Prog Med Phys.
2015 Dec;26(4):250-257. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.250.
Development of Manual Multi-Leaf Collimator for Proton Therapy in National Cancer Center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Proton Therapy Center, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea. sblee@ncc.re.kr
- KMID: 2151759
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.250
Abstract
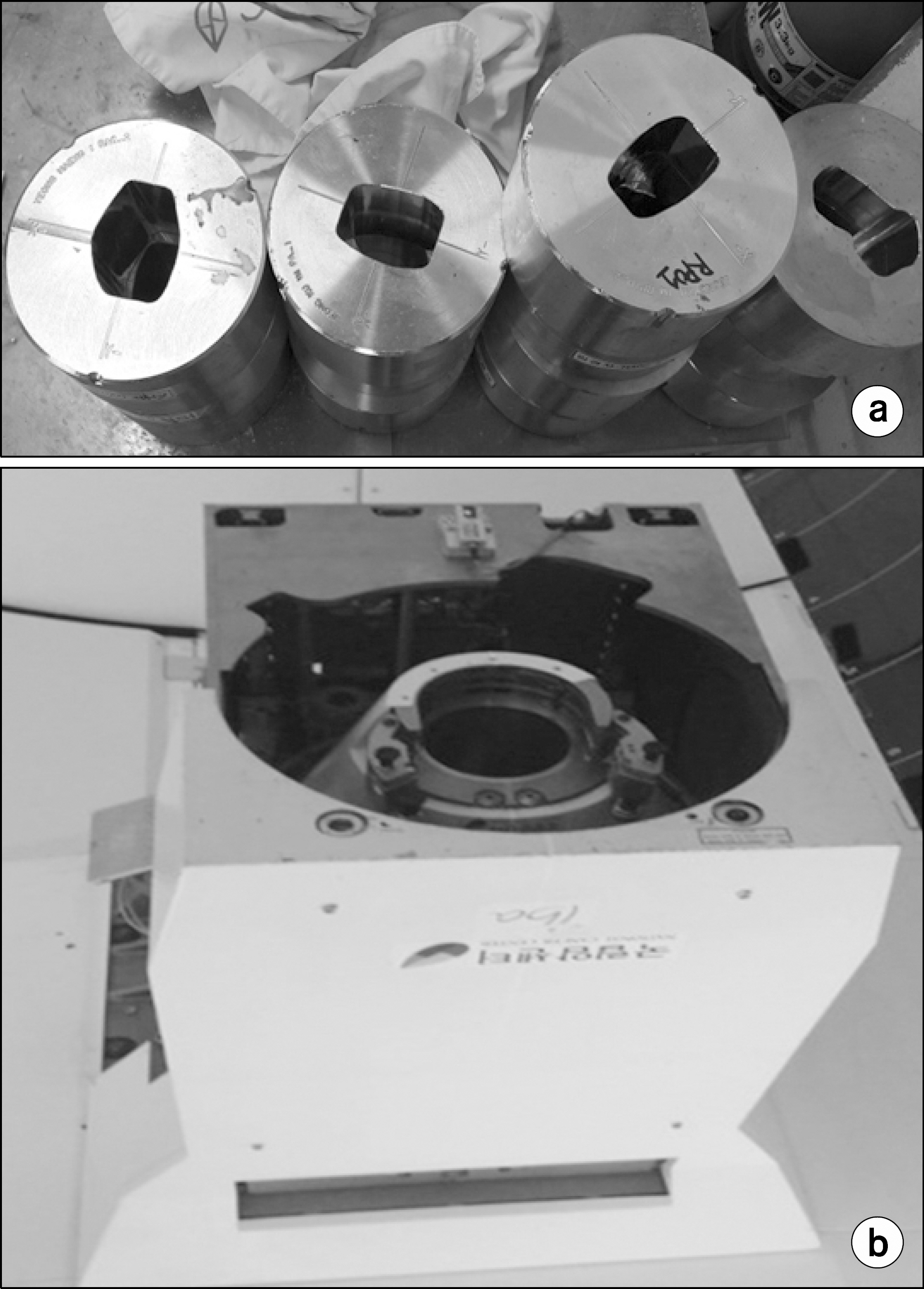
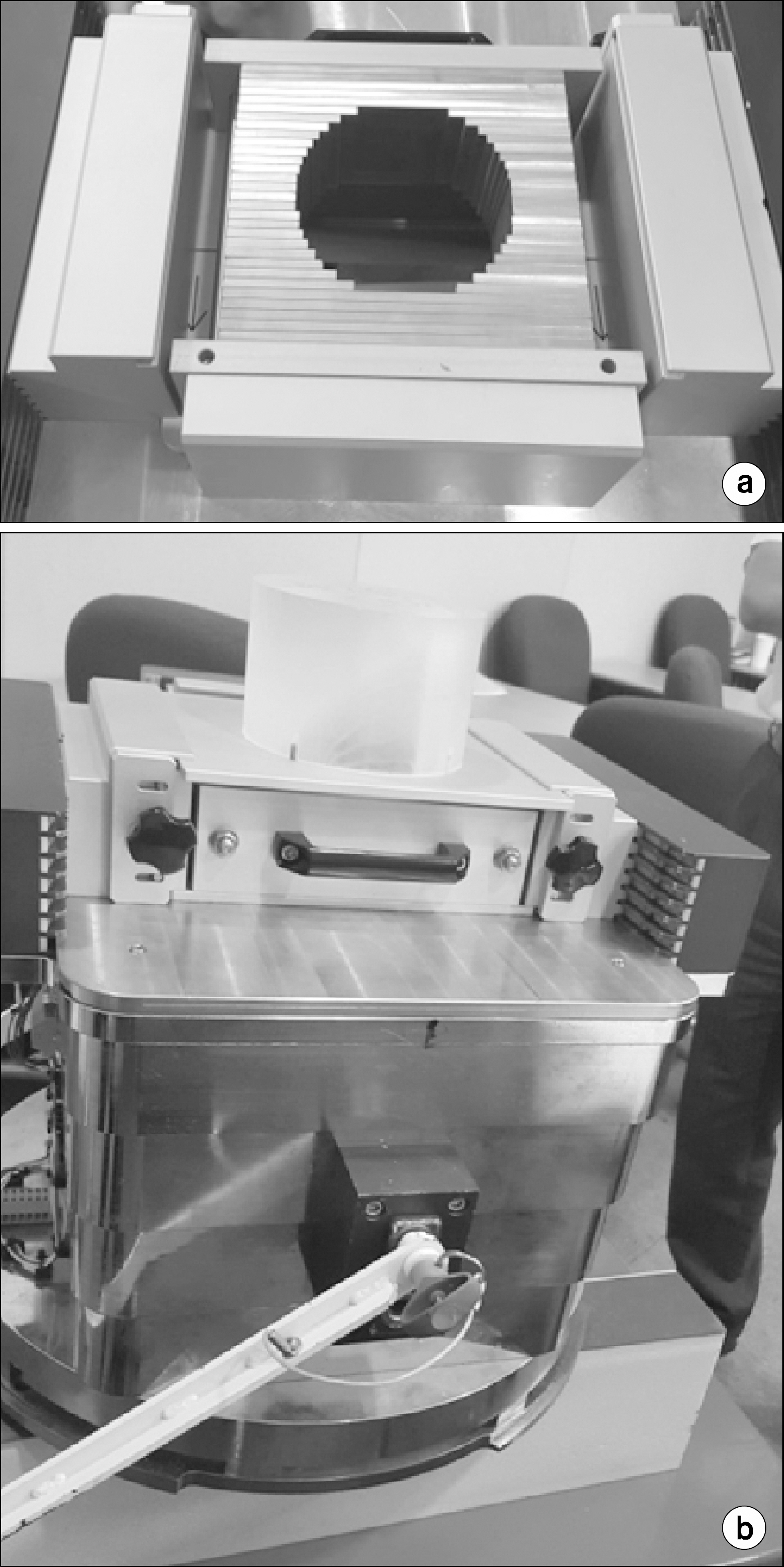
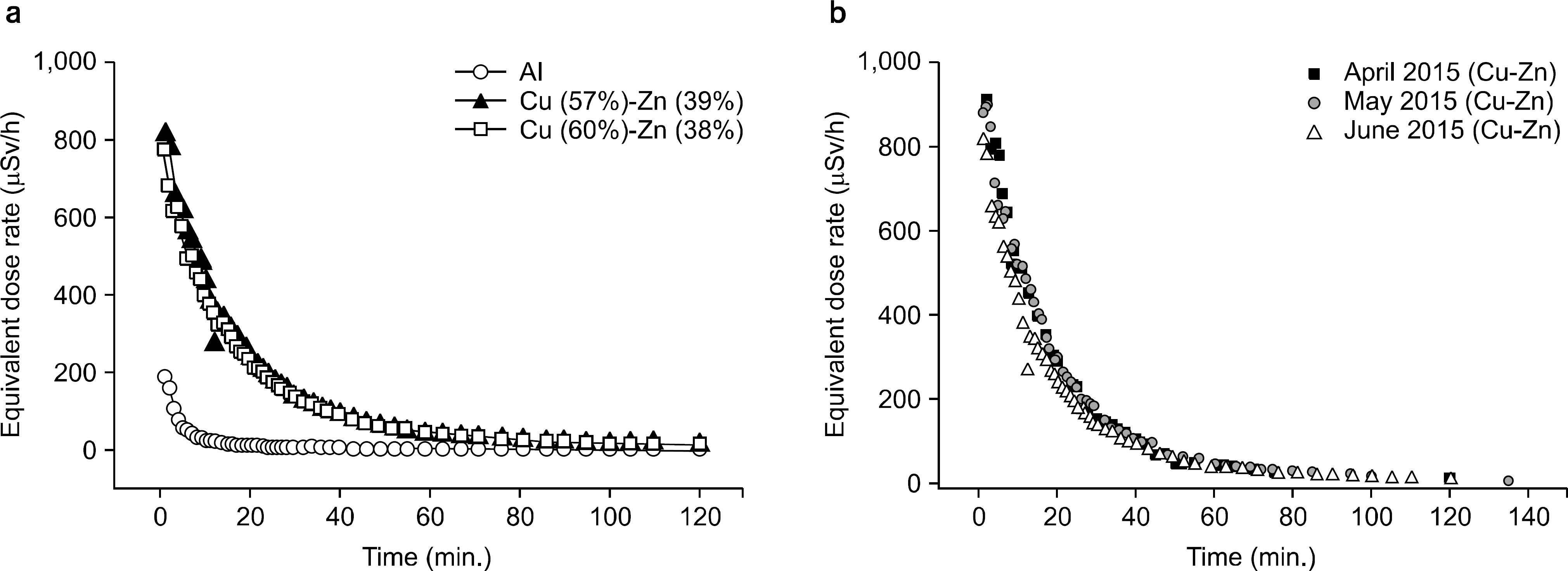
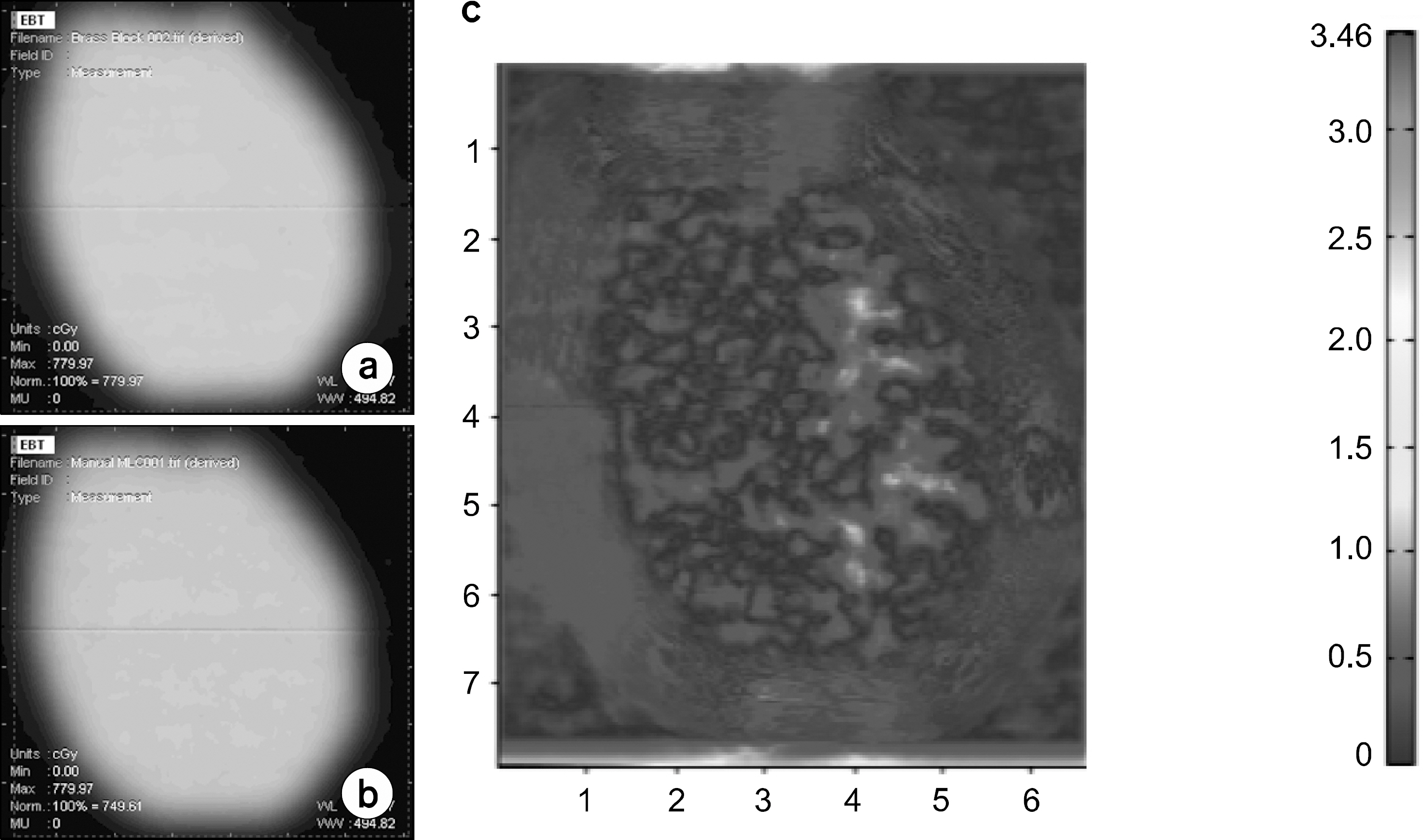
- Multi-leaf collimator (MLC) systems are frequently used to deliver photon-based radiation, and allow conformal shaping of treatment beams. Many proton beam centers currently make use of aperture and snout systems, which involve use of a snout to shape and focus the proton beam, a brass aperture to modify field shape, and an acrylic compensator to modulate depth. However, it needs a lot of time and cost of preparing treatment, therefore, we developed the manual MLC for solving this problem. This study was carried out with the intent of designing an MLC system as an alternative to an aperture block system. Radio-activation and dose due to primary proton beam leakage and the presence of secondary neutrons were taken into account during these iterations. Analytical calculations were used to study the effects of leaf material on activation. We have fabricated tray model for adoption with a wobbling snout (30x40 cm2) system which used uniform scanning beam. We designed the manual MLC and tray and can reduce the cost and time for treatment. After leakage test of new tray, we upgrade the tray with brass and made the safety tool. First, we have tested the radio-activation with usually brass and new brass for new manual MLC. It shows similar behavior and decay trend. In addition, we have measured the leakage test of a gantry with new tray and MLC tray, while we exposed the high energy with full modulation process on film dosimetry. The radiation leakage is less than 1%. From these results, we have developed the design of the tray and upgrade for safety. Through the radio-activation behavior, we figure out the proton beam leakage level of safety, where there detects the secondary particle, including neutron. After developing new design of the tray, it will be able to reduce the time and cost of proton treatment. Finally, we have applied in clinic test with original brass aperture and manual MLC and calculated the gamma index, 99.74% between them.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Arzt L, Ralston S. Proton Foundation 2011 Survey Reveals 32% Increase in Pediatric Cases Treated at U.S. Proton Centers. Virgnia beach, VA PRWEB, September 19 (. 2012.2. Khan FM, Gibbons JP. The Physics of Radiation Therapy. 5th ed., Wolters Kluwer, Philadelphia, PA (. 2014. ), pp. 524.3. Hong CS, Lim J, Ju SG, Shin E, Han Y, Ahn YC. Comparison of the efficacy of 2D dosimetry systems in the pretreatment verification of IMRT. Radiation Oncology Journal. 27(2):91–102. 2009.
Article4. Galvin JM. The Multileaf collimator –a complete guide. 41st AAPM: 2787–9625 (. 1999.5. Lee JS, Kim JN. Efficient data acquisition technique for clinical application of multileaf collimator. The Journal of the Korea Contests Association. 8(11):182–188. 2008.
Article6. Mckenna WG, et al. Development of a multileaf collimator for Proton radiotherapy. Defense Technical Information Center. Fort Belvoir, VA (. 2005.7. Farr JB, Mauqhan RL, Yudelev M, Blosser E, Brandon J, Hprste T, Forman JD. Compact multileaf collimator for conformal and intensity modulated fast neutron therapy: electrometechenical design and validation. Med Phys. 33(9):3313–3320. 2006.8. Moskvin V, Cheng CW, Das IJ. Pitfalls of tungsten multileaf collimator in proton beam therapy. Med Phys. 38(12):6395–6406. 2011.
Article9. Dartz J, Maughan RL, and Orton CG. The disadvantages of a multileaf collimator for proton radiotherapy outweigh its advantages. Med Phys. 41(2):020601. 2014.10. Tsunemoto H, Morita S, Ishikawa T, Furukawa S, Kawachi K, Kanai T, Ohara H, Kitagawa T, and Inada T. Proton therapy in Japan. Radiation Research-Official Journal of the Radiation Research Society. 104(2):X234–S243. 1985.
Article11. Agosteo S, Birattari C, Caravaggioc M, Silarid M, Tosi G. Secondary neutron and photon dose in proton therapy. Radiation and Oncology. 48(3):293–305. 1998.
Article12. Brenner DJ, Elliston CD, Hall EJ, and Raganetti H. Reduction of the secondary neutron dose in passively scattered proton radiotherapy, using an optimized pre-collimator/collimator. Phys Med Biol. 54:6065–6078. 2009.
Article13. Kim DW, Chung WK, Shin J, Lim TK, Shin D, Lee SB, Yoon M, Park SY, Shin DO, Cho JK. Secondary neutron dose measurement for proton eye treatment using an eye snout with a borated neutron absorber. Radiation Oncology. 8:182. 2013.
Article14. Lee SH, Shin DH, Yoon M, Shin J, Rah JE, Kwak J, Park SY, Shin KH, Lee DH, Ahn SH, Kim DY, Cho KH, Lee SB. A study of radiation exposure in proton therapy facility. Progress in Medical Physics. 20:37–42. 2009.15. Lee SH, Cho SK, You SH, Shin DH, Park SY, Lee SB. Evaluation of Radioactivity Induced by Patientspecific Devices in Proton therapy. J Kor Phys Soc. 60(1):125–128. 2012.
Article16. Vatnitsky SM. Radiachromic film dosimetry for clinical proton beams. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 48(5):643–651. 1997.17. Niroomand-Rad A, Blackwell CR, Coursey BM, Gall KP, Galvin JM, McLaughlin WL, Meigooni AS, Nath R, Rodgers JE, Soares CG. Radiochromic film dosimetry: Recommendations of AAPM radiation therapy committee task group 55. Med. Phys. 25(11):2093–2115. 1998.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical
- Analysis of the Multi-Leaf Collimator Quality Assurance for the HalcyonTM Linear Accelerator
- Development of Dual-mode Signal Processing Module for Multi-slit Prompt-gamma Camera
- The Sosimetric Effects on Scallop Penumbra from Multi-leaf Collimator by Daily Patient Setup Error in Radiation Therapy with Photon
- Erratum: Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical