J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2013 Dec;21(4):189-191. 10.4250/jcu.2013.21.4.189.
Intermittent, Non Cyclic Severe Mechanical Aortic Valve Regurgitation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea. mariahyeon@hotmail.com
- 2Division of Cardiac Surgery, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Division of Cardiology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2135419
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2013.21.4.189
Abstract
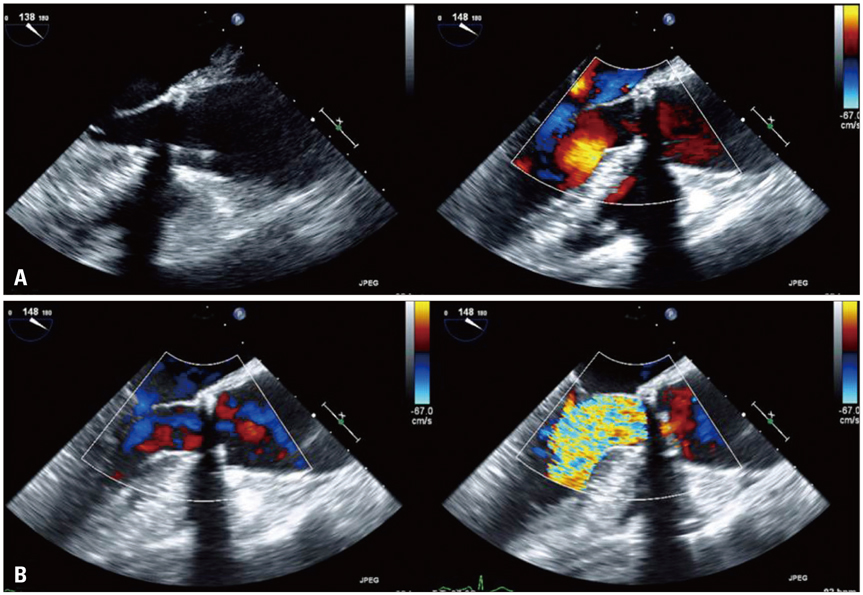
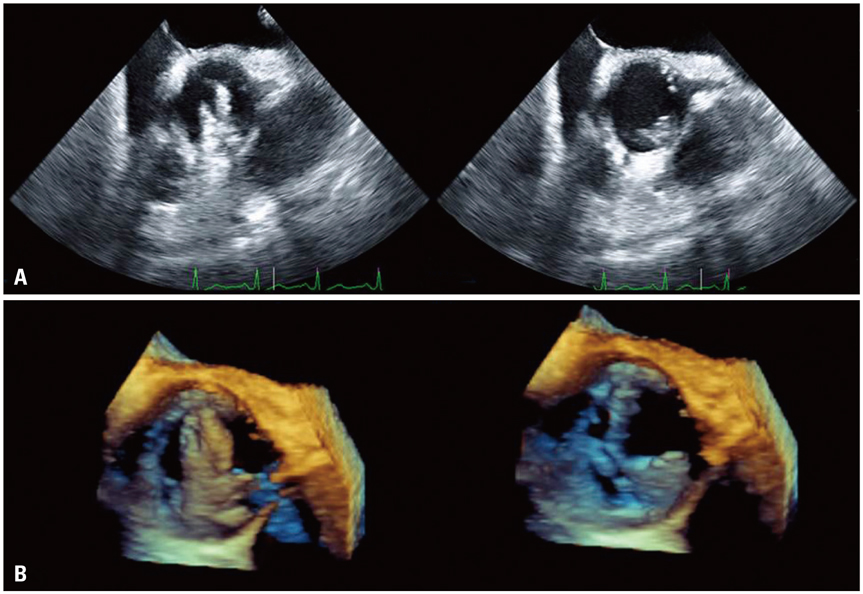
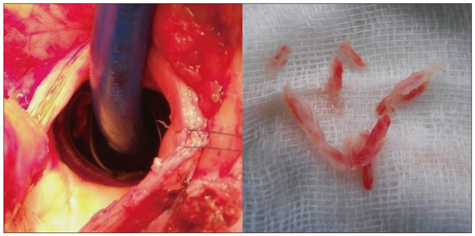
- Mechanical aortic prosthesis dysfunction can result from thrombosis or pannus formation. We describe an unusual case of intermittent, non cyclic mechanical aortic prosthesis dysfunction due to pannus formation with thrombus in the absence of systolic restriction of disk excursion, that presented with intermittent severe aortic regurgitation.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bouma BJ, Koster R. Dysfunction of an aortic prosthetic valve. Heart. 2005; 91:1120.
Article2. Robles P, Jimenez Nacher JJ, Rubio A, Huelmos A, Lopez L. Intermittent aortic regurgitation in a case of mechanical prosthesis dysfunction. Int J Cardiol. 2005; 102:525–527.
Article3. Galli CA, Muratori M, Montorsi P, Barili F, Polvani G, Pepi M. Cyclic intermittent aortic regurgitation of a mechanical bileaflet aortic valve prosthesis: diagnosis and clinical implications. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007; 20:1315.e5–1315.e8.
Article4. Karagiannis SE, Karatasakis G, Spargias K, Louka L, Poldermans D, Cokkinos DV. Intermittent acute aortic valve regurgitation: a case report of a prosthetic valve dysfunction. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2008; 9:291–293.
Article5. Cianciulli TF, Saccheri MC, Lax JA, Guidoin R, Zhang Z, Guerra JE, Prezioso HA, Vidal LA. Intermittent acute aortic regurgitation of a mechanical bileaflet aortic valve prosthesis: diagnosis and clinical implications. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2009; 10:446–449.
Article6. Giroux SK, Labinaz MX, Grisoli D, Klug AP, Veinot JP, Burwash IG. Intermittent, noncyclic dysfunction of a mechanical aortic prosthesis by pannus formation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010; 23:107.e1–107.e3.
Article7. Teshima H, Hayashida N, Yano H, Nishimi M, Tayama E, Fukunaga S, Akashi H, Kawara T, Aoyagi S. Obstruction of St Jude Medical valves in the aortic position: histology and immunohistochemistry of pannus. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003; 126:401–407.
Article8. Barbetseas J, Nagueh SF, Pitsavos C, Toutouzas PK, Quiñones MA, Zoghbi WA. Differentiating thrombus from pannus formation in obstructed mechanical prosthetic valves: an evaluation of clinical, transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic parameters. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998; 32:1410–1417.
Article9. Rizzoli G, Guglielmi C, Toscano G, Pistorio V, Vendramin I, Bottio T, Thiene G, Casarotto D. Reoperations for acute prosthetic thrombosis and pannus: an assessment of rates, relationship and risk. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1999; 16:74–80.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Avulsion of Aortic Commissure: Rare Cause of Aortic Regurgitation: 2 case reports
- Congenital Quadricuspid Aortic Valve
- Anterior Mitral Leaflat Perforation in Patients with Bicuspid Aortic Valve Endocarditis
- Assessment of Mitral Stenosis by Doppler Echocardiography: Influence of Regurgitation on Doppler Pressure Half-Time
- Two Cases of Quadricuspid Aortic Valve Associated with Aortic Regurgitation and Infective Endocarditis