Electrolyte Blood Press.
2008 Dec;6(2):86-95. 10.5049/EBP.2008.6.2.86.
Magnesium Metabolism
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine and Kidney Research Institute, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea. sjwdr@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2134810
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2008.6.2.86
Abstract
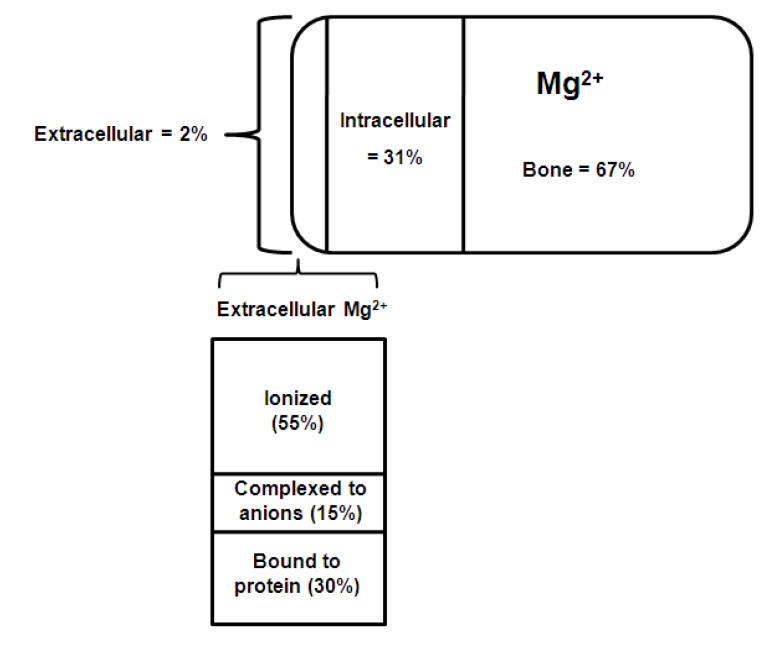
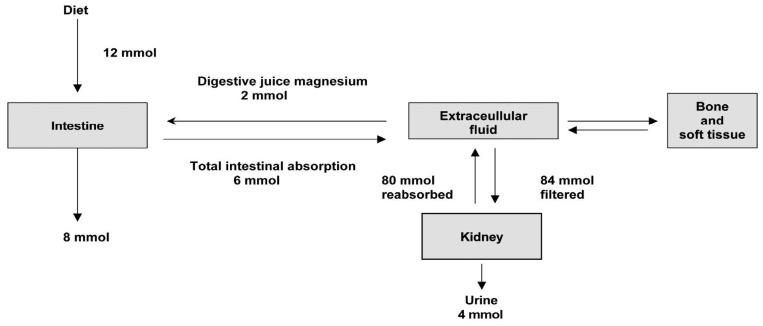
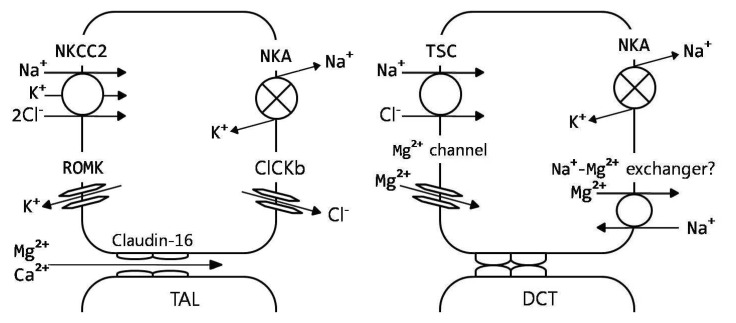
- Magnesium is the second most common intracellular divalent cation. Magnesium balance in the body is controlled by a dynamic interplay among intestinal absorption, exchange with bone, and renal excretion. Intestinal magnesium absorption proceeds in both a passive paracellular and an active transcellular manner. Regulation of serum magnesium concentrations is achieved mainly by control of renal magnesium reabsorption. Only 20% of filtered magnesium is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule, whereas 60% is reclaimed in the cortical thick ascending limb (TAL) and another 5-10% in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT). The passive paracellular transport of magnesium in the TAL is closely related with the mutations in claudin-16/paracellin-1 and is responsible for familial hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis. The active transcellular transport of magnesium in the DCT was similarly enhanced by the realization that defects in transient receptor potential melastatin 6 (TRPM6) cause hypomagnesemia with secondary hypocalcemia. This channel regulates the apical entry of magnesium into epithelia and alters whole-body magnesium homeostasis by controlling urinary excretion. TRPM6 is regulated at the transcriptional level by acid-base status, 17beta-estradiol, and both FK506 and cyclosporine. The molecular identity of the protein responsible for the basolateral exit of magnesium from the epithelial cell remains unidentified.
MeSH Terms
-
Absorption
Cyclosporine
Epithelial Cells
Extremities
Homeostasis
Hypercalciuria
Hypocalcemia
Intestinal Absorption
Magnesium
Nephrocalcinosis
Renal Tubular Transport, Inborn Errors
Tacrolimus
Transcytosis
Transient Receptor Potential Channels
Cyclosporine
Hypocalcemia
Magnesium
Renal Tubular Transport, Inborn Errors
Tacrolimus
Transient Receptor Potential Channels
Figure
Reference
-
1. Swaminathan R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin Biochem Rev. 2003; 24:47–66. PMID: 18568054.2. Noronha JL, Matuschak GM. Magnesium in critical illness: metabolism, assessment, and treatment. Intensive Care Med. 2002; 28:667–679. PMID: 12107669.
Article3. DuBose TD, Hamm LL. Acid-base and electrolyte disorders : a companion to Brenner & Rector's the kidney. 2002. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 435–487.4. de Rouffignac C, Quamme G. Renal magnesium handling and its hormonal control. Physiol Rev. 1994; 74:305–322. PMID: 8171116.
Article5. Saris NE, Mervaala E, Karppanen H, Khawaja JA, Lewenstam A. Magnesium. An update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin Chim Acta. 2000; 294:1–26. PMID: 10727669.6. Nadler JL, Rude RK. Disorders of magnesium metabolism. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1995; 24:623–641. PMID: 8575413.
Article7. Kayne LH, Lee DB. Intestinal magnesium absorption. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1993; 19:210–217. PMID: 8264506.8. Quamme GA, Rabkin SW. Cytosolic free magnesium in cardiac myocytes: identification of a Mg2+ influx pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990; 167:1406–1412. PMID: 2322282.9. Yu AS. Evolving concepts in epithelial magnesium transport. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2001; 10:649–653. PMID: 11496060.
Article10. Konrad M, Weber S. Recent advances in molecular genetics of hereditary magnesium-losing disorders. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003; 14:249–260. PMID: 12506158.
Article11. al-Ghamdi SM, Cameron EC, Sutton RA. Magnesium deficiency: pathophysiologic and clinical overview. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994; 24:737–752. PMID: 7977315.
Article12. Bringhurst FR, Demay MB, Krane SM, Kronenberg HM. Fauci AS, editor. Bone and mineral metabolism in health and disease. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2008. 17th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;p. 2365–2377.13. Alexander RT, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ. Molecular determinants of magnesium homeostasis: insights from human disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 19:1451–1458. PMID: 18562569.
Article14. Fox C, Ramsoomair D, Carter C. Magnesium: its proven and potential clinical significance. South Med J. 2001; 94:1195–1201. PMID: 11811859.15. Whang R, Ryder KW. Frequency of hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia. Requested vs routine. JAMA. 1990; 263:3063–3064. PMID: 2342219.
Article16. Prebble JJ. Primary infantile hypomagnesaemia: report of two cases. J Paediatr Child Health. 1995; 31:54–56. PMID: 7748693.
Article17. Torralbo A, Portoles J, Perez Perez AJ, Barrientos A. Hypomagnesemic hypocalcemia in chronic renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993; 21:167–171. PMID: 8430677.
Article18. Yu ASL. Brenner BM, Rector FC, editors. Disturbances of magnesium metabolism. Brenner & Rector's the kidney. 2000. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;p. 1055–1070.19. Swaminathan R. Davies DM, Ferner RE, Glanville HD, editors. Disorders of metabolism 2. Davies's Textbook of Adverse Drug Reactions. 1998. 5th ed. Arnold, Edward;p. 442–540.20. Ellison DH. Renal magnification by EGF. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008; 23:1497–1499. PMID: 18299299.
Article21. Dorup I. Magnesium and potassium deficiency. Its diagnosis, occurrence and treatment in diuretic therapy and its consequences for growth, protein synthesis and growth factors. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1994; 618:1–55. PMID: 8036903.22. Panichpisal K, Angulo-Pernett F, Selhi S, Nugent KM. Gitelman-like syndrome after cisplatin therapy: a case report and literature review. BMC Nephrol. 2006; 7:10. PMID: 16723030.
Article23. Allen GG, Barratt LJ. Effect of cisplatin on the transepithelial potential difference of rat distal tubule. Kidney Int. 1985; 27:842–847. PMID: 2410659.
Article24. Markmann M, Rothman R, Reichman B, Hakes T, Lewis JL Jr, Rubin S, et al. Persistent hypomagnesemia following cisplatin chemotherapy in patients with ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1991; 117:89–90. PMID: 2007614.
Article25. Huey CG, Chan KM, Wong ET, Nelson JM, Durand M. Los Angeles County-University of Southern California Medical Center clinical pathology case conference: extreme hypermagnesemia in a neonate. Clin Chem. 1995; 41:615–618. PMID: 7720255.
Article26. Oren S, Rapoport J, Zlotnik M, Brami JL, Heimer D, Chaimovitz C. Extreme hypermagnesemia due to ingestion of Dead Sea water. Nephron. 1987; 47:199–201. PMID: 3683688.
Article27. Swaminathan R. Davison AM, editor. Hypo - hypermagnesemia. Oxford textbook of clinical nephrology. 1998. 2nd ed. Oxford ; New York: Oxford University Press;p. 271–310.28. Jaing TH, Hung IJ, Chung HT, Lai CH, Liu WM, Chang KW. Acute hypermagnesemia: a rare complication of antacid administration after bone marrow transplantation. Clin Chim Acta. 2002; 326:201–203. PMID: 12417113.
Article29. Hutchison AJ, Merchant M, Boulton HF, Hinchcliffe R, Gokal R. Calcium and magnesium mass transfer in peritoneal dialysis patients using 1.25 mmol/L calcium, 0.25 mmol/L magnesium dialysis fluid. Perit Dial Int. 1993; 13:219–223. PMID: 8369353.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A comparison of ritodrine and magnesium sulfate for the suppression of preterm labor
- Magnesium Sulfate in the Treatment of Torsade De Pointes
- Magnesium: a versatile drug for anesthesiologists
- Respiratory Depression after Anesthesia in an Eclamptic Patient Treated with Magnesium Sulfate
- About uses of magnesium during perioperative period