Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Sep;7(5):467-475. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.467.
The Prevalence of Toxocariasis and Diagnostic Value of Serologic Tests in Asymptomatic Korean Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Health Promotion, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Allergy, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dcchoi@skku.edu
- KMID: 2147955
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.5.467
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Toxocariasis is the most common cause of peripheral blood eosinophilia in Korea and produces eosinophilic infiltration in various organs, including the lung. However, the prevalence of toxocariasis in the general population is rarely reported.
METHODS
We investigated the seroprevalence of Toxocara larval antibody among asymptomatic people who attended Samsung Medical Center for a health checkup, including low-dose chest computed tomography (CT) between March 2012 and December 2013. A total of 633 people (400 men and 233 women) were prospectively recruited.
RESULTS
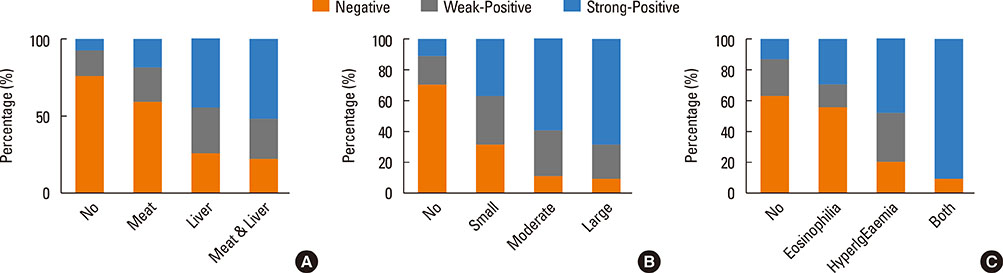
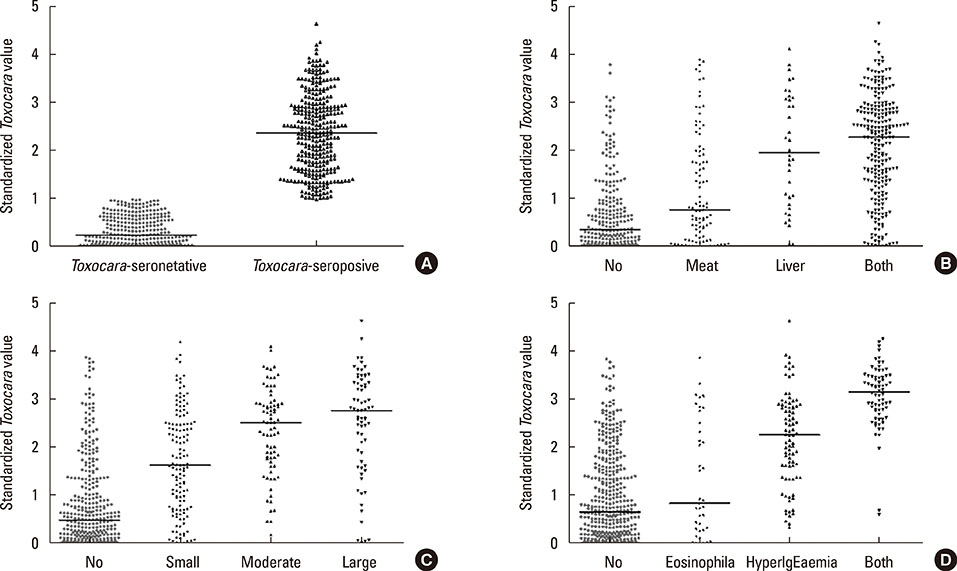
The Toxocara-seropositive rate was 51.2% using the current cutoff value based on Toxocara enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (67.0% for men and 24.0% for women). In the multivariate-adjusted model, age (odds ratio [OR], 1.08; 95% confidence intervals [CI], 1.04-1.11), male sex (OR, 3.47; 95% CI, 2.26-5.33), rural residence (OR, 1.55; 95% CI, 1.05-2.30), and history of raw liver intake (OR, 8.52; 95% CI, 3.61-20.11) were significantly associated with Toxocara seropositivity. When subjects were divided into 3 groups using cutoff values base on weak positive and strong positive control optical densities (ODs), the ORs for peripheral blood eosinophilia and serum hyperIgEaemia were 0.31 (95% CI, 0.02-2.89) in the weakpositive group and 36.64 (95% CI, 11.73-111.42) in the strong positive group compared to the seronegative group. Similarly, ORs for the solid nodule with surrounding halo were 2.54 (95% CI, 0.60-10.84) in the weak positive group and 15.08 (95 CI 4.09-55.56) in the strong positive group compared to the seronegative group.
CONCLUSIONS
The study indicated that the Toxocara-seropositive rate obtained by using the current cutoff value based on ELISA was high in the asymptomatic population in Korea. The results of this study suggest that active toxocariasis may be more frequently seen in the Toxocara-strong positive group than in the Toxocara-weak positive group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Recent advances in the classification and management of hypereosinophilia
Chan Sun Park, Sang Pyo Lee
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(6):387-395. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.6.387.Prevalence of Self-reported Allergic Diseases and IgE Levels: A 2010 KNHANES Analysis
Hye Jung Park, Eun-Jin Kim, Dankyu Yoon, Jeom Kyu Lee, Woo-Sung Chang, Yoen-Mi Lim, Jung-Won Park, Joo-Shil Lee
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(4):329-339. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.329.Eosinophilic Meningitis Associated with Toxocariasis
Jin Kyo Choi, Jin Woo Lee, Yong Hui Park, Seo Hyun Kim
J Neurocrit Care. 2015;8(2):115-117. doi: 10.18700/jnc.2015.8.2.115.
Reference
-
1. Magnaval JF, Glickman LT, Dorchies P, Morassin B. Highlights of human toxocariasis. Korean J Parasitol. 2001; 39:1–11.2. Kang SW, Jang H, Jeong WS. Prevalence of intestinal parasites from dogs in Korea. Korean J Vet Public Health. 2000; 24:195–202.3. Sommerfelt IE, Rosa A, Duchene A, Degregorio O, López C, Pisanú A, et al. Toxocara canis in experimentally infected pigs: migratory pattern and tissue lesions. Vet Parasitol. 2004; 125:323–334.4. Fitzgerald PR, Mansfield ME. Visceral larva migrans (Toxocara canis) in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1970; 31:561–565.5. Olson LJ, Petteway MB. Invasion of the spinal cord of mice by Toxocara canis. J Parasitol. 1972; 58:413–414.6. Taira K, Permin A, Kapel CM. Establishment and migration pattern of Toxocara canis larvae in chickens. Parasitol Res. 2003; 90:521–523.7. Helwigh AB, Lind P, Nansen P. Visceral larva migrans: migratory pattern of Toxocara canis in pigs. Int J Parasitol. 1999; 29:559–565.8. Rahman A, Begum N, Nooruddin M, Rahman MS, Hossain MA, Song HJ. Prevalence and risk factors of helminth infections in cattle of Bangladesh. Korean J Vet Serv. 2009; 32:265–273.9. Glickman LT, Schantz PM. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of zoonotic toxocariasis. Epidemiol Rev. 1981; 3:230–250.10. Beaver PC. The nature of visceral larva migrans. J Parasitol. 1969; 55:3–12.11. Kang YB, Wee SH, Kim SH, Jang H, Choi SH. Fluctuation of internal parasite infections in industrialized piggeries in Korea. Korean J Vet Public Health. 1989; 13:15–19.12. Cheong KS, Kim JT, Lee MJ, Jung BD, Ahn DC, Kim JT, et al. Prevalence of internal parasites in housed cattle farms in Gangwon-do. Korean J Vet Serv. 2007; 30:175–181.13. Cho HT, Chung KY, Suh MD. A survey of the internal parasites of holstein cattle in western Gyeongnam area. Korean J Vet Res. 1986; 26:329–336.14. Lee JK, Park YJ. A survey of internal parasitism in dairy cows and Korean native cattle in Chonnam area. Rural Dev Rev. 1981; 16:61–66.15. Despommier D. Toxocariasis: clinical aspects, epidemiology, medical ecology, and molecular aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003; 16:265–272.16. Choi D, Lim JH, Choi DC, Lee KS, Paik SW, Kim SH, et al. Transmission of Toxocara canis via ingestion of raw cow liver: a cross-sectional study in healthy adults. Korean J Parasitol. 2012; 50:23–27.17. Kwon NH, Oh MJ, Lee SP, Lee BJ, Choi DC. The prevalence and diagnostic value of toxocariasis in unknown eosinophilia. Ann Hematol. 2006; 85:233–238.18. Chang S, Lim JH, Choi D, Park CK, Kwon NH, Cho SY, et al. Hepatic visceral larva migrans of Toxocara canis: CT and sonographic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:W622–W629.19. Inoue K, Inoue Y, Arai T, Nawa Y, Kashiwa Y, Yamamoto S, et al. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia due to visceral larva migrans. Intern Med. 2002; 41:478–482.20. Lee JY, Kim BJ, Lee SP, Jeung YJ, Oh MJ, Park MS, et al. Toxocariasis might be an important cause of atopic myelitis in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:1024–1030.21. Caldera F, Burlone ME, Genchi C, Pirisi M, Bartoli E. Toxocara encephalitis presenting with autonomous nervous system involvement. Infection. 2013; 41:691–694.22. Choi D, Lim JH, Choi DC, Paik SW, Kim SH, Huh S. Toxocariasis and ingestion of raw cow liver in patients with eosinophilia. Korean J Parasitol. 2008; 46:139–143.23. Park HY, Lee SU, Huh S, Kong Y, Magnaval JF. A seroepidemiological survey for toxocariasis in apparently healthy residents in Gangwon-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 2002; 40:113–117.24. Seo M, Yoon SC. A seroepidemiological survey of toxocariasis among eosinophilia patients in Chungcheongnam-do. Korean J Parasitol. 2012; 50:249–251.25. Lim JH, Lee KS. Eosinophilic infiltration in Korea: idiopathic? Korean J Radiol. 2006; 7:4–6.26. Schantz PM. Toxocara larva migrans now. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989; 41:21–34.27. Barriga OO. A critical look at the importance, prevalence and control of toxocariasis and the possibilities of immunological control. Vet Parasitol. 1988; 29:195–234.28. Kim HS, Jin Y, Choi MH, Kim JH, Lee YH, Yoon CH, et al. Significance of serum antibody test for toxocariasis in healthy healthcare examinees with eosinophilia in Seoul and Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2014; 29:1618–1625.29. Ryu BH, Park JS, Jung YJ, Kang SK, Lee SH, Choi SJ. Clinical and serological findings in patients with toxocariasis in the Pohang region: the features of toxocariasis in Pohang. Korean J Med. 2013; 84:203–210.30. Lee SP. Hightlights and diagnostic dilemma of toxocariasis. Korean J Med. 2013; 84:200–202.31. Abo-Shehada MN, Herbert IV. The migration of larval Toxocara canis in mice. II. Post-intestinal migration in primary infections. Vet Parasitol. 1984; 17:75–83.32. Kennedy MW, Tierney J, Ye P, McMonagle FA, McIntosh A, McLaughlin D, et al. The secreted and somatic antigens of the third stage larva of Anisakis simplex, and antigenic relationship with Ascaris suum, Ascaris lumbricoides, and Toxocara canis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988; 31:35–46.33. Bass JL, Mehta KA, Glickman LT, Blocker R, Eppes BM. Asymptomatic toxocariasis in children. A prospective study and treatment trial. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 1987; 26:441–446.34. Małafiej E, Spiewak E. The significance of the level of antibodies in the evaluation of the effects of treatment of toxocariasis. Wiad Parazytol. 2001; 47:805–810.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hightlights and Diagnostic Dilemma of Toxocariasis
- Reversible Encephalopathy Caused by Reactive Hypereosinophilia due to Toxocariasis
- A case of human toxocariasis with hypereosinophilic syndrome confirmed by serologic test
- Cerebral Toxocariasis Presented With Seizure and Memory Disturbance
- Eosinophilic Myocarditis-Associated Toxocariasis