Korean J Urol.
2015 Feb;56(2):157-163. 10.4111/kju.2015.56.2.157.
Delayed redo pyeloplasty fails to recover lost renal function after failed pyeloplasty: Early sonographic changes that correlate with a loss of differential renal function
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swhan@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2133281
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2015.56.2.157
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate changes in differential renal function (DRF), as a functional outcome, in children who underwent redo pyeloplasty for management of failed pyeloplasty and to examine the factors that affect functional outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2002 and November 2010, a total of 18 patients who underwent redo pyeloplasty for persistent ureteropelvic junction obstruction after failed pyeloplasty were enrolled in this study. We assessed perioperative factors and evaluated changes in renal cortical thickness (RCT), renal function, and hydronephrosis by use of serial ultrasound and diuretic renography.
RESULTS
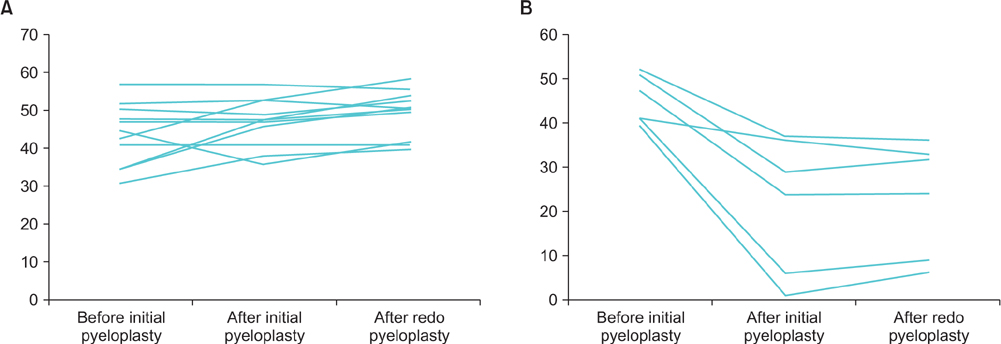
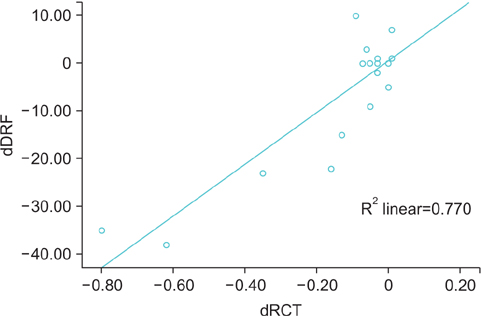
The mean follow-up period was 44.83+/-28.86 months. After redo pyeloplasty, prevention of further functional deterioration was observed in only 12 of the 18 patients. After dividing the patients according to this observation, we discovered significant differences in both change in DRF (dDRF) and change in RCT (dRCT) (difference between before and after initial pyeloplasty) between the two groups (p<0.001). Additionally, we noted a significant positive correlation between dRCT and dDRF. All patients showed improvements in hydronephrosis grade and relief of symptoms compared with before redo pyeloplasty.
CONCLUSIONS
Redo pyeloplasty should be considered in cases of failed pyeloplasty to preserve renal function and obtain relief from symptoms. If patients show severe deterioration of DRF or a decrease in RCT after initial pyeloplasty, preservation of DRF in these patients after redo pyeloplasty could be difficult. Therefore, redo pyeloplasty should be performed before severe deterioration of DRF or decrease in RCT.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Child
Child, Preschool
Disease Progression
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Hydronephrosis/etiology/ultrasonography
Infant
Kidney/*physiopathology/ultrasonography
Kidney Cortex/pathology
Kidney Function Tests/methods
Kidney Pelvis/*surgery/ultrasonography
Male
Postoperative Period
Prognosis
Reoperation/adverse effects/methods
Retrospective Studies
Treatment Failure
Treatment Outcome
Ureteral Obstruction/complications/pathology/*surgery
Ureteral Obstruction/*surgery
Figure
Reference
-
1. Salem YH, Majd M, Rushton HG, Belman AB. Outcome analysis of pediatric pyeloplasty as a function of patient age, presentation and differential renal function. J Urol. 1995; 154:1889–1893.2. Lim DJ, Walker RD 3rd. Management of the failed pyeloplasty. J Urol. 1996; 156(2 Pt 2):738–740.3. Thomas JC, DeMarco RT, Donohoe JM, Adams MC, Pope JC 4th, Brock JW 3rd. Management of the failed pyeloplasty: a contemporary review. J Urol. 2005; 174:2363–2366.4. Anderson JC, Hynes W. Retrocaval ureter; a case diagnosed pre-operatively and treated successfully by a plastic operation. Br J Urol. 1949; 21:209–214.5. Ng CS, Yost AJ, Streem SB. Management of failed primary intervention for ureteropelvic junction obstruction: 12-year, single-center experience. Urology. 2003; 61:291–296.6. Fernbach SK, Maizels M, Conway JJ. Ultrasound grading of hydronephrosis: introduction to the system used by the Society for Fetal Urology. Pediatr Radiol. 1993; 23:478–480.7. Moghazi S, Jones E, Schroepple J, Arya K, McClellan W, Hennigar RA, et al. Correlation of renal histopathology with sonographic findings. Kidney Int. 2005; 67:1515–1520.8. Braga LH, Lorenzo AJ, Skeldon S, Dave S, Bagli DJ, Khoury AE, et al. Failed pyeloplasty in children: comparative analysis of retrograde endopyelotomy versus redo pyeloplasty. J Urol. 2007; 178:2571–2575.9. Helmy TE, Sarhan OM, Hafez AT, Elsherbiny MT, Dawaba ME, Ghali AM. Surgical management of failed pyeloplasty in children: single-center experience. J Pediatr Urol. 2009; 5:87–89.10. Seixas-Mikelus SA, Jenkins LC, Williot P, Greenfield SP. Pediatric pyeloplasty: comparison of literature meta-analysis of laparoscopic and open techniques with open surgery at a single institution. J Urol. 2009; 182:2428–2432.11. Romao RL, Koyle MA, Pippi Salle JL, Alotay A, Figueroa VH, Lorenzo AJ, et al. Failed pyeloplasty in children: revisiting the unknown. Urology. 2013; 82:1145–1147.12. Heinlen JE, Manatt CS, Bright BC, Kropp BP, Campbell JB, Frimberger D. Operative versus nonoperative management of ureteropelvic junction obstruction in children. Urology. 2009; 73:521–525.13. Szavay PO, Luithle T, Seitz G, Warmann SW, Haber P, Fuchs J. Functional outcome after laparoscopic dismembered pyeloplasty in children. J Pediatr Urol. 2010; 6:359–363.14. Materny J, Mazurkiewicz I, Gawrych E, Birkenfeld B, Zorga P. Does Hynes-Anderson pyeloplasty improve renal function? Ann Acad Med Stetin. 2010; 56:95–102.15. Harraz AM, Helmy T, Taha DE, Shalaby I, Sarhan O, Dawaba M, et al. Changes in differential renal function after pyeloplasty in children. J Urol. 2013; 190:4 Suppl. 1468–1473.16. Beland MD, Walle NL, Machan JT, Cronan JJ. Renal cortical thickness measured at ultrasound: is it better than renal length as an indicator of renal function in chronic kidney disease? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:W146–W149.17. Kaplon DM, Lasser MS, Sigman M, Haleblian GE, Pareek G. Renal parenchyma thickness: a rapid estimation of renal function on computed tomography. Int Braz J Urol. 2009; 35:3–8.18. Park K, Baek M, Cho SY, Choi H. Time course of hydronephrotic changes following unilateral pyeloplasty. J Pediatr Urol. 2013; 9(6 Pt A):779–783.19. Bhat GS, Maregowda S, Jayaram S, Siddappa S. Is renal biopsy a better predictor of the outcome of pyeloplasty in adult ureteropelvic junction obstruction? Urology. 2012; 79:321–325.20. Rosen S, Peters CA, Chevalier RL, Huang WY. The kidney in congenital ureteropelvic junction obstruction: a spectrum from normal to nephrectomy. J Urol. 2008; 179:1257–1263.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Outcome of Tubeless Dismembered Pyeloplasty in Adult Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction and Significance of Double-J Ureteral Stenting
- The effect of dismembered pyeloplasty on renal function in patients with ureteropelvic junction obstruction
- Obstruction of the Ureteropelvic Junction in Children: Functional Evaluation of the Obstructed Kidney Postoperatively Using the 99mTc-DMSA Renal Scan
- Change of Hydronephrosis after Pyeloplasty in Children with Unilateral Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction
- Optimal Timing of Surgery of Hydronephrosis Due to Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction in Neonates and Infants