Cancer Res Treat.
2015 Jul;47(3):441-447. 10.4143/crt.2013.219.
Concurrent Chemoradiation with Low-Dose Weekly Cisplatin in Locally Advanced Stage IV Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. jinpyeong@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2148493
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2013.219
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Concurrent chemoradiation (CRT) with 3-weekly doses of cisplatin is a standard treatment for loco-regionally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, treatment with 3-weekly doses of cisplatin is often associated with several adverse events. Therefore, we conducted this retrospective analysis to determine the efficacy and tolerance of CRT with a low weekly dose of cisplatin in stage IV HNSCC patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Medical records of patients who were diagnosed with stage IV HNSCC and received concurrent CRT were analyzed. All patients were treated weekly with cisplatin at 20-30 mg/m2 until radiotherapy was completed.
RESULTS
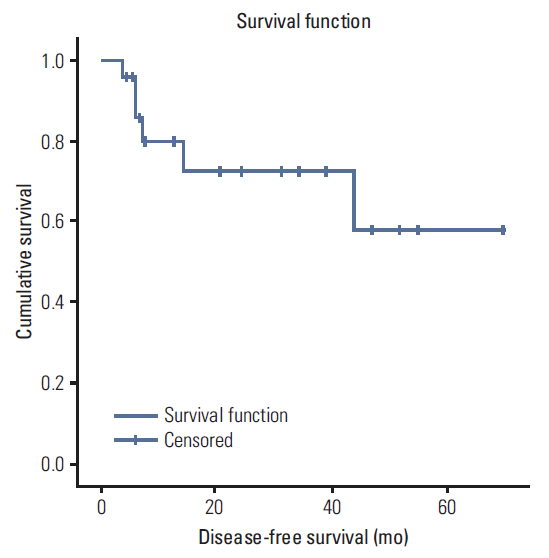
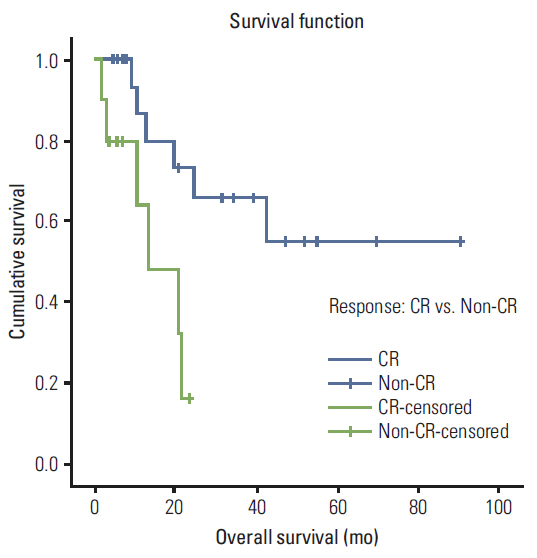
A total of 35 patients were reviewed. Median follow up was 10.7 months (range, 1.7 to 90.5 months), the median radiation dose was 7,040 cGy, and the median dose of cisplatin received was 157 mg/m2. Eleven patients received docetaxel combination chemotherapy. Overall, 25 patients (71.4%) achieved complete response (CR), eight (22.9%) showed partial response. The median overall survival was 42.7 months, the 3-year survival rate was 51.2% and the 3 year disease-free survival rate was 72.8%. Overall survival was improved in patients who achieved CR relative to others (59.7 months vs. 13.4 months; p=0.008). There were significant differences in survival between patients who received docetaxel combination and cisplatin alone (51.8 months vs. 7.9 months; p=0.009). Grade 3-4 adverse events included stomatitis (82.9%), dermatitis (22.9%), infection (11.4%), dysphagia (8.6%), and neutropenia (5.7%).
CONCLUSION
CRT with low dose weekly cisplatin is likely effective and tolerable, even in patients with locally advanced-stage IV HNSCC.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prognostic Value of Combined Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand and p16 Expression Predicting Responsiveness to Radiotherapy in Patients with Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Minsu Kwon, Dae Hwan Kim, Ki Ju Cho, Youngchul Kim, Jin Pyeong Kim, Bae Kwon Jeong, Jong Sil Lee, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jung Je Park
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2019;62(12):712-719. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2019.00619.
Reference
-
References
1. Pignon JP, Bourhis J, Domenge C, Designe L. Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head and neck squamouscell carcinoma: three meta-analyses of updated individual data. MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy on head and neck cancer. Lancet. 2000; 355:949–55.2. Forastiere AA, Goepfert H, Maor M, Pajak TF, Weber R, Morrison W, et al. Concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy for organ preservation in advanced laryngeal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:2091–8.
Article3. Budach W, Hehr T, Budach V, Belka C, Dietz K. A meta-analysis of hyperfractionated and accelerated radiotherapy and combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy regimens in unresected locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. BMC Cancer. 2006; 6:28.
Article4. Traynor AM, Richards GM, Hartig GK, Khuntia D, Cleary JF, Wiederholt PA, et al. Comprehensive IMRT plus weekly cisplatin for advanced head and neck cancer: the University of Wisconsin experience. Head Neck. 2010; 32:599–606.
Article5. Adelstein DJ, Li Y, Adams GL, Wagner H Jr, Kish JA, Ensley JF, et al. An intergroup phase III comparison of standard radiation therapy and two schedules of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:92–8.
Article6. Al-Sarraf M, Pajak TF, Marcial VA, Mowry P, Cooper JS, Stetz J, et al. Concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy with cisplatin in inoperable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: an RTOG Study. Cancer. 1987; 59:259–65.
Article7. Machtay M, Moughan J, Trotti A, Garden AS, Weber RS, Cooper JS, et al. Factors associated with severe late toxicity after concurrent chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer: an RTOG analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:3582–9.
Article8. Ho KF, Swindell R, Brammer CV. Dose intensity comparison between weekly and 3-weekly cisplatin delivered concurrently with radical radiotherapy for head and neck cancer: a retrospective comparison from New Cross Hospital, Wolverhampton, UK. Acta Oncol. 2008; 47:1513–8.
Article9. Steinmann D, Cerny B, Karstens JH, Bremer M. Chemoradiotherapy with weekly cisplatin 40 mg/m(2) in 103 head-and-neck cancer patients: a cumulative dose-effect analysis. Strahlenther Onkol. 2009; 185:682–8.10. Jeremic B, Shibamoto Y, Stanisavljevic B, Milojevic L, Milicic B, Nikolic N. Radiation therapy alone or with concurrent low-dose daily either cisplatin or carboplatin in locally advanced unresectable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a prospective randomized trial. Radiother Oncol. 1997; 43:29–37.
Article11. Huguenin P, Beer KT, Allal A, Rufibach K, Friedli C, Davis JB, et al. Concomitant cisplatin significantly improves locoregional control in advanced head and neck cancers treated with hyperfractionated radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:4665–73.
Article12. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005; 55:74–108.
Article13. Cooper JS, Pajak TF, Forastiere AA, Jacobs J, Campbell BH, Saxman SB, et al. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1937–44.
Article14. Chan AT, Leung SF, Ngan RK, Teo PM, Lau WH, Kwan WH, et al. Overall survival after concurrent cisplatin-radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005; 97:536–9.
Article15. Homma A, Inamura N, Oridate N, Suzuki S, Hatakeyama H, Mizumachi T, et al. Concomitant weekly cisplatin and radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011; 41:980–6.
Article16. Espeli V, Zucca E, Ghielmini M, Giannini O, Salatino A, Martucci F, et al. Weekly and 3-weekly cisplatin concurrent with intensity-modulated radiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell cancer. Oral Oncol. 2012; 48:266–71.
Article17. Otty Z, Skinner MB, Dass J, Collins M, Mooi J, Thuraisingam K, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of weekly low-dose cisplatin concurrent with radiotherapy in head and neck cancer patients. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2011; 7:287–92.
Article18. Kose F, Besen A, Sumbul T, Sezer A, Karadeniz C, Disel U, et al. Weekly cisplatin versus standard three-weekly cisplatin in concurrent chemoradiotherapy of head and neck cancer: the Baskent University experience. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011; 12:1185–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracial infusion and cisplatin for locally advanced, untreated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- Comparison of concurrent chemoradiation therapy with weekly cisplatin versus monthly fluorouracil plus cisplatin in FIGO stage IIB-IVA cervical cancer
- The Efficacy of an Induction Chemotherapy Combination with Docetaxel, Cisplatin, and 5-FU Followed by Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Advanced Head and Neck Cancer
- Chemotherapy of Head and Neck Cancer
- Organ Preservation for the Management of Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer