J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2014 Sep;21(3):134-138. 10.4184/jkss.2014.21.3.134.
Sequestrated Intradural Disc Herniation Around Couns Medullaris: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea. hyparkys@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2144776
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2014.21.3.134
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A case report.
OBJECTIVES
To report a rare case of intradural disc herniation (IDH) around conus medullaris. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: IDH is rare with an incidence of less than 1% of all lumbar disc herniations. It is important to differentiate IDH from other condition with accurate diagnosis and subsequent surgical treatment. IDH has a higher risk of neurologic deficit, like conus medullaris syndrome and cauda equina syndrome.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
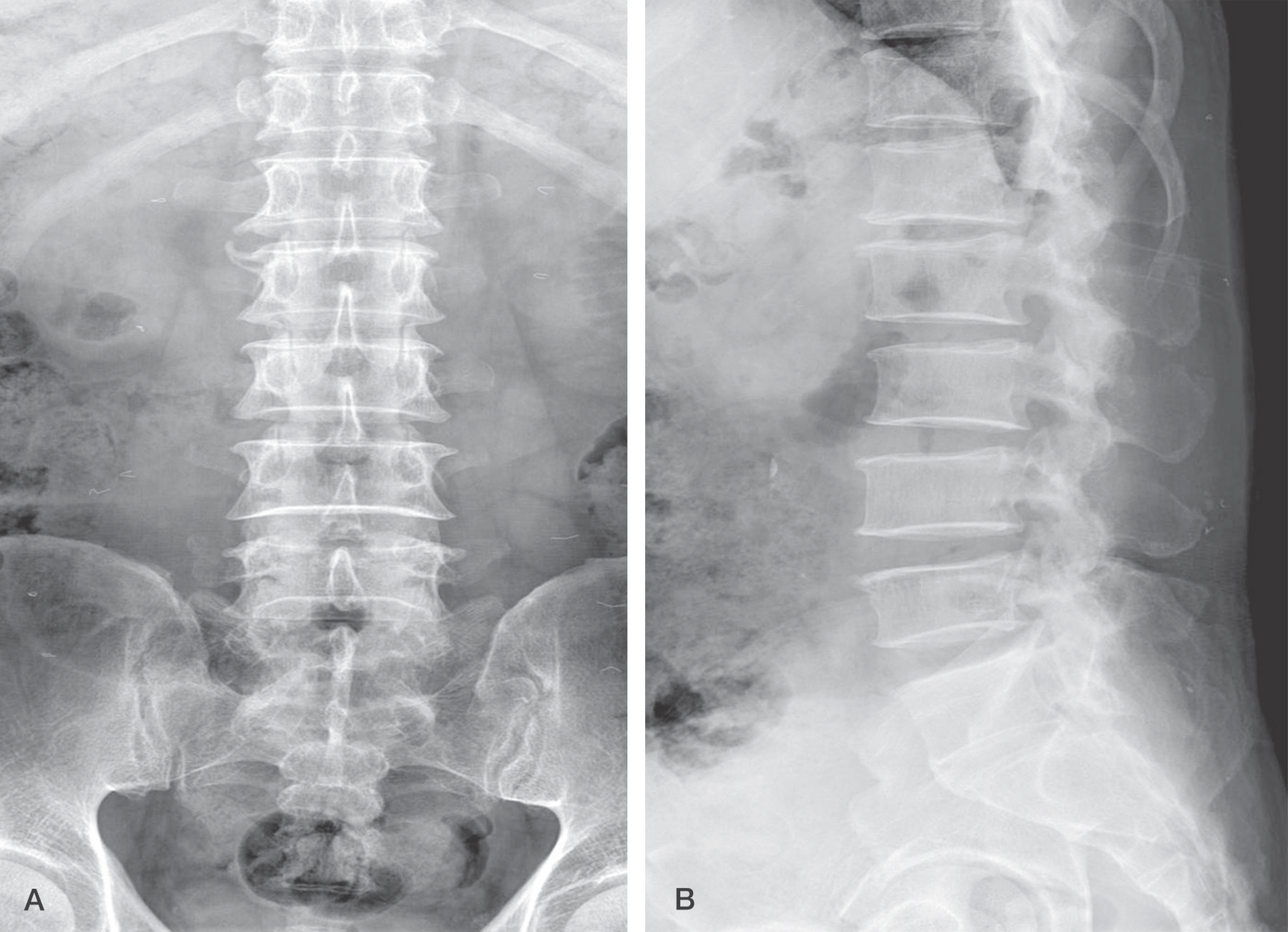
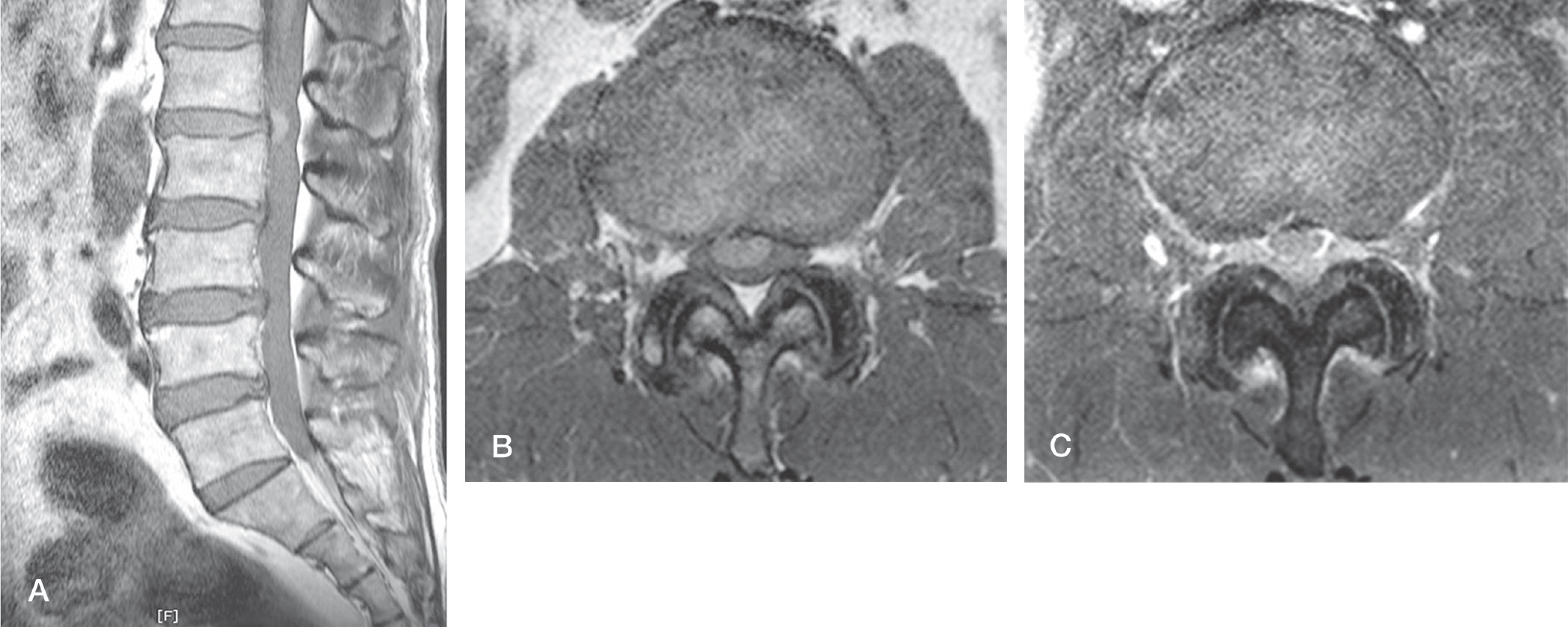
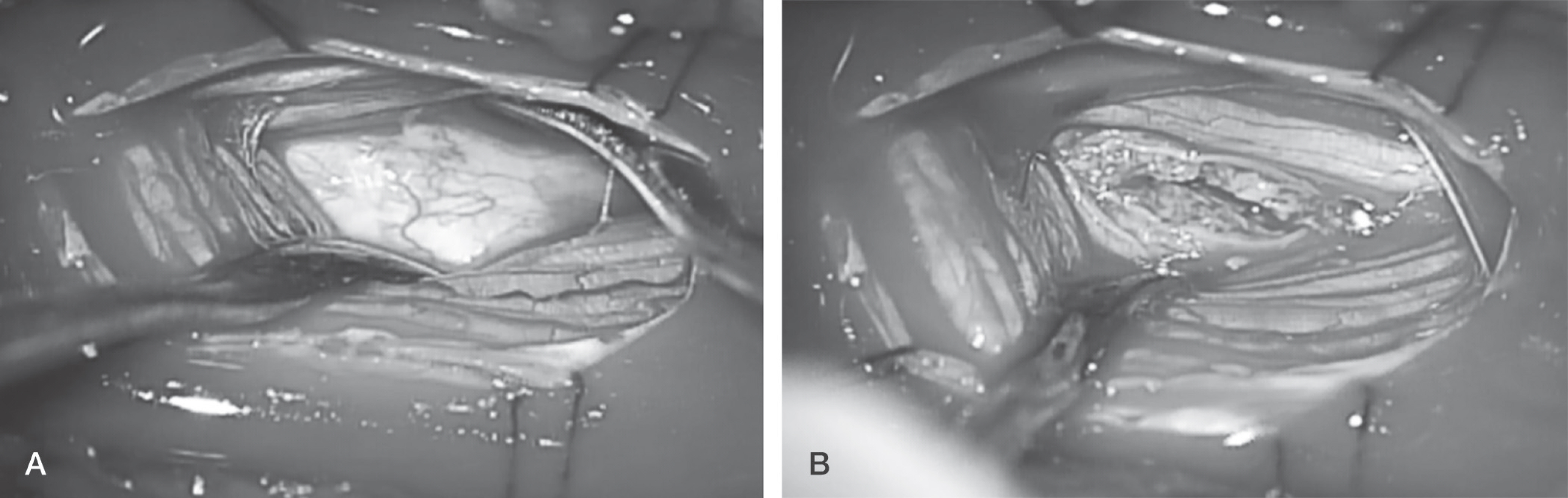
A 62 year-old male was affected by lumbar back pain radiating to the anterolateral aspect of the right thigh for 5 days. MRI showed a mass that existed on the anterior portion of the conus medullaris. We performed partial laminectomy at the L1-L2level. The mass located anteriorly in the intradural space was eliminated after durotomy by a posterior approach.
RESULTS
We confirmed the IDH for histopathology.
CONCLUSIONS
IDH usually needs accurate differential diagnosis. Preoperative MRI scans are necessary to differentiate IDH from other intradural lesions. The confirmative diagnosis can be done only in the operative field.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Epstein NE, Syrquin MS, Epstein JA, Decker RE. Intradural disc herniations in the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine: report of three cases and review of the literature. J Spinal Disord. 1990; 3:396–403.2. Kataoka O, Nishibayashi Y, Sho T. Intradural lumbar disc herniation. Report of three cases with a review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989; 14:529–33.3. Connolly PJ, Rosenbaum AE, Sacks T, Kopacz KJ. In-complete intradural lumbar disk herniation. Orthopedics. 1997; 20:977–9.
Article4. Eisenberg RA, Bremer AM, Northup HM. Intradural herniated cervical disk: a case report and review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1986; 7:492–4.5. Blikra G. Intradural herniated lumbar disc. J Neurosurg. 1969; 31:676–9.
Article6. Yildizhan A, Pasaoglu A, Okten T, Ekinci N, Aycan K, Aral O. Intradural disc herniations pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis and treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1991; 110:160–5.
Article7. Liu CC, Huang CT, Lin CM, Liu KN. Intradural disc herniation at L5 level mimicking an intradural spinal tumor. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(Suppl 2):S326–9.
Article8. Hidalgo-Ovejero AM, Garcia-Mata S, Gozzi-Vallejo S, Izco-Cabezon T, Martinez-Morentin J, Martinez-Grande M. Intradural disc herniation and epidural gas: something more than a casual association? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:E463–7.
Article9. Hida K, Iwasaki Y, Abe H, Shimazaki M, Matsuzaki T. Magnetic resonance imaging of intradural lumbar disc herniation. J Clin Neurosci. 1999; 6:345–7.
Article10. Tali ET, Gultekin S. Spinal infections. Eur Radiol. 2005; 15:599–607.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lumbar Intradural Disc Herniation Mimicking a Chondroma
- Dorsal Herniation of Cauda Equina Due to Sequestrated Intradural Disc
- Huge Intradural Lumbar Disc Herniation Mimicking an Intradural Spinal Tumor: A Case Report
- Intradural Lumbar Disc Rupture
- Intradural Disc Herniation at L5-S1 Mimicking an Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Tumor: A Case Report