J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Jun;25(6):882-887. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.882.
Clinical Efficacy of a 24-months Course of Lamivudine Therapy in Patients with HBeAg Negative Chronic Hepatitis B: A Long-term Prospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Gastroenterology, Liver Cirrhosis Clinical Research Center, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leeks519@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2150867
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.882
Abstract
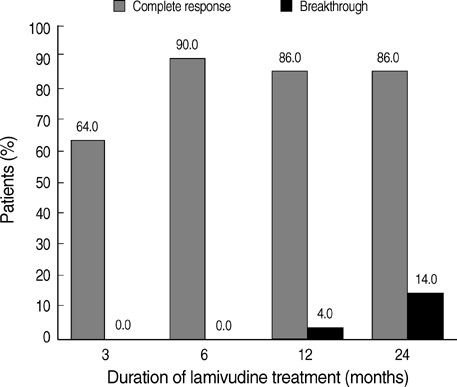
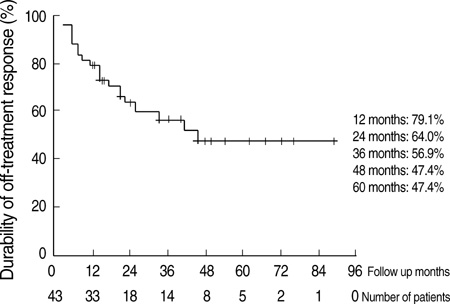
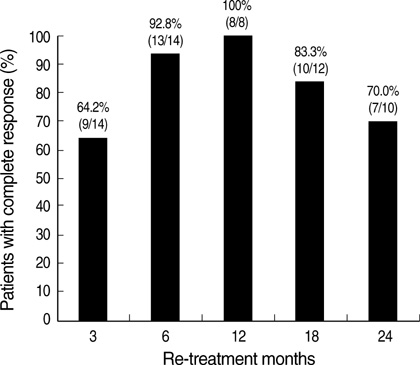
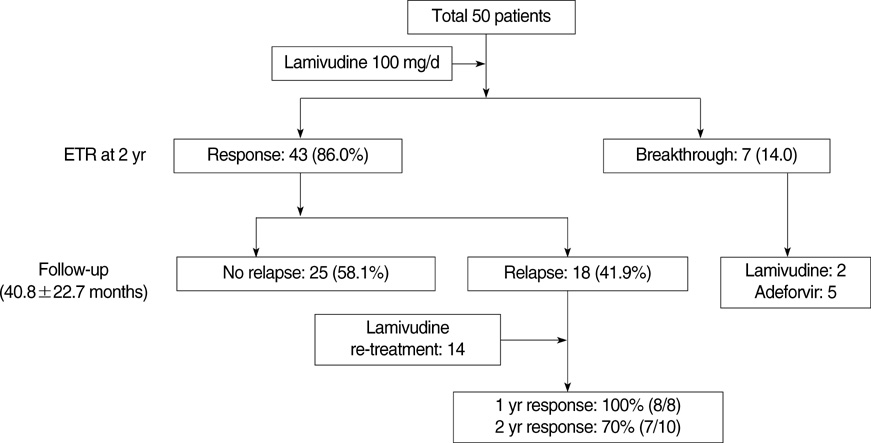
- The optimal duration of oral nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy for HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B (CHB) has not been defined. The aim of this study was to investigate the clinical efficacy of 24-months course of lamivudine therapy in patients with HBeAg negative CHB in Korea. A total of 50 Korean patients with HBeAg negative CHB were prospectively enrolled. The patients received 100 mg/day of lamivudine orally for 24 months. Patients who showed complete response at 24 months to lamivudine therapy stopped treatment, and regular follow-up was done thereafter. The mean follow-up duration after cessation of therapy was 40.8+/-22.7 (range 12-96) months. The complete response rate at months 12 and 24 were 86.0% (43/50) and 86.0% (43/50), respectively, and the clinical breakthrough at months 12 and 24 were 4.0% (2/50) and 14.0% (7/50), respectively. The expected durability of responses at months 12, 24, and 36 after cessation of lamivudine therapy in 43 complete responders was 79.1%, 64.0%, and 56.9%, respectively. In conclusion, a 24-months course of lamivudine therapy shows high end-treatment response rate and substantial durability of initial response after cessation of therapy in HBeAg negative CHB patients in Korea.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hadziyannis SJ, Vassilopoulos D. Hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2001. 34:617–624.
Article2. Lok AS, Heathcote EJ, Hoofnagle JH. Management of hepatitis B: 2000--summary of a workshop. Gastroenterology. 2001. 120:1828–1853.
Article3. Yoo BC, Park JW, Kim HJ, Lee DH, Cha YJ, Park SM. Precore and core promoter mutations of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B in Korea. J Hepatol. 2003. 38:98–103.
Article4. Song BC, Cui XJ, Kim H. Hepatitis B virus genotypes in Korea: an endemic area of hepatitis B virus infection. Intervirology. 2005. 48:133–137.
Article5. Lee JM, Ahn SH, Chang HY, Shin JE, Kim DY, Sim MK, Hong SP, Chung HJ, Kim SO, Han KH, Chon CY, Moon YM. Reappraisal of HBV genotypes and clinical significance in Koreans using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Korean J Hepatol. 2004. 10:260–270.6. Bonino F, Rosina F, Rizzetto M, Rizzi R, Chiaberge E, Tardanico R, Callea F, Verme G. Chronic hepatitis in HBsAg carriers with serum HBV-DNA and anti-HBe. Gastroenterology. 1986. 90:1268–1273.
Article7. Brunetto MR, Giarin MM, Oliveri F, Chiaberge E, Baldi M, Alfarano A, Serra A, Saracco G, Verme G, Will H. Wild-type and e antigen-minus hepatitis B viruses and course of chronic hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991. 88:4186–4190.
Article8. Hadziyannis SJ, Papatheodoridis GV, Vassilopoulos D. Treatment of HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. Semin Liver Dis. 2003. 23:81–88.
Article9. Hadziyannis SJ, Papatheodoridis GV, Dimou E, Laras A, Papaioannou C. Efficacy of long-term lamivudine monotherapy in patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2000. 32:847–851.
Article10. Rizzetto M, Volpes R, Smedile A. Response of pre-core mutant chronic hepatitis B infection to lamivudine. J Med Virol. 2000. 61:398–402.
Article11. Papatheodoridis GV, Dimou E, Laras A, Papadimitropoulos V, Hadziyannis SJ. Course of virologic breakthroughs under long-term lamivudine in HBeAg-negative precore mutant HBV liver disease. Hepatology. 2002. 36:219–226.
Article12. Papatheodoridis GV, Dimou E, Dimakopoulos K, Manolakopoulos S, Rapti I, Kitis G, Tzourmakliotis D, Manesis E, Hadziyannis SJ. Outcome of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B on long-term nucleos(t)ide analog therapy starting with lamivudine. Hepatology. 2005. 42:121–129.
Article13. Lai CL, Shouval D, Lok AS, Chang TT, Cheinquer H, Goodman Z, DeHertogh D, Wilber R, Zink RC, Cross A, Colonno R, Fernandes L. Entecavir versus lamivudine for patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:1011–1020.
Article14. Santantonio T, Mazzola M, Iacovazzi T, Miglietta A, Guastadisegni A, Pastore G. Long-term follow-up of patients with anti-HBe/HBV DNA-positive chronic hepatitis B treated for 12 months with lamivudine. J Hepatol. 2000. 32:300–306.
Article15. Manolakopoulos S, Karatapanis S, Elefsiniotis J, Mathou N, Vlachogiannakos J, Iliadou E, Kougioumtzan A, Economou M, Triantos C, Tzourmakliotis D, Avgerinos A. Clinical course of lamivudine monotherapy in patients with decompensated cirrhosis due to HBeAg negative chronic HBV infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. 99:57–63.
Article16. Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2007. 45:507–539.
Article17. de Franchis R, Hadengue A, Lau G, Lavanchy D, Lok A, McIntyre N, Mele A, Paumgartner G, Pietrangelo A, Rodes J, Rosenberg W, Valla D. EASL International Consensus Conference on Hepatitis B. 13-14 September, 2002 Geneva, Switzerland. Consensus statement (long version). J Hepatol. 2003. 39:Suppl 1. S3–S25.18. Liaw YF, Leung N, Guan R, Lau GK, Merican I, McCaughan G, Gane E, Kao JH, Omata M. Asian-Pacific consensus statement on the management of chronic hepatitis B: a 2005 update. Liver Int. 2005. 25:472–489.
Article19. Dienstag JL, Goldin RD, Heathcote EJ, Hann HW, Woessner M, Stephenson SL, Gardner S, Gray DF, Schiff ER. Histological outcome during long-term lamivudine therapy. Gastroenterology. 2003. 124:105–117.
Article20. Buti M, Cotrina M, Jardi R, de Castro EC, Rodriguez-Frias F, Sanchez-Avila F, Esteban R, Guardia J. Two years of lamivudine therapy in anti-HBe-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2001. 8:270–275.
Article21. Fung SK, Wong F, Hussain M, Lok AS. Sustained response after a 2-yr course of lamivudine treatment of hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2004. 11:432–438.22. Lok AS, Hussain M, Cursano C, Margotti M, Gramenzi A, Grazi GL, Jovine E, Benardi M, Andreone P. Evolution of hepatitis B virus polymerase gene mutations in hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients receiving lamivudine therapy. Hepatology. 2000. 32:1145–1153.
Article23. Chang YS, Yim JY, Cho NY, Choi CW, Baek SJ, Ahn SH, Choi DW, Kwon YD, Kim SS, Kwon OS, Kim JH, Yeon JE, Song JW, Byun KS, Lee CH. Viral breakthrough in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients receiving lamivudine therapy. Korean J Hepatol. 2002. 8:397–404.24. Shin JW, Chung YH, Choi MH, Kim JA, Ryu SH, Jang MK, Kim IS, Park NH, Lee HC, Lee YS, Suh DJ. Precore stop codon mutation of hepatitis B virus is associated with low breakthrough rate following long-term lamivudine therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005. 20:844–849.
Article25. Lau DT, Khokhar MF, Doo E, Ghany MG, Herion D, Park Y, Kleiner DE, Schmid P, Condreay LD, Gauthier J, Kuhns MC, Liang TJ, Hoofnagle JH. Long-term therapy of chronic hepatitis B with lamivudine. Hepatology. 2000. 32:828–834.26. Cho SW, Hahm KB, Kim JH. Reversion from precore/core promoter mutants to wild-type hepatitis B virus during the course of lamivudine therapy. Hepatology. 2000. 32:1163–1169.
Article27. Hasegawa K, Huang J, Rogers SA, Blum HE, Liang TJ. Enhanced replication of a hepatitis B virus mutant associated with an epidemic of fulminant hepatitis. J Virol. 1994. 68:1651–1659.
Article28. Guidotti LG, Matzke B, Pasquinelli C, Shoenberger JM, Rogler CE, Chisari FV. The hepatitis B virus (HBV) precore protein inhibits HBV replication in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1996. 70:7056–7061.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The management and treatment of chronic hepatitis B in Korean children
- Long-term Efficacy and Durability of Lamivudine Therapy in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Clinical Experience with Long-term Lamivudine Therapy toDetermine the Adequate Duration of Treatment in Childrenand Adolescents with HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B
- Efficacy of Lamivudine Re-treatment and Relapse Patterns after Initial Lamivudine Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
- The Effect of Lamivudine Therapy for Chronic Liver Disease due to Hepatitis B Virus Infection