J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Sep;56(3):278-280. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.3.278.
Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. painsurgery@gmail.com
- KMID: 2339972
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.3.278
Abstract
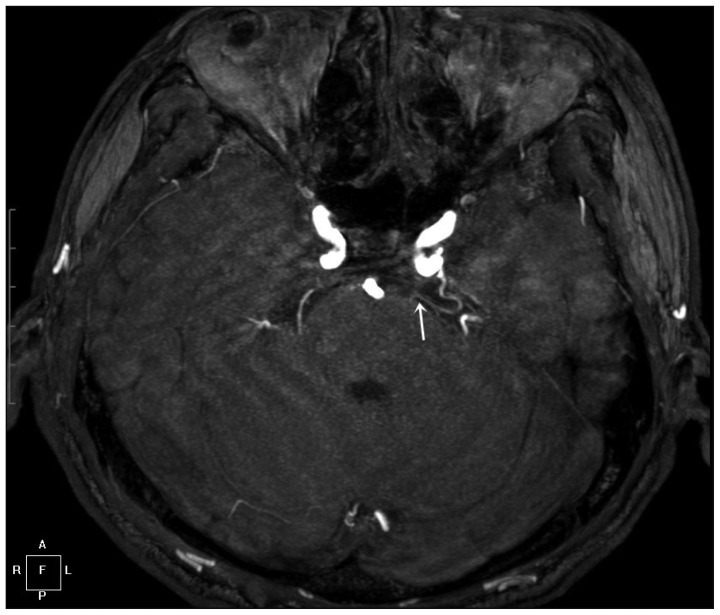
- A 66-year-old man presented with typical trigeminal neuralgia (TN). Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) revealed a primitive trigeminal artery (PTA) that came into contact with the trigeminal nerve. Based on MRA, we performed microvascular decompression (MVD). In the operational field, we confirmed the PTA location and performed MVD successfully. Postoperatively, the patient's pain subsided without any complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Azab W, Delashaw J, Mohammed M. Persistent primitive trigeminal artery : a review. Turk Neurosurg. 2012; 22:399–406. PMID: 22843453.2. Fukuda M, Kameyama S, Takahashi H, Tanaka R. Trigeminal neuralgia caused by the vertebral artery associated with primitive trigeminal artery and agenesis of the internal carotid artery. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1998; 38:367–370. PMID: 9689822.
Article3. Garg RK, Malhotra HS, Verma R. Trigeminal neuralgia. J Indian Med Assoc. 2011; 109:631–636. PMID: 22480095.4. Lee SH, Koh JS, Lee CY. Trigeminal neuralgia caused by an anomalous posterior inferior cerebellar artery from the primitive trigeminal artery : case report. Cerebellum. 2011; 10:199–203. PMID: 21279490.
Article5. Liu JK, Apfelbaum RI. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2004; 15:319–334. PMID: 15246340.
Article6. O'uchi E, O'uchi T. Persistent primitive trigeminal arteries (PTA) and its variant (PTAV) : analysis of 103 cases detected in 16,415 cases of MRA over 3 years. Neuroradiology. 2010; 52:1111–1119. PMID: 20309534.7. Schmid AH. Presistent trigeminal artery. An autopsy report. Neuroradiology. 1974; 7:173–175. PMID: 4842039.8. Tamura Y, Shimano H, Kuroiwa T, Miki Y. Trigeminal neuralgia associated with a primitive trigeminal artery variant : case report. Neurosurgery. 2003; 52:1217–1219. discussion 1219-1220. PMID: 12699569.
Article9. Tokimura H, Atsuchi M, Kawasaki T, Sato E, Todoroki K, Asakura T, et al. [Trigeminal neuralgia associated with primitive trigeminal artery : report of two cases]. No Shinkei Geka. 1990; 18:209–213. PMID: 2336149.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery Aneurysm: A Case Report
- 2 Cases of Persistent Primitive Trigeminal Artery
- Trigeminal Neuralgia with Persistent Trigeminal Artery Variant and Schwannomatosis of the Abducens and Lower Cranial Nerves: A Case Report
- Contralateral Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Acoustic Neurinoma
- Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Epidermoid Tumor in the Cerebellopontine Angle