Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2012 Jan;4(1):55-57. 10.4168/aair.2012.4.1.55.
Fulminant and Fatal Multiple Organ Failure in a 12-Year-Old Boy With Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea. jsjs87@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Severance Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2130381
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.1.55
Abstract
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Mp) is a unique pathogen that causes not only pulmonary but also extrapulmonary manifestations that must be rapidly diagnosed. A 12-year-old boy, with no relevant medical history, presented with fever, severe epigastric pain, and vomiting. Laboratory findings showed fulminant and cholestatic hepatitis, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, acute kidney injury, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, acute myocardial infarction, and rhabdomyolysis. His clinical condition rapidly deteriorated during intubation and continuous renal replacement therapy. Despite intensive treatment, he did not recover. We report a case of fulminant and fatal multiple organ failure in a previously healthy boy with Mp infection, describing the possible pathomechanisms of multiple organ failure involved in the disease.
MeSH Terms
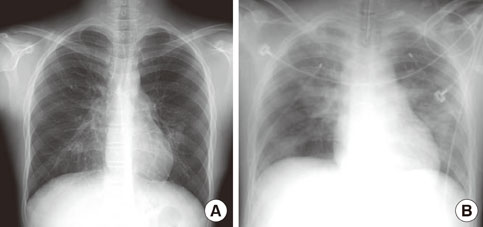
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Child of Severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia with Multiple Organ Failure Treated with ECMO and CRRT
Woojin Hwang, Yoonjin Lee, Eunjee Lee, Jiwon M. Lee, Hong Ryang Kil, Jae Hyeon Yu, Eun Hee Chung
Pediatr Infect Vaccine. 2019;26(1):71-79. doi: 10.14776/piv.2019.26.e9.
Reference
-
1. Chong YP, Jung KS, Lee KH, Kim MN, Moon SM, Park S, Hur J, Kim DM, Jeon MH, Woo JH. The bacterial etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in Korea: A nationwide prospective multicenter study. Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:397–403.2. Eun BW, Kim NH, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Korean children: the epidemiology of pneumonia over an 18-year period. J Infect. 2008. 56:326–331.3. Kottayam R, Rozenberg G, Cohn RJ. Unusual haematologic manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Paediatr Child Health. 2007. 43:80–82.4. Timitilli A, Di Rocco M, Nattero G, Tacchella A, Giacchino R. Unusual manifestations of infections due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children. Infez Med. 2004. 12:113–117.5. Atkinson TP, Balish MF, Waites KB. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, pathogenesis and laboratory detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008. 32:956–973.6. Waites KB, Talkington DF. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004. 17:697–728.7. Narita M. Pathogenesis of extrapulmonary manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection with special reference to pneumonia. J Infect Chemother. 2010. 16:162–169.8. Gehrs BC, Friedberg RC. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Am J Hematol. 2002. 69:258–271.9. Smith LG. Mycoplasma pneumonia and its complications. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2010. 24:57–60.10. Berg CP, Kannan TR, Klein R, Gregor M, Baseman JB, Wesselborg S, Lauber K, Stein GM. Mycoplasma antigens as a possible trigger for the induction of antimitochondrial antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2009. 29:797–809.11. Carrascosa MF, Lucena MI, Andrade RJ, Caviedes JR, Lavín AC, Mones JC, Rivero AP, Serrano VB. Fatal acute hepatitis after sequential treatment with levofloxacin, doxycycline, and naproxen in a patient presenting with acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Ther. 2009. 31:1014–1019.12. Tagliabue C, Salvatore CM, Techasaensiri C, Mejias A, Torres JP, Katz K, Gomez AM, Esposito S, Principi N, Hardy RD. The impact of steroids given with macrolide therapy on experimental Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory infection. J Infect Dis. 2008. 198:1180–1188.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia with a Fulminant Course in a Previously Healthy Boy
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection Presented with Multiple Neurological Complications
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- A Case of a 14-Year-Old Girl Who Developed Dermatomyositis Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- A Case of Fatal Myocarditis Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia