Statistical Considerations in Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. roman00@naver.com
- KMID: 2149101
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.23
Abstract
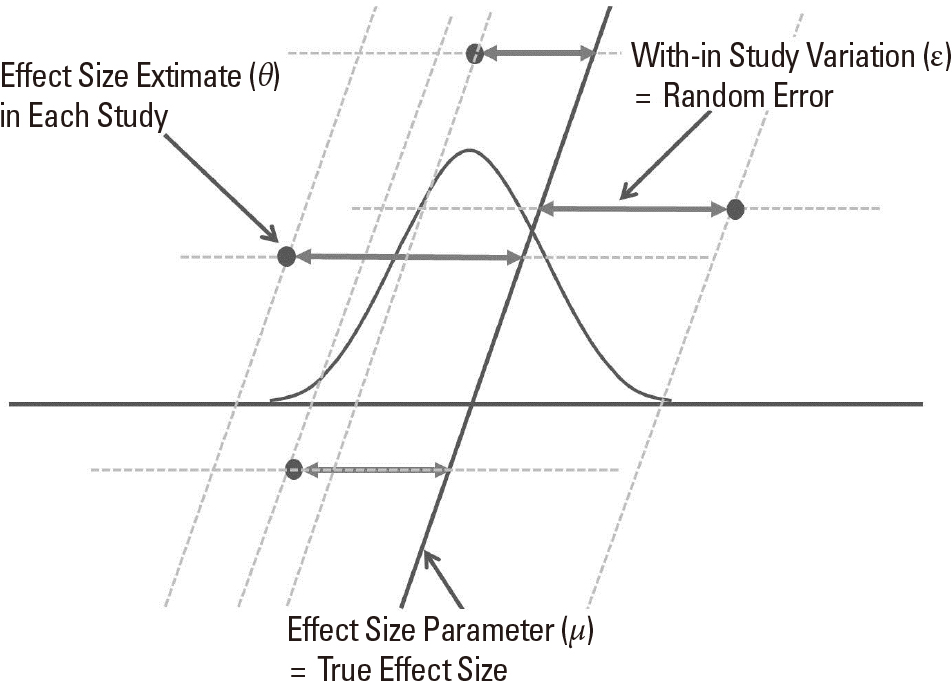
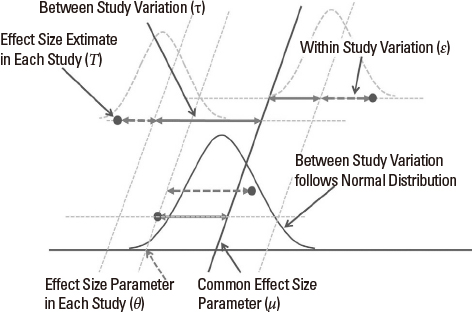
- The increase in medical research has led to a large body of related studies. The huge volume of research brings about a problem of how to organize and summarize the findings of studies. Meta-analysis is a statistical technique for combining the results from two or more studies, which addresses a similar hypothesis in a similar way. Meta-analysis includes the complete coverage of all relevant studies, and describes the results of each study via a quantitative index of effect size. Meta-analysis presents the precise estimate of treatment effect via combining these estimates across studies. Further, meta-analysis looks for the presence, degree and cause of heterogeneity, and explores the robustness of the main findings using statistical techniques. The author dealt with the some statistical issues and considerations which should be considered in conducting and presenting meta-analysis with explanation (ie. Effect size, Fixed and Random effect model, Heterogeneity, Reporting bias, and Meta-analysis Packages). This article may remind readers to conduct and evaluate the meta-analysis systematically and comprehensively.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 6 articles
-
Effects of the Variables related to the Health Action Process Approach Model on Physical Activity: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis
Yun Choi, Sook Ja Yang, Hye Young Song
J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2018;29(3):359-370. doi: 10.12799/jkachn.2018.29.3.359.Relationship between Organizational Culture and Job Satisfaction among Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analysis
Hee Jin Chung, Sung Hee Ahn
J Korean Acad Nurs Adm. 2019;25(3):157-166. doi: 10.11111/jkana.2019.25.3.157.Use, application, and interpretation of systematic reviews and meta-analyses
Hyun Kang
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2021;74(5):369-370. doi: 10.4097/kja.21374.Introduction to systematic review and meta-analysis
EunJin Ahn, Hyun Kang
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2018;71(2):103-112. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2018.71.2.103.How to understand and conduct evidence-based medicine
Hyun Kang
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2016;69(5):435-445. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2016.69.5.435.The umbrella review: a useful strategy in the rain of evidence
Geun Joo Choi, Hyun Kang
Korean J Pain. 2022;35(2):127-128. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.127.
Reference
-
1. Greenhalgh T. How to read a paper: papers that summarise other papers (systematic reviews and meta-analyses). BMJ. 1997; 315:672–675.
Article2. Higgins JP, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. updated March 2011. Available from: http://www.cochrane-handbook.org.3. Wolf FM. Meta-Analysis: Quantitative Method for Research Synthesis. Beverly Hills, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc;1986.4. Pillemer DB, Light RJ. Synthesizing outcomes: how to use research evidence from many studies. Harvard Educ Rev. 1980; 50:176–195.
Article5. Egger M, Smith GD. Bias in location and selection of studies. BMJ. 1998; 316:61–66.6. Egger M, Smith GD, Altman DG. Systematic reviews in health care: meta-analysis in context. London: BMJ Publishing Group;2001.7. Furberg CD, Morgan TM. Lessons from overviews of cardiovascular trials. Stat Med. 1987; 6:295–306.
Article8. Hedges LV, Olkin I. Statistical methods for meta-analysis. Academic Press: 1985.9. Rosenthal R. Parametric measures of effect size. In : Cooper H, Hedges LV, editors. The handbook of research synthesis. New York: Russell Sage Foundation;1994. p. 231–244.10. Baumeister RF. Self-regulation, ego depletion, and inhibition. Neuropsychologia. 2014; 65:313–319.
Article11. Fisher RA. Frequency distribution of the values of the correlation coefficient in samples from an indefinitely large population. Biometrika. 1915; 10:507–521.
Article12. Egger M, Smith GD, Phillips AN. Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. BMJ. 1997; 315:1533.
Article13. DerSimonian R, Kacker R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trials. 2007; 28:105–114.
Article14. Fleiss JL. Analysis of data from multiclinic trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986; 7:267–275.
Article15. Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003; 327:557–560.
Article16. Song F, Sheldon TA, Sutton AJ, Abrams KR, Jones DR. Methods for exploring heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Eval Health Prof. 2001; 24:126–151.
Article17. Thompson SG, Higgins JP. How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Stat Med. 2002; 21:1559–1573.
Article18. Simes RJ. Confronting publication bias: a cohort design for meta-analysis. Stat Med. 1987; 6:11–29.
Article19. Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Contour-enhanced meta-analysis funnel plots help distinguish publication bias from other causes of asymmetry. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008; 61:991–996.
Article20. Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994; 50:1088–1101.
Article21. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315:629–634.
Article22. Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 2000; 56:455–463.
Article