Anat Cell Biol.
2015 Dec;48(4):268-274. 10.5115/acb.2015.48.4.268.
Anatomical study of the nerve regeneration after selective neurectomy in the rabbit: clinical application for esthetic calf reduction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Research Institute of Medical Science, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. anatomy@kku.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Masan University, Masan, Korea.
- KMID: 2133267
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2015.48.4.268
Abstract
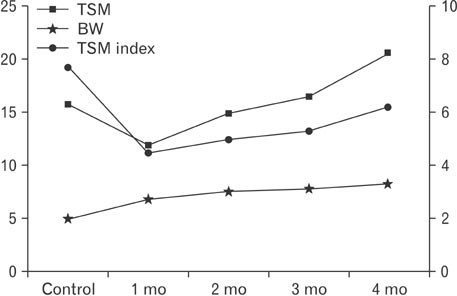
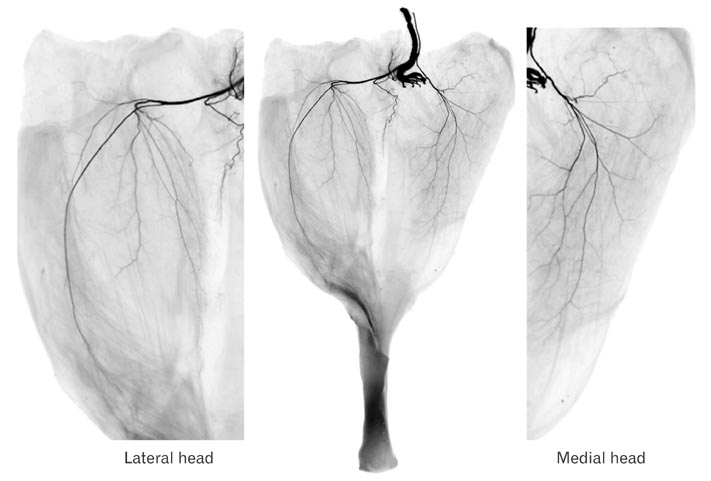
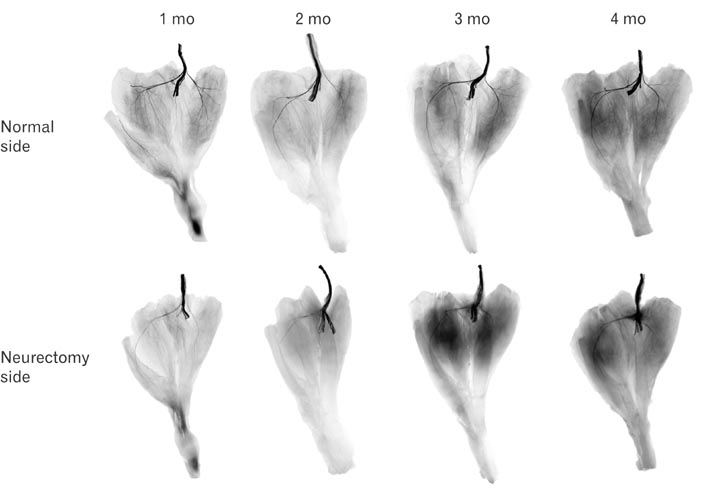
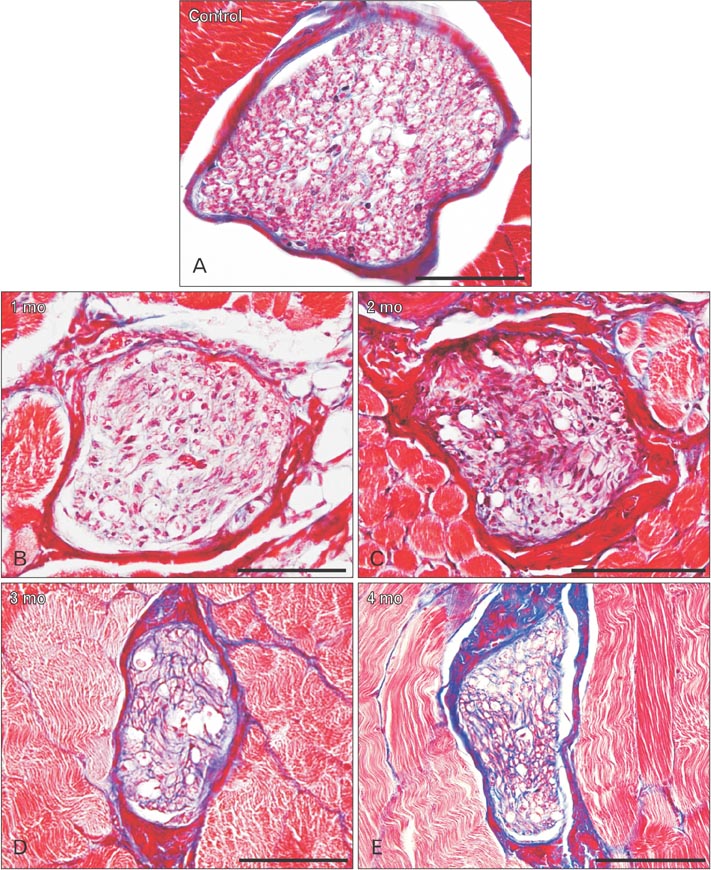
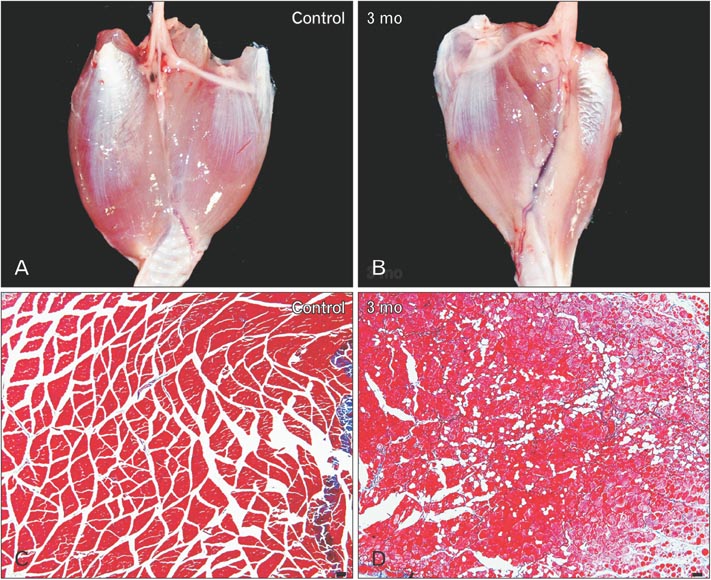
- The purposes of this study were therefore to characterize the degeneration and regeneration of nerves to the calf muscles after selective neurectomy, both macroscopically and microscopically, and to determine the incidence of such regeneration in a rabbit model. Seventy four New Zealand white rabbits were used. Selective neurectomy to the triceps surae muscles was performed, and the muscles were subsequently harvested and weighed 1-4 months postneurectomy. The gastrocnemius muscles were stained with Sihler's solution to enable the macroscopic observation of any nerve regeneration that may have occurred subsequent to neurectomy. The change in triceps surae muscle weight was measured along the time course of the experiment. After neurectomy, nerve degeneration was followed by regeneration in all cases. The weight of the triceps surae muscle decreased dramatically between completion of the neurectomy and 1 month postneurectomy, but increased thereafter. The nerve branches were weakly stained with Sihler's solution until 2 months postneurectomy, and then strongly stained after 3 months. The number of myelinated axons was decreased at 2 month after neurectomy compared to nonneurectomized controls, but then gradually increased thereafter. Although there are currently no reports on the incidence of recovery after calf reduction, it may be a very common occurrence in the clinical field based on our findings. The findings of this study provide fundamental anatomical and surgical information to aid planning and practice in calf-reduction surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 40th ed. London: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier;2008.2. Kim IG, Hwang SH, Lew JM, Lee HY. Endoscope-assisted calf reduction in Orientals. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 106:713–718.3. Lee JT, Wang CH, Cheng LF, Lin CM, Huang CC, Chien SH. Subtotal resection of gastrocnemius muscles for hypertrophic muscular calves in Asians. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006; 118:1472–1483.4. Park YJ, Jo YW, Bang SI, Kim HJ, Lim SY, Mun GH, Hyon WS, Oh KS. Radiofrequency volume reduction of gastrocnemius muscle hypertrophy for cosmetic purposes. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2007; 31:53–61.5. Kim NH, Chung JH, Park RH, Park JB. The use of botulinum toxin type A in aesthetic mandibular contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005; 115:919–930.6. Lee HJ, Lee DW, Park YH, Cha MK, Kim HS, Ha SJ. Botulinum toxin a for aesthetic contouring of enlarged medial gastrocnemius muscle. Dermatol Surg. 2004; 30:867–871.7. Fong TH, Wong CH, Lin JY, Liao CK, Ho LY, Tsai FC. Correction of asymmetric calf hypertrophy with differential selective neurectomy. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2010; 34:335–339.8. Kim SC, Kang MH, Ock JJ. Calf-contouring surgery of gastrocnemius hypertrophy: selective neurectomy of the sural nerve. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2008; 32:889–893.9. Tsai FC, Mardini S, Fong TH, Kang JH, Chou CM. Selective neurectomy of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles for calf hypertrophy: an anatomical study and 700 clinical cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 122:178–187.10. Tsai FC, Hsieh MS, Chou CM. Comparison between neurectomy and botulinum toxin A injection for denervated skeletal muscle. J Neurotrauma. 2010; 27:1509–1516.11. Ahad MA, Fogerson PM, Rosen GD, Narayanaswami P, Rutkove SB. Electrical characteristics of rat skeletal muscle in immaturity, adulthood and after sciatic nerve injury, and their relation to muscle fiber size. Physiol Meas. 2009; 30:1415–1427.12. de Castro Rodrigues A, Andreo JC, Rosa GM Jr, dos Santos NB, Moraes LH, Lauris JR. Fat cell invasion in long-term denervated skeletal muscle. Microsurgery. 2007; 27:664–667.13. Gutmann E, Sanders FK. Recovery of fibre numbers and diameters in the regeneration of peripheral nerves. J Physiol. 1943; 101:489–518.14. Irintchev A, Draguhn A, Wernig A. Reinnervation and recovery of mouse soleus muscle after long-term denervation. Neuroscience. 1990; 39:231–243.15. Sung DH, Han TR, Park WH, Je Bang H, Kim JM, Chung SH, Woo EJ. Phenol block of peripheral nerve conduction: titrating for optimum effect. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 82:671–676.16. Hwang K, Kim YJ, Chung IH, Won HS, Tanaka S, Lee SI. Innervation of calf muscles in relation to calf reduction. Ann Plast Surg. 2003; 50:517–522.17. Sheverdin VA, Hur MS, Won SY, Song WC, Hu KS, Koh KS, Kim HJ. Extra- and intramuscular nerves distributions of the triceps surae muscle as a basis for muscle resection and botulinum toxin injections. Surg Radiol Anat. 2009; 31:615–621.18. Liu AT, Yu DZ, Chen G, Dang RS, Zhang YF, Zhang WJ, Liu BL, Jiang H. Profiling of innervations of mimetic muscles in fresh human cadavers using a modified Sihler's technique. Muscle Nerve. 2010; 42:88–94.19. Mu L, Sanders I. Sihler's whole mount nerve staining technique: a review. Biotech Histochem. 2010; 85:19–42.20. Won SY, Rha DW, Kim HS, Jung SH, Park ES, Hu KS, Kim HJ. Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of the adductor longus and gracilis muscles demonstrated with Sihler staining: guidance for botulinum toxin injection. Muscle Nerve. 2012; 46:80–85.21. Yu DZ, Liu AT, Zhang JL, Dang RS, Chen G, Liu BL, Han T, Yi J, Nagasao T, Jiang H. Two methods can simultaneously display both intramuscular nerves and blood vessels. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012; 129:401–411.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Restoration of calf deformities in a 35-year-old man following 2 calf reduction surgical procedures
- Histopathologic Findings of Rabbit Cilia after Application of Radio Frequency Wave
- Selective Neurectomy of Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle for the Calf Reduction
- Comparison of Regeneration Effects of Direct and Alternating Microcurrent Therapy on Atrophied Calf Muscle in a Rabbit
- Neurectomy of Nerve Branch to Medial Gastrocnemius Muscle for Calf Reduction