Cancer Res Treat.
2009 Sep;41(3):132-137.
The Role of Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Supratentorial Low-grade Oligodendrogliomas: Comparative Analysis with Immediate Radiotherapy versus Surgery Alone
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ihkim@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
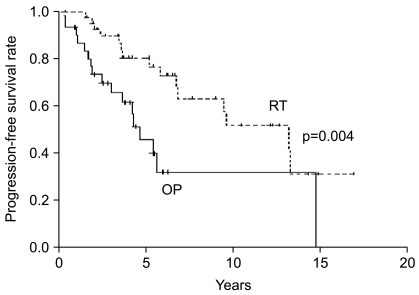
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the role of immediate postoperative radiotherapy (RT) in adult patients with a low-grade oligodendroglioma (LODG). MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 74 patients, older than 15 years, were treated in our institution between April 1990 and March 2006 for newly diagnosed LODGs. After surgery, 43 patients were treated with immediate RT with a total dose of 54~55.8 Gy with 1.8 Gy fractions (RT group) and 31 patients were followed with no adjuvant RT (OP group). All patients were closely observed until tumor progression or death with frequent work-ups including neurological examinations and MRI. Primary endpoints were overall survival and progression-free survival. The median follow-up duration of survivors was 6.2 years in the RT group and 5.8 years in the OP group. RESULTS: Median progression-free survival was 13.2 years in the RT group and 4.6 years in the OP group; multivariate analysis confirmed improved outcome with the use of immediate RT (hazard ratio, 0.22; 95% confidence interval-CI, 0.09~0.55; p<0.001). Median overall survival was 14.9 years in the RT group and 9.8 years in the OP group; the use of adjuvant RT was also associated with a trend toward better overall survival after immediate RT based on multivariate analysis (hazard ratio, 0.3; 95% CI, 0.08~1.17; p=0.082). No severe RT related complications were observed. CONCLUSION: Immediate RT following surgery appears to be an effective treatment modality for supratentorial LODGs. However, the potential benefit of adjuvant RT for overall survival needs to be tested prospectively in the future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mork SJ, Lindegaard KF, Halvorsen TB, Lehmann EH, Solgaard T, Hatlevoll R, et al. Oligodendroglioma: incidence and biological behavior in a defined population. J Neurosurg. 1985; 63:881–889. PMID: 4056902.2. Daumas-Duport C, Varlet P, Tucker ML, Beuvon F, Cervera P, Chodkiewicz JP. Oligodendrogliomas. Part I: Patterns of growth, histological diagnosis, clinical and imaging correlations: a study of 153 cases. J Neurooncol. 1997; 34:37–59. PMID: 9210052.3. Coons SW, Johnson PC, Scheithauer BW, Yates AJ, Pearl DK. Improving diagnostic accuracy and interobserver concordance in the classification and grading of primary gliomas. Cancer. 1997; 79:1381–1393. PMID: 9083161.
Article4. Gannett DE, Wisbeck WM, Silbergeld DL, Berger MS. The role of postoperative irradiation in the treatment of oligodendroglioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994; 30:567–573. PMID: 7928487.
Article5. CBTRUS. Primary brain tumors in the united states. Statistical Report 1997-2001. 2004. Hinsdale: CBTRUS.6. Karim AB, Maat B, Hatlevoll R, Menten J, Rutten EH, Thomas DG, et al. A randomized trial on dose-response in radiation therapy of low-grade cerebral glioma: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Study 22844. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996; 36:549–556. PMID: 8948338.
Article7. van den Bent MJ, Afra D, de Witte O, Ben Hassel M, Schraub S, Hoang-Xuan K, et al. Long-term efficacy of early versus delayed radiotherapy for low-grade astrocytoma and oligodendroglioma in adults: the EORTC 22845 randomised trial. Lancet. 2005; 366:985–990. PMID: 16168780.
Article8. Shaw E, Arusell R, Scheithauer B, O'Fallon J, O'Neill B, Dinapoli R, et al. Prospective randomized trial of low- versus high-dose radiation therapy in adults with supratentorial low-grade glioma: initial report of a North Central Cancer Treatment Group/Radiation Therapy Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:2267–2276. PMID: 11980997.
Article9. Berrino F. The EUROCARE Study: strengths, limitations and perspectives of population-based, comparative survival studies. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14(Suppl 5):S9–S13.
Article10. Combs SE, Schulz-Ertner D, Thilmann C, Edler L, Debus J. Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in the management of primary oligodendroglioma and oligoastrocytoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 62:797–802. PMID: 15936562.
Article11. Nijjar TS, Simpson WJ, Gadalla T, McCartney M. Oligodendroglioma. The Princess Margaret Hospital experience (1958-1984). Cancer. 1993; 71:4002–4006. PMID: 8508366.
Article12. Olson JD, Riedel E, DeAngelis LM. Long-term outcome of low-grade oligodendroglioma and mixed glioma. Neurology. 2000; 54:1442–1448. PMID: 10751254.
Article13. Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer BW, Kelly PJ. A histologic and cytologic method for the spatial definition of gliomas. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987; 62:435–449. PMID: 2437411.
Article14. Bauman G, Pahapill P, Macdonald D, Fisher B, Leighton C, Cairncross G. Low grade glioma: a measuring radiographic response to radiotherapy. Can J Neurol Sci. 1999; 26:18–22. PMID: 10068802.15. Wallner KE, Gonzales M, Sheline GE. Treatment of oligodendrogliomas with or without postoperative irradiation. J Neurosurg. 1988; 68:684–688. PMID: 3357029.
Article16. Lindegaard KF, Mork SJ, Eide GE, Halvorsen TB, Hatlevoll R, Solgaard T, et al. Statistical analysis of clinicopathological features, radiotherapy, and survival in 170 cases of oligodendroglioma. J Neurosurg. 1987; 67:224–230. PMID: 3598683.
Article17. Shimizu KT, Tran LM, Mark RJ, Selch MT. Management of oligodendrogliomas. Radiology. 1993; 186:569–572. PMID: 8421767.
Article18. Schiffer D, Dutto A, Cavalla P, Bosone I, Chiò A, Villani R, et al. Prognostic factors in oligodendroglioma. Can J Neurol Sci. 1997; 24:313–319. PMID: 9398978.
Article19. Allam A, Radwi A, El Weshi A, Hassounah M. Oligodendroglioma: an analysis of prognostic factors and treatment results. Am J Clin Oncol. 2000; 23:170–175. PMID: 10776979.
Article20. Celli P, Nofrone I, Palma L, Cantore G, Fortuna A. Cerebral oligodendroglioma: prognostic factors and life history. Neurosurgery. 1994; 35:1018–1034. PMID: 7885546.21. Yeh SA, Lee TC, Chen HJ, Lui CC, Sun LM, Wang CJ, et al. Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of patients with supratentorial low-grade oligodendroglioma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002; 54:1405–1409. PMID: 12459363.
Article22. Kiebert GM, Curran D, Aaronson NK, Bolla M, Menten J, Rutten EH, et al. EORTC Radiotherapy Co-operative Group. Quality of life after radiation therapy of cerebral low-grade gliomas of the adult: results of a randomised phase III trial on dose response (EORTC trial 22844). Eur J Cancer. 1998; 34:1902–1909. PMID: 10023313.
Article23. Klein M, Heimans JJ, Aaronson NK, van der Ploeg HM, Grit J, Muller M, et al. Effect of radiotherapy and other treatment-related factors on mid-term to long-term cognitive sequelae in low-grade gliomas: a comparative study. Lancet. 2002; 360:1361–1368. PMID: 12423981.
Article24. Feigenberg SJ, Amdur RJ, Morris CG, Mendenhall WM, Marcus RB Jr, Friedman WA. Oligodendroglioma: does deferring treatment compromise outcome? Am J Clin Oncol. 2003; 26:e60–e66. PMID: 12796617.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Postoperative Radiotherapy for Low Grade Glioma of the Brain
- The Role of Radiotherapy in the Management of Supratentorial Low Grade Astrocytoma
- Primary Spinal Cord Oligodendroglioma with Postoperative Adjuvant Radiotherapy: A Case Report
- Radiotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma in the Elderly: What Is the Standard?
- Cystic Supratentorial Astrocytoma: Case Report