Korean Circ J.
2013 Jul;43(7):500-503. 10.4070/kcj.2013.43.7.500.
A Delayed, Unusual Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema after Intravascular Administration of Non-Ionic, Low Osmolar Radiocontrast Media for Coronary Angiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drjcna@nate.com
- KMID: 2145508
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2013.43.7.500
Abstract
- Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema (NCPE) is a rare adverse reaction to iodinated radiocontrast media (RCM), in which all previous cases were immediate reactions. A 56-year-old male was given iopamidol, a non-ionic, low osmolar RCM, during coronary artery angiography. He developed pulmonary edema and fever a day after the procedure. Despite diuretic therapy, the patient's pulmonary edema worsened and his high fever persisted. The patient's pulmonary edema was eventually resolved with intravenous steroid treatment. We interpreted the patient's condition as NCPE manifesting as a delayed reaction to RCM. To our knowledge, our case is the first to show NCPE as a delayed hypersensitivity reaction.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
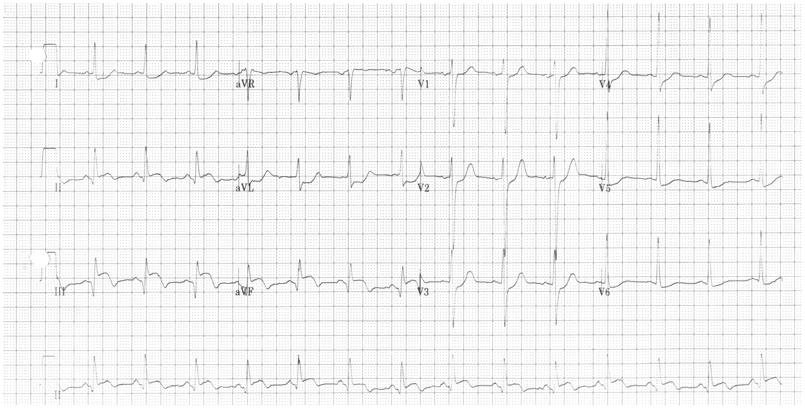
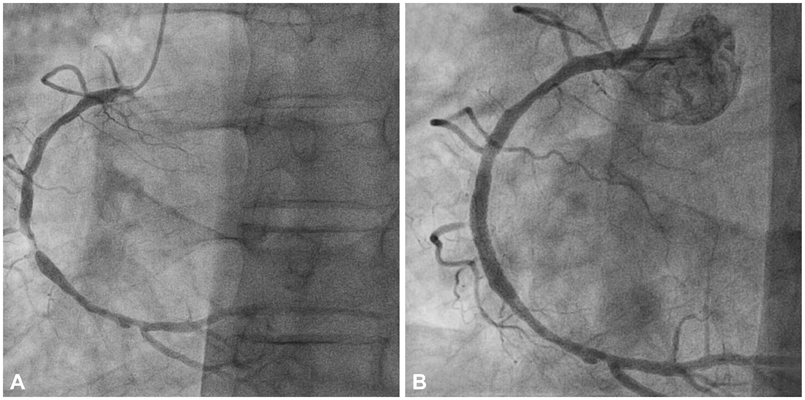
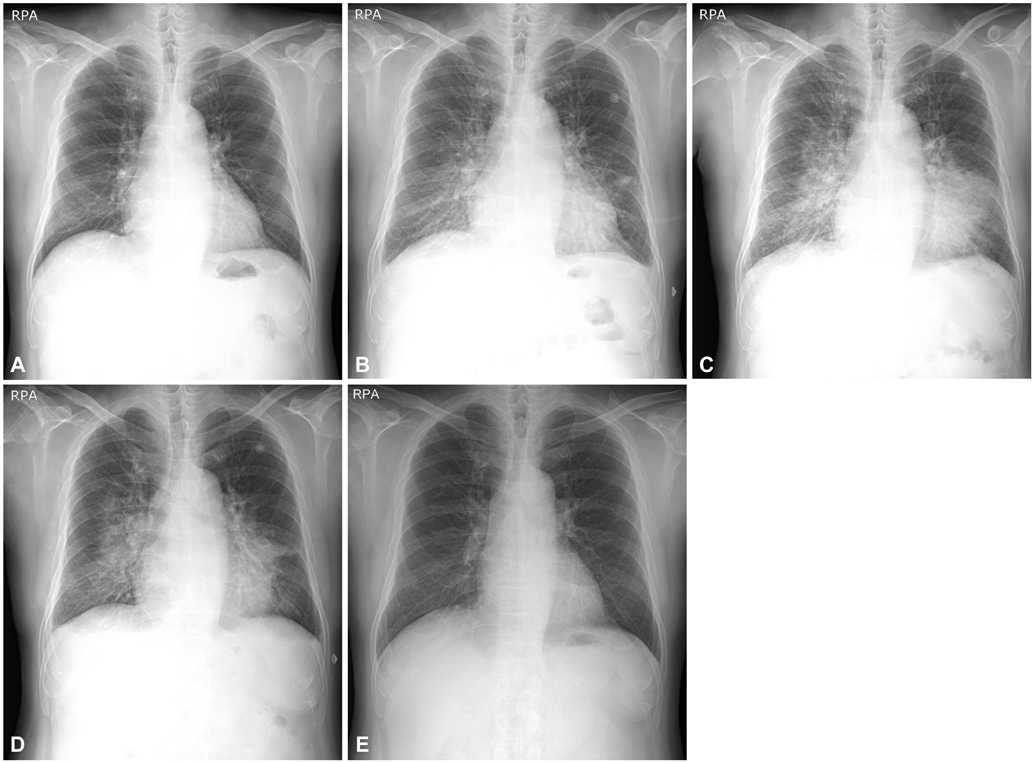
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brockow K. Immediate and delayed reactions to radiocontrast media: is there an allergic mechanism? Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009; 29:453–468.2. Brockow K, Christiansen C, Kanny G, et al. Management of hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media. Allergy. 2005; 60:150–158.3. Namasivayam S, Kalra MK, Torres WE, Small WC. Adverse reactions to intravenous iodinated contrast media: a primer for radiologists. Emerg Radiol. 2006; 12:210–215.4. Nayak KR, White AA, Cavendish JJ, Barker CM, Kandzari DE. Anaphylactoid reactions to radiocontrast agents: prevention and treatment in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. J Invasive Cardiol. 2009; 21:548–551.5. Bellin MF, Stacul F, Webb JA, et al. Late adverse reactions to intravascular iodine based contrast media: an update. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21:2305–2310.6. Webb JA, Stacul F, Thomsen HS, Morcos SK. Members Of The Contrast Media Safety Committee Of The European Society Of Urogenital Radiology. Late adverse reactions to intravascular iodinated contrast media. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13:181–184.7. Christiansen C. Late-onset allergy-like reactions to X-ray contrast media. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002; 2:333–339.8. Christiansen C, Pichler WJ, Skotland T. Delayed allergy-like reactions to X-ray contrast media: mechanistic considerations. Eur Radiol. 2000; 10:1965–1975.9. Goldsmith SR, Steinberg P. Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema induced by nonionic low-osmolality radiographic contrast media. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995; 96(5 Pt 1):698–699.10. Bristedt P, Tylén U. Pulmonary edema following intravenous injection of nonionic low-osmolar contrast medium--appearance on HRCT. A case report. Acta Radiol. 1998; 39:81–83.11. Nakajima T, Takahashi T, Umezawa K, Shimizu K, Okada H, Kaneko U. [Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema induced by non-ionic radiographic contrast media during the coil embolization for a ruptured cerebral aneurysm]. No Shinkei Geka. 2005; 33:703–707.12. Paul RE, George G. Fatal non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema after intravenous non-ionic radiographic contrast. Lancet. 2002; 359:1037–1038.13. Hauggaard A. Non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema after intravenous administration of non-ionic contrast media. Acta Radiol. 1996; 37:823–825.14. Newman B. Delayed adverse reaction to nonionic contrast agents. Pediatr Radiol. 2001; 31:597–599.15. Ramesh S, Reisman RE. Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema due to radiocontrast media. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1995; 75:308–310.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Non-Ionic Contrast Media on Q-T Interval and ST-T Wave of ECG during Coronary Angiography
- Cytotoxicity of Low - osmolar Nonionic and High - osmolar lonic Contrast Media: Comparative Study Using Gallbladder Epithelial Cell
- Clinical application of intravascular administration of non-ionic, low osmolar contrast agent, ioversol(Optiray320) and its side effects comparison with meglumine iothalamate
- A case of anaphylactoid reaction to nonionic contrast agent, Iodixanol (Visipaque(R)) during coronary angiography
- In vitro study on the anticoagulant effect of the water soluble contrast material: diatrizoate, ioxaglate and iopromide