Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2014 Oct;2(2):62-68. 10.14791/btrt.2014.2.2.62.
A Suggestion of Modified Classification of Trigeminal Schwannomas According to Location, Shape, and Extension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cjkim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2134273
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2014.2.2.62
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Comprehensive knowledge of the anatomical features of trigeminal schwannomas (TSs) is essential in planning surgery to achieve complete tumor resection. In the current report, we propose a modified classification of TSs according to their location of origin, shape, and extension into the adjacent compartment, and discuss appropriate surgical strategies with this classification.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 49 patients with TS who were treated surgically by a single neurosurgeon at the Asan Medical Center between 1993 and 2013.
RESULTS
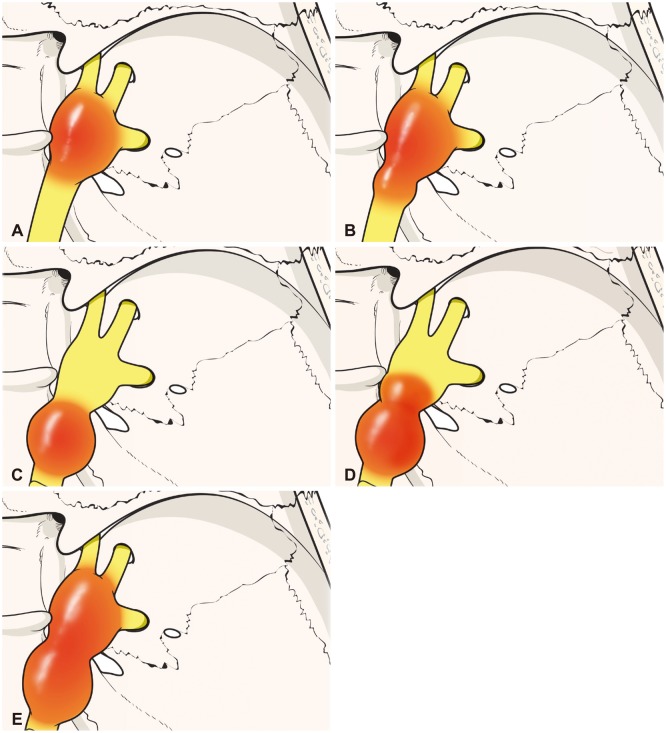
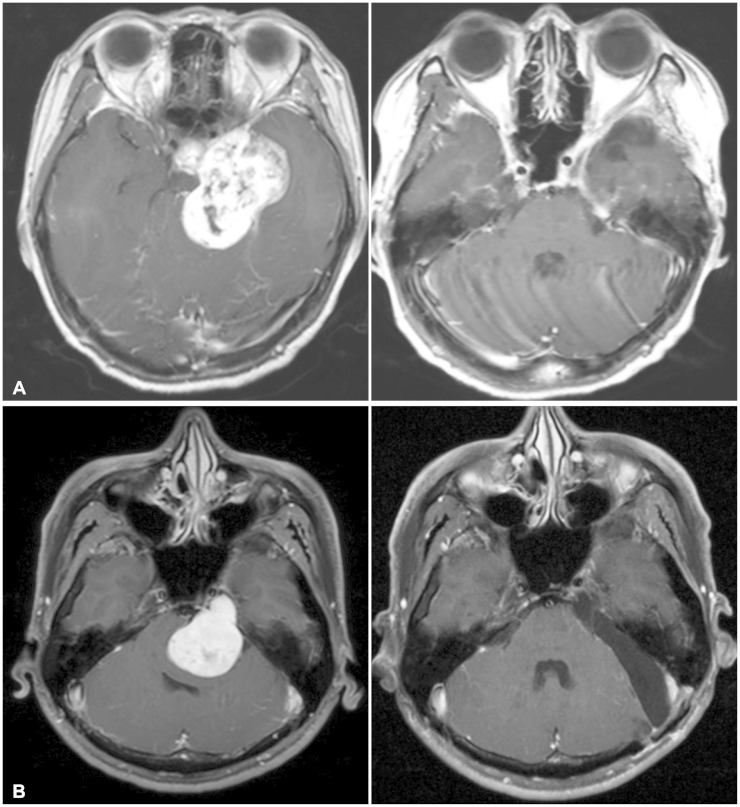
There were 22 males and 27 females, with the median age of 40 years (range, 21-75 years). Median tumor size was 4.0 cm in diameter (2.0-7.0 cm). Tumors were classified as follows: Type M (confined to the middle fossa; 8 cases, 19.0%), P (confined to the posterior fossa; 2 cases, 4.8%), MP (involving equally both middle and posterior fossae; 5 cases, 11.9%), Mp (predominantly middle fossa with posterior fossa extension; 6 cases, 14.3%), Pm (predominantly posterior fossa with middle fossa extension; 16 cases, 38.1%), Me (predominantly middle fossa with extracranial extension; 4 cases, 9.5%). Surgical approach was chosen depending on the tumor classification. More specifically, a frontotemporal craniotomy and extradural approach with or without zygomatic or orbitozygomatic osteotomy was applied to M- or Mp-type tumors; a lateral suboccipital craniotomy with or without suprameatal approach was applied to the majority of P- or Pm-type tumors; and a posterior transpetrosal approach was used in four tumors (three Pm and one MP). Gross total resection was achieved in 95.9% of patients, and the overall recurrence rate was 4.1% (2 patients). Postoperatively, trigeminal symptoms were improved or unchanged in 51.0% of cases (25 patients). Surgical complications included meningitis (5 patients) and cerebrospinal fluid leakage (3 patients). There was no mortality.
CONCLUSION
TSs are well to be classified with our modified classification and able to be removed effectively and safely by selecting appropriate surgical approaches.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Rare Locations of Schwannomas: A Few Comments
Mohamed Amin Ghobadifar
Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2015;3(1):64-64. doi: 10.14791/btrt.2015.3.1.64.
Reference
-
1. Fukaya R, Yoshida K, Ohira T, Kawase T. Trigeminal schwannomas: experience with 57 cases and a review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev. 2010; 34:159–171. PMID: 20963463.
Article2. Goel A, Shah A, Muzumdar D, Nadkarni T, Chagla A. Trigeminal neurinomas with extracranial extension: analysis of 28 surgically treated cases. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113:1079–1084. PMID: 19895193.
Article3. Liu XD, Xu QW, Che XM, Yang DL. Trigeminal neurinomas: clinical features and surgical experience in 84 patients. Neurosurg Rev. 2009; 32:435–444. PMID: 19633876.
Article4. Wanibuchi M, Fukushima T, Zomordi AR, Nonaka Y, Friedman AH. Trigeminal schwannomas: skull base approaches and operative results in 105 patients. Neurosurgery. 2012; 70(1 Suppl Operative):132–143. discussion 143-4. PMID: 21796003.
Article5. Zhang L, Yang Y, Xu S, Wang J, Liu Y, Zhu S. Trigeminal schwannomas: a report of 42 cases and review of the relevant surgical approaches. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009; 111:261–269. PMID: 19081670.
Article6. Pollack IF, Sekhar LN, Jannetta PJ, Janecka IP. Neurilemomas of the trigeminal nerve. J Neurosurg. 1989; 70:737–745. PMID: 2709114.7. Jefferson G. The trigeminal neurinomas with some remarks on malignant invasion of the gasserian ganglion. Clin Neurosurg. 1953; 1:11–54. PMID: 14379464.
Article8. Goel A, Muzumdar D, Raman C. Trigeminal neuroma: analysis of surgical experience with 73 cases. Neurosurgery. 2003; 52:783–790. discussion 790. PMID: 12657173.
Article9. Guthikonda B, Theodosopoulos PV, van Loveren H, Tew JM Jr, Pensak ML. Evolution in the assessment and management of trigeminal schwannoma. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118:195–203. PMID: 18090871.
Article10. Samii M, Migliori MM, Tatagiba M, Babu R. Surgical treatment of trigeminal schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 1995; 82:711–718. PMID: 7714594.
Article11. Lesoin F, Rousseaux M, Villette L, et al. Neurinomas of the trigeminal nerve. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1986; 82:118–122. PMID: 3491493.
Article12. Yoshida K, Kawase T. Trigeminal neurinomas extending into multiple fossae: surgical methods and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91:202–211. PMID: 10433308.
Article13. Al-Mefty O, Ayoubi S, Gaber E. Trigeminal schwannomas: removal of dumbbell-shaped tumors through the expanded Meckel cave and outcomes of cranial nerve function. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:453–463. PMID: 11883829.
Article14. Taha JM, Tew JM Jr, van Loveren HR, Keller JT, el-Kalliny M. Comparison of conventional and skull base surgical approaches for the excision of trigeminal neurinomas. J Neurosurg. 1995; 82:719–725. PMID: 7714595.
Article15. Dolenc VV. Frontotemporal epidural approach to trigeminal neurinomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1994; 130:55–65. PMID: 7725943.
Article16. McCormick PC, Bello JA, Post KD. Trigeminal schwannoma. Surgical series of 14 cases with review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1988; 69:850–860. PMID: 3057125.17. Hasegawa T, Kida Y, Yoshimoto M, Koike J. Trigeminal schwannomas: results of gamma knife surgery in 37 cases. J Neurosurg. 2007; 106:18–23. PMID: 17236483.
Article18. Pamir MN, Peker S, Bayrakli F, Kiliç T, Ozek MM. Surgical treatment of trigeminal schwannomas. Neurosurg Rev. 2007; 30:329–337. discussion 337. PMID: 17676346.
Article19. Yasui T, Hakuba A, Kim SH, Nishimura S. Trigeminal neurinomas: operative approach in eight cases. J Neurosurg. 1989; 71:506–511. PMID: 2795170.
Article20. Schisano G, Olivecrona H. Neurinomas of the Gasserian ganglion and trigeminal root. J Neurosurg. 1960; 17:306–322. PMID: 14442838.
Article21. Konovalov AN, Spallone A, Mukhamedjanov DJ, Tcherekajev VA, Makhmudov UB. Trigeminal neurinomas. A series of 111 surgical cases from a single institution. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996; 138:1027–1035. PMID: 8911538.
Article22. Day JD, Fukushima T. The surgical management of trigeminal neuromas. Neurosurgery. 1998; 42:233–240. discussion 240-1. PMID: 9482173.
Article23. Sarma S, Sekhar LN, Schessel DA. Nonvestibular schwannomas of the brain: a 7-year experience. Neurosurgery. 2002; 50:437–448. discussion 438-9. PMID: 11841710.
Article24. Bordi L, Compton J, Symon L. Trigeminal neuroma. A report of eleven cases. Surg Neurol. 1989; 31:272–276. PMID: 2928920.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Morphometric study on the trigeminal ganglion and the intracranial ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular nerves in Korean adults
- Trigeminal Neuralgia with Persistent Trigeminal Artery Variant and Schwannomatosis of the Abducens and Lower Cranial Nerves: A Case Report
- Neurinomas of the Trigeminal Nerve: Report of 4 Cases
- Extracranial Trigeminal Schwannoma Involving the Inferior Alveolar Canal
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery