J Korean Med Sci.
2015 May;30(5):549-551. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.549.
Cross-reactivity of Toxocariasis with Crude Antigen of Toxascaris leonina Larvae by ELISA
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Parasitology and Tropical Medicine, Institute of Endemic Diseases, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hst@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, Qingdao University College of Medicine, Qingdao, China.
- 3Department of Parasitology, Hallym University, College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2155466
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.549
Abstract
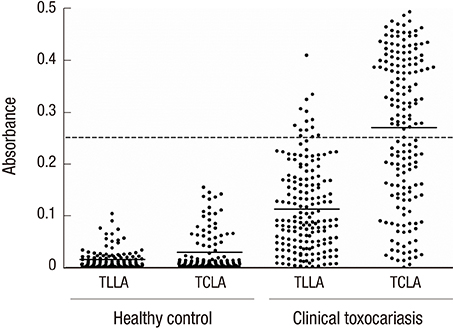
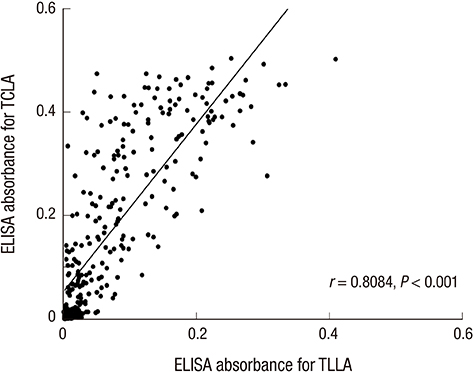
- Roundworms of Toxocara canis and Toxascaris leonina are common gastrointestinal helminths of canids over the world. Humans are infected with T. canis larvae through ingestion of infective eggs in contaminated environments or larvae by consumption of raw or uncooked meat or livers. Recently, patients of clinically diagnosed toxocariasis are increasing and require correct diagnosis in Korea. The present study investigated serological cross-reactivity between crude antigens of T. canis (TCLA) and T. leonina (TLLA) larvae. We collected serum specimens from 177 toxocariasis patients who were clinically suspected in the Seoul National University Hospital and 115 healthy controls. An ELISA method for toxocariasis was used to evaluate diagnostic efficacy of TLLA for serodiagnosis of human toxocariasis. The IgG ELISA using TLLA gave 14 (14.3%) positives of 98 TCLA positive specimens among 177 suspected toxocariasis patients. Most of them showed high absorbances with TCLA. In conclusion, there is a partial cross reaction between serum specimens of toxocariasis and TLLA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibodies, Helminth/blood
Antigens, Helminth/*immunology
Cross Reactions
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Humans
Immunoglobulin G/blood
Larva/immunology/metabolism
Toxascaris/growth & development/*immunology/isolation & purification
Toxocara canis/growth & development/*immunology/isolation & purification
Toxocariasis/*diagnosis/parasitology
Antibodies, Helminth
Antigens, Helminth
Immunoglobulin G
Figure
Reference
-
1. Smith H, Holland C, Taylor M, Magnaval JF, Schantz P, Maizels R. How common is human toxocariasis? Towards standardizing our knowledge. Trends Parasitol. 2009; 25:182–188.2. Park HY, Lee SU, Huh S, Kong Y, Magnaval JF. A seroepidemiological survey for toxocariasis in apparently healthy residents in Gangwon-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2002; 40:113–117.3. Kwon NH, Oh MJ, Lee SP, Lee BJ, Choi DC. The prevalence and diagnostic value of toxocariasis in unknown eosinophilia. Ann Hematol. 2006; 85:233–238.4. Seo M, Yoon SC. A seroepidemiological survey of toxocariasis among eosinophilia patients in Chungcheongnam-do. Korean J Parasitol. 2012; 50:249–251.5. Kim HS, Jin Y, Choi MH, Kim JH, Lee YH, Yoon CH, Hwang EH, Kang H, Ahn SY, Kim GJ, et al. Significance of serum antibody test for toxocariasis in healthy healthcare examinees with eosinophilia in Seoul and Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:1618–1625.6. Lim JH. Foodborne eosinophilia due to visceral larva migrans: a disease abandoned. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:1–2.7. Fillaux J, Magnaval JF. Laboratory diagnosis of human toxocariasis. Vet Parasitol. 2013; 193:327–336.8. de Savigny DH, Voller A, Woodruff AW. Toxocariasis: serological diagnosis by enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Pathol. 1979; 32:284–288.9. Jin Y, Shen C, Huh S, Sohn WM, Choi MH, Hong ST. Serodiagnosis of toxocariasis by ELISA using crude antigen of Toxocara canis larvae. Korean J Parasitol. 2013; 51:433–439.10. Min HK. An Epidemiological study on zoonoses in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1981; 19:60–75.11. Kim YH, Huh S. Prevalence of Toxocara canis, Toxascaris leonina and Dirofilaria immitis in dogs in Chuncheon, Korea (2004). Korean J Parasitol. 2005; 43:65–67.12. Jacquier P, Gottstein B, Stingelin Y, Eckert J. Immunodiagnosis of toxocarosis in humans: evaluation of a new enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. J Clin Microbiol. 1991; 29:1831–1835.13. Romasanta A, Romero JL, Arias M, Sánchez-Andrade R, López C, Suárez JL, Diaz P, Díez-Baños P, Morrondo P, Paz-Silva A. Diagnosis of parasitic zoonoses by immunoenzymatic assays--analysis of cross-reactivity among the excretory/secretory antigens of Fasciola hepatica, Toxocara canis, and Ascaris suum. Immunol Invest. 2003; 32:131–142.14. Ishida MM, Rubinsky-Elefant G, Ferreira AW, Hoshino-Shimizu S, Vaz AJ. Helminth antigens (Taenia solium, Taenia crassiceps, Toxocara canis, Schistosoma mansoni and Echinococcus granulosus) and cross-reactivities in human infections and immunized animals. Acta Trop. 2003; 89:73–84.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of Toxocara canis, Toxascaris leonina and Dirofilaria immitis in dogs in Chuncheon, Korea (2004)
- Serodiagnosis of Toxocariasis by ELISA Using Crude Antigen of Toxocara canis Larvae
- Hightlights and Diagnostic Dilemma of Toxocariasis
- Excretory-secretory antigen is better than crude antigen for the serodiagnosis of clonorchiasis by ELISA
- Cross-reactivity between sera from dogs experimentally infected with Dirofilaria immitis and crude extract of Toxocara canis