Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Sep;5(3):145-149. 10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.145.
Are Systemic Voriconazole and Caspofungin Ototoxic? An Experimental Study with Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey. dremineaydin@gmail.com
- 2Department of Otolaryngology, Ankara Numune Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey.
- 3Department of General Surgery, Ankara Training and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey.
- 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Acibadem Fulya Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey.
- KMID: 2134597
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2012.5.3.145
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
To determine whether systemic administration of voriconazole and caspofungin causes ototoxicity.
METHODS
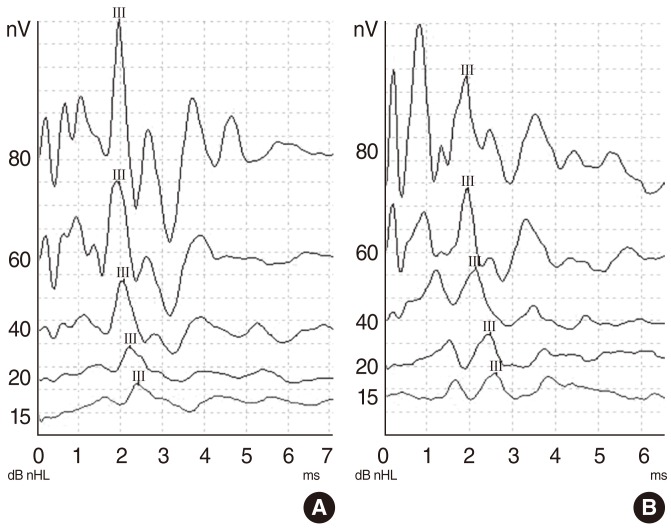
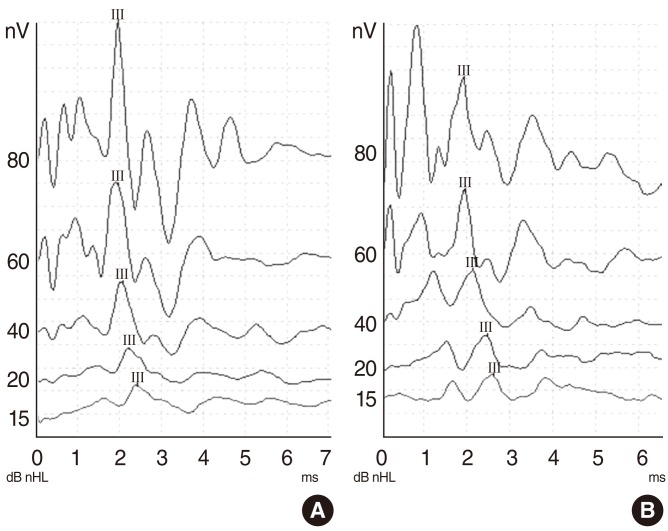
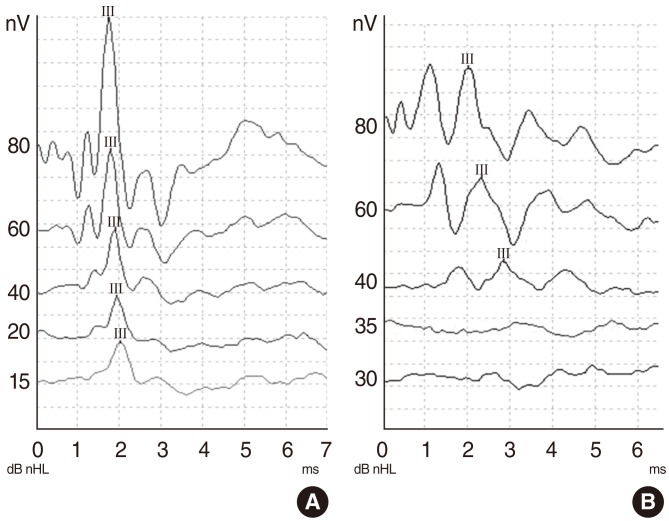
This study was conducted on 32 healthy male Wistar albino rats. The baseline auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds of all animals were obtained under general anesthesia. Then, the rats were randomly divided into 4 groups (groups I-IV), each group consisting of 8 rats. Rats in group I were injected intraperitoneally with voriconazole 10 mg/kg/day for 7 days, and the rats in the group II were injected intraperitoneally with caspofungin 5 mg/kg/day for 7 days. Group III received 120 mg/kg/day gentamicin for 7 days. Group IV received saline for 7 days. The animals were then observed for 7 days, and on 14th day of the trial, posttreatment ABRs of both ears were recorded.
RESULTS
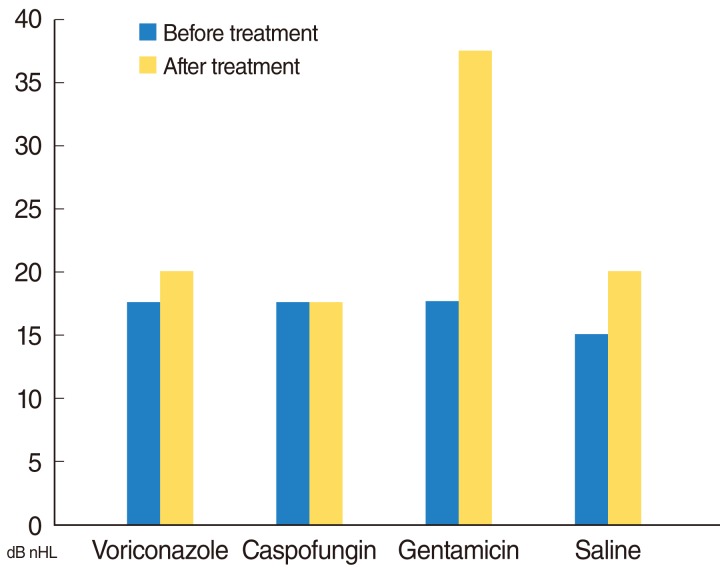
We did not find any significant differences between pretreatment and posttreatment median ABR thresholds in the voriconazole, caspofungin, or saline groups. In the gentamicin group, there was a statistically significant difference between pretreatment and posttreatment ABR thresholds.
CONCLUSION
Caspofungin and voriconazole did not change ABR thresholds in speech frequencies after a 7-day-period of their administration. We believe that further animal studies must be performed after administration of these agents for a longer time period, and these findings must be consolidated with histopathological investigations.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Eschenauer G, Depestel DD, Carver PL. Comparison of echinocandin antifungals. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007; 3. 3(1):71–97. PMID: 18360617.
Article2. Nakaya K, Oshima T, Kudo T, Aoyagi I, Katori Y, Ota J, et al. New treatment for invasive fungal sinusitis: three cases of chronic invasive fungal sinusitis treated with surgery and voriconazole. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2010; 4. 37(2):244–249. PMID: 19553042.
Article3. Tsiodras S, Zafiropoulou R, Giotakis J, Imbrios G, Antoniades A, Manesis EK. Deep sinus aspergillosis in a liver transplant recipient successfully treated with a combination of caspofungin and voriconazole. Transpl Infect Dis. 2004; 3. 6(1):37–40. PMID: 15225226.
Article4. Pfaller MA, Boyken L, Hollis RJ, Kroeger J, Messer SA, Tendolkar S, et al. In vitro susceptibility of clinical isolates of Aspergillus spp. to anidulafungin, caspofungin, and micafungin: a head-to-head comparison using the CLSI M38-A2 broth microdilution method. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 10. 47(10):3323–3325. PMID: 19710267.5. Vennewald I, Klemm E. Otomycosis: diagnosis and treatment. Clin Dermatol. 2010; 3. 28(2):202–211. PMID: 20347664.
Article6. Aycicek A, Cetinkaya Z, Kiyici H, Kenar F, Asik G, Kiraz N. The effects of caspofungin and voriconazole in an experimental fungal infection of the ear due to Aspergillus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 11. 266(11):1703–1709. PMID: 19340446.
Article7. Parize P, Chandesris MO, Lanternier F, Poiree S, Viard JP, Bienvenu B, et al. Antifungal therapy of Aspergillus invasive otitis externa: efficacy of voriconazole and review. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 3. 53(3):1048–1053. PMID: 19104029.8. Said T, Nampoory MR, Nair MP, Al-Saleh M, Al-Haj KH, Halim MA, et al. Safety of caspofungin for treating invasive nasal sinus aspergillosis in a kidney transplant recipient. Transplant Proc. 2005; 9. 37(7):3038–3040. PMID: 16213297.
Article9. van de Sande WW, van Vianen W, ten Kate MT, Vissers J, Laurijsens J, Tavakol M, et al. Caspofungin prolongs survival of transiently neutropenic rats with advanced-stage invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 4. 52(4):1345–1350. PMID: 18195059.
Article10. Tom LW. Ototoxicity of common topical antimycotic preparations. Laryngoscope. 2000; 4. 110(4):509–516. PMID: 10763995.
Article11. Shine NP, Coates H. Systemic ototoxicity: a review. East Afr Med J. 2005; 10. 82(10):536–539. PMID: 16450683.
Article12. Gurkov R, Eshetu T, Miranda IB, Berens-Riha N, Mamo Y, Girma T, et al. Ototoxicity of artemether/lumefantrine in the treatment of falciparum malaria: a randomized trial. Malar J. 2008; 9. 7:179. PMID: 18796142.
Article13. Shi Y, Martin WH. ABR and DPOAE detection of cochlear damage by gentamicin. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1997; 8(3):141–155. PMID: 9429983.
Article14. Baylancicek S, Serin GM, Ciprut A, Sari M, Akdas F, Tutkun A. Ototoxic effect of topical ciclopirox as an antimycotic preparation. Otol Neurotol. 2008; 10. 29(7):910–913. PMID: 18698269.
Article15. Ozturkcan S, Dundar R, Katilmis H, Ilknur AE, Aktas S, Haciomeroglu S. The ototoxic effect of boric acid solutions applied into the middle ear of guinea pigs. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 5. 266(5):663–667. PMID: 18795310.
Article16. van Tol A, van Rijswijk J. Aspergillus mastoiditis, presenting with unexplained progressive otalgia, in an immunocompetent (older) patient. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 10. 266(10):1655–1657. PMID: 19052763.
Article17. Dunn JJ, Wolfe MJ, Trachtenberg J, Kriesel JD, Orlandi RR, Carroll KC. Invasive fungal sinusitis caused by Scytalidium dimidiatum in a lung transplant recipient. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 12. 41(12):5817–5819. PMID: 14662991.18. Amonoo-Kuofi K, Tostevin P, Knight JR. Aspergillus mastoiditis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report. Skull Base. 2005; 5. 15(2):109–112. PMID: 16148971.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New Systemic Antifungal Agents and Clinical Applications
- Systemic New Antifungal Agents
- Voriconazole plus caspofungin for treatment of invasive fungal infection in children with acute leukemia
- In Vitro Antifungal Activities of Amphotericin B, Fluconazole, Itraconazole, Terbinafine, Caspofungin, Voriconazole, and Posaconazole against 30 Clinical Isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans var. neoformancs
- Voriconazole-refractory invasive aspergillosis