J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Dec;56(12):1961-1964. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.12.1961.
Treatment of Lower Eyelid Swelling after Retrobulbar Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection in Phthisis Bulbi
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Myongji Hospital, Seonam University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. prpp2001@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2148761
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.12.1961
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report treatment with hyaluronidase of lower lid swelling lasting for 1 year after retrobulbar hyaluronic acid filler injection due to phthisis bulbi.
CASE SUMMARY
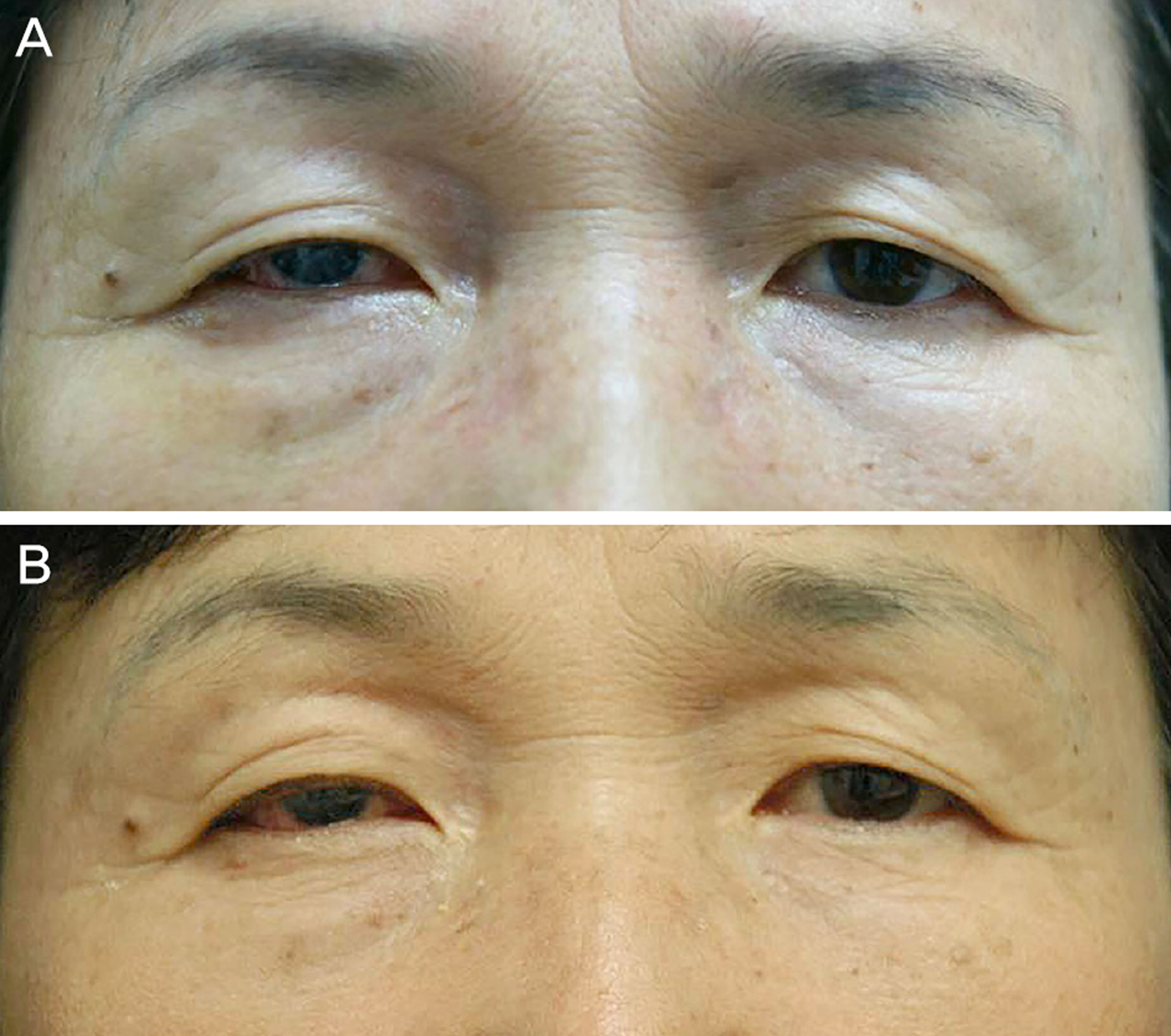
A 54-year-old female presented with right lower eyelid swelling lasting 1 year. There was no tenderness in the right lower eyelid but Tyndall effect was observed. Ultrasonographic findings showed soft tissue swelling in the right lower eyelid. The patient had 3 mm enophthalmos in the right eye on exophthalmometry due to phthisis bulbi resulting from trauma 10 years prior to presentation. Retrobulbar hyaluronic acid filler (Juvederm voluma; Allergan, Irvine, CA, USA) injections were performed to increase orbital volume; 2 mL of filler was injected in the retrobulbar space twice at 1-month interval. After injections, the patient experienced right lower lid swelling lasting 1 year. The patient was diagnosed with lower eyelid swelling due to anterior filler displacement. Hyaluronidase (H-lase inj 1,500 IU/A; Gunil, Seoul, Korea) was reconstituted in 10 mL of normal saline and 0.1 mL (15 IU) of reconstituted hyaluronidase was injected into the right lower eyelid subcutaneously at 5 different areas. At 5 weeks following injections, the lower eyelid swelling was rarely observed and she was satisfied with the result.
CONCLUSIONS
Long-lasting lower lid swelling after retrobulbar hyaluronic acid filler injection can be quickly and effectively treated with hyaluronidase injections.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Rubin PA, Rumelt S. Functional indications for enophthalmos A repair. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999; 15:284–92.2. Ji YH, Woo KI, Kim YD. Porous polyethylene in the repair of late posttraumatic enophthalmos. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1–10.3. Hilton S, Schrumpf H, Buhren BA. . Hyaluronidase injection for the treatment of eyelid edema: a retrospective analysis of 20 patients. Eur J Med Res. 2014; 19:30.
Article4. Menon H, Thomas M, D’silva J. Low dose of Hyaluronidase to treat over correction by HA filler-a case report. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010; 63:e416–7.
Article5. Park TH, Seo SW, Kim JK, Chang CH. Clinical experience with hyaluronic acid-filler complications. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011; 64:892–6.
Article6. Paik DW, Jang IB, Kim JS. . A case of visual loss and oph-thalmoplegia following injection of hyaluronic acid into the glabella. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:971–6.
Article7. Cahill KV, Burns JA. Volume augmentation of the anophthalmic orbit with cross-linked collagen (Zyplast). Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:1684–6.
Article8. Hunter PD, Baker SS. The treatment of enophthalmos by orbital in-jection of fat autograft. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1994; 120:835–9.
Article9. Huang ZL, Ma L. Restoration of enophthalmos in anophthalmic socket by HTR polymer. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 21:318–21.
Article10. Vagefi MR, McMullan TF, Burroughs JR. . Injectable calcium hydroxylapatite for orbital volume augmentation. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2007; 9:439–42.
Article11. Buchanan AG, Holds JB, Vagefi MR. . Anterior filler displace-ment following injection of calcium hydroxylapatite gel (Radiesse) for anophthalmic orbital volume augmentation. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012; 28:335–7.
Article12. Brody HJ. Use of hyaluronidase in the treatment of granulomatous hyaluronic acid reactions or unwanted hyaluronic acid misplacement. Dermatol Surg. 2005; 31:(8 Pt 1). 893–7.
Article13. Lambros V. The use of hyaluronidase to reverse the effects of hya-luronic acid filler. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 114:277.
Article14. Jordan DR, Stoica B. Filler migration: a number of mechanisms to consider. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015; 31:257–62.15. Rao V, Chi S, Woodward J. Reversing facial fillers: interactions be-tween hyaluronidase and commercially available hyaluronic-acid based fillers. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014; 13:1053–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Retrobulbar Filler Injections for Correcting Enophthalmos Associated with Phthisis Bulbi or Anophthalmos
- Effect of Ultrasound-guided Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection in Anophthalmic Enophthalmos Syndrome
- Hyaluronidase: An overview of its properties, applications, and side effects
- Facial Pseudocyst Caused by Hyaluronic Acid Filler Injection: A Case Report
- The Stability of the ALSA Plasma Gel Filler and the Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Rabbits