Blood Res.
2015 Dec;50(4):227-234. 10.5045/br.2015.50.4.227.
Immunophenotypic markers in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the prognostic significance of CD20 and TdT expression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dani@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cjpark@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2133757
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2015.50.4.227
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Efforts to overcome poor outcomes in patients with adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have focused on combining new therapeutic agents targeting immunophenotypic markers (IPMs) with classical cytotoxic agents; therefore, it is important to evaluate the clinical significance of IPMs.
METHODS
Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients with adult ALL were retrospectively analyzed. The percentage of blasts expressing IPMs at diagnosis was measured by multicolor flow cytometry analysis. Samples in which > or =20% of blasts expressed an IPM were considered positive.
RESULTS
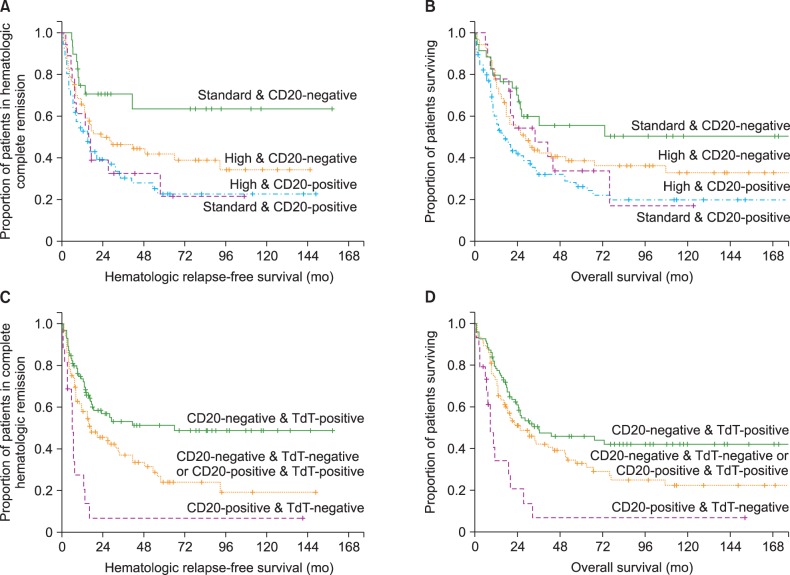
Among the total patient population (N=230), almost all (92%) were in first or second hematological complete remission (HCR) and 54% received allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (allo-HCT). Five-year hematologic relapse-free survival (HRFS) and overall survival (OS) rates were 36% and 39%, respectively, and 45.6% and 80.5% of patients were positive for the IPMs CD20 and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), respectively. Expression of CD20, CD13, CD34, and TdT was associated with HRFS rate, and expression of CD20 and CD13 was associated with OS rate, as was the performance of allo-HCT. In multivariate analysis, positivity for CD20 (HRFS: hazard ratio [HR], 2.21, P<0.001; OS: HR, 1.63, P=0.015) and negativity for TdT (HRFS: HR, 2.30, P=0.001) were both significantly associated with outcomes. When patients were categorized into three subgroups according to positivity for CD20 and TdT, there were significant differences in HRFS and OS among the subgroups.
CONCLUSION
Positivity for CD20 and TdT expression and clinical risk group were prognostic factors in adult ALL.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gökbuget N, Stanze D, Beck J, et al. Outcome of relapsed adult lymphoblastic leukemia depends on response to salvage chemotherapy, prognostic factors, and performance of stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012; 120:2032–2041. PMID: 22493293.
Article2. Hallböök H, Gustafsson G, Smedmyr B, et al. Treatment outcome in young adults and children >10 years of age with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Sweden: a comparison between a pediatric protocol and an adult protocol. Cancer. 2006; 107:1551–1561. PMID: 16955505.3. Fielding AK, Rowe JM, Buck G, et al. UKALLXII/ECOG2993: addition of imatinib to a standard treatment regimen enhances long-term outcomes in Philadelphia positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2014; 123:843–850. PMID: 24277073.
Article4. Kim DY, Joo YD, Lim SN, et al. Nilotinib combined with multiagent chemotherapy for newly diagnosed Philadelphiapositive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2015; 126:746–756. PMID: 26065651.
Article5. Ravandi F, O'Brien S, Thomas D, et al. First report of phase 2 study of dasatinib with hyper-CVAD for the frontline treatment of patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2010; 116:2070–2077. PMID: 20466853.
Article6. Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993). Blood. 2008; 111:1827–1833. PMID: 18048644.7. Cho BS, Lee S, Kim YJ, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation is a potential therapeutic approach for adults with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia in remission: results of a prospective phase 2 study. Leukemia. 2009; 23:1763–1770. PMID: 19440217.
Article8. Eom KS, Shin SH, Yoon JH, et al. Comparable long-term outcomes after reduced-intensity conditioning versus myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for adult high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia in complete remission. Am J Hematol. 2013; 88:634–641. PMID: 23620000.
Article9. Mohty M, Labopin M, Volin L, et al. Reduced-intensity versus conventional myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Blood. 2010; 116:4439–4443. PMID: 20716774.
Article10. Zugmaier G, Gökbuget N, Klinger M, et al. Long-term survival and T-Cell kinetics in adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia who achieved minimal residual disease response following treatment with Anti-CD19 BiTE® antibody construct blinatumomab. Blood. 2015; [Epub ahead of print].11. Topp MS, Gökbuget N, Stein AS, et al. Safety and activity of blinatumomab for adult patients with relapsed or refractory B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:57–66. PMID: 25524800.
Article12. Thomas DA, O'Brien S, Faderl S. Chemoimmunotherapy with a modified hyper-CVAD and rituximab regimen improves outcome in de novo Philadelphia chromosome-negative precursor B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3880–3889. PMID: 20660823.
Article13. Jabbour E, O'Brien S, Huang X. Prognostic factors for outcome in patients with refractory and relapsed acute lymphocytic leukemia treated with inotuzumab ozogamicin, a CD22 monoclonal antibody. Am J Hematol. 2015; 90:193–196. PMID: 25407953.
Article14. Thomas DA, O'Brien S, Jorgensen JL, et al. Prognostic significance of CD20 expression in adults with de novo precursor B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009; 113:6330–6337. PMID: 18703706.
Article15. Linker CA, Levitt LJ, O'Donnell M, Forman SJ, Ries CA. Treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia with intensive cyclical chemotherapy: a follow-up report. Blood. 1991; 78:2814–2822. PMID: 1835410.
Article16. Lee SM, Lee WS, Shin HJ, et al. Escalated daunorubicin dosing as an induction treatment for Philadelphia-negative adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2013; 92:1101–1110. PMID: 23558905.
Article17. Lim SN, Joo YD, Lee KH, et al. Long-term follow-up of imatinib plus combination chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2015; 90:1013–1020. PMID: 26228525.
Article18. Bachanova V, Sandhu K, Yohe S, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation overcomes the adverse prognostic impact of CD20 expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2011; 117:5261–5263. PMID: 21403127.
Article19. Thomas DA. Rituximab as therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2010; 8:168–171. PMID: 20400931.20. Maury S, Huguet F, Leguay T, et al. Adverse prognostic significance of CD20 expression in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-negative B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2010; 95:324–328. PMID: 19773266.
Article21. Seegmiller AC, Kroft SH, Karandikar NJ, McKenna RW. Characterization of immunophenotypic aberrancies in 200 cases of B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009; 132:940–949. PMID: 19926587.
Article22. Jeha S, Behm F, Pei D, et al. Prognostic significance of CD20 expression in childhood B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2006; 108:3302–3304. PMID: 16896151.
Article23. Pituch-Noworolska A, Hajto B, Mazur B, et al. Expression of CD20 on acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells in children. Neoplasma. 2001; 48:182–187. PMID: 11583286.24. Hetherington ML, Huntsman PR, Smith RG, Buchanan GR. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-containing peripheral blood mononuclear cells during remission of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: low sensitivity and specificity prevent accurate prediction of relapse. Leuk Res. 1987; 11:537–543. PMID: 3474480.
Article25. van Wering ER, Veerman AJ, van der Linden-Schrever BE. Diagnosis of meningeal involvement in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: cytomorphology and TdT. Eur J Haematol. 1988; 40:250–255. PMID: 3281860.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Classification and Prognostic Significance of Immunophenotypic Subgroups in Non-T-ALL(I)
- A Case of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Maturation
- Acute leukemias with unusual immunophenotypes
- A Case of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Trisomy 5 as a Sole Chromosomal Anomaly: A Prognostic Significance
- Advances in the Treatment of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia