate correction of hyponatraemia. J Clin Neurosci. 2011; 18:587–589. PMID: 21273078.
Article3. Lohr JW. Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia: association with hypokalemia. Am J Med. 1994; 96:408–413. PMID: 8192171.
Article4. Martin RJ. Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: the osmotic demyelination syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75(Suppl 3):iii22–iii28. PMID: 15316041.
Article5. Menger H, Jörg J. Outcome of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis (n=44). J Neurol. 1999; 246:700–705. PMID: 10460448.6. Miller GM, Baker HL Jr, Okazaki H, Whisnant JP. Central pontine myelinolysis and its imitators: MR findings. Radiology. 1988; 168:795–802. PMID: 3406409.
Article7. Musana AK, Yale SH. Central pontine myelinolysis: case series and review. WMJ. 2005; 104:56–60. PMID: 16218318.8. Pradhan S, Jha R, Singh MN, Gupta S, Phadke RV, Kher V. Central pontine myelinolysis following 'slow' correction of hyponatremia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1995; 97:340–343. PMID: 8599905.
Article9. Razvi SS, Leach JP. Asymptomatic pontine myelinolysis. Eur J Neurol. 2006; 13:1261–1263. PMID: 17038043.
Article10. Sajith J, Ditchfield A, Katifi HA. Extrapontine myelinolysis presenting as acute parkinsonism. BMC Neurol. 2006; 6:33. PMID: 16961933.
Article11. Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology. 2000; 217:331–345. PMID: 11058626.
Article12. Singh DK, Rastogi M, Husain M. Central pontine myelinolysis in a pediatric head injury patient. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2010; 46:51–53. PMID: 20516740.
Article13. Wright DG, Laureno R, Victor M. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain. 1979; 102:361–385. PMID: 455045.
Article14. Yuh WT, Simonson TM, D'Alessandro MP, Smith KS, Hunsicker LG. Temporal changes of MR findings in central pontine myelinolysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995; 16(4 Suppl):975–977. PMID: 7611089.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis with early hypermetabolism on 18FDG-PET scan
- A Case of Subacute Onset Choreoathetosis as Sequelae of Central Pontine and Extrapontine Myelinolysis
- Neuropsychological Findings of Extrapontine Myelinolysis without Central Pontine Myelinolysis: Initial and Follow-up Evaluation
- Central and Extrapontine Myelinolysis after Alcohol Withdrawal and Correction of Hypernatremia in a Chronic Alcoholic: a Case Report
- Central Pontine and EXtrapontine Myelinolysis