J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2010 Sep;51(9):1258-1263. 10.3341/jkos.2010.51.9.1258.
The Comparison of Surgical Results Between Non-accommodative and Partially Accommodative Esotropia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. mychoi@chungbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 2122294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2010.51.9.1258
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To examine the differences in surgical results between non-accommodative esotropia (NAE) and partially accommodative esotropia (PAE).
METHODS
This retrospective study included 47 patients undergoing surgery for pediatric esotropia, defined as esotropia with a decrease in the deviated angle of greater than ten prism diopters (PD) upon administration of hyperopic spectacles. On the other hand, NAE was defined as esotropia with a decrease in the deviated angle of less than 10PD. We compared age at surgery, deviated angle at surgery, frequency of amblyopia, and deviated angle at each postoperative period in two groups.
RESULTS
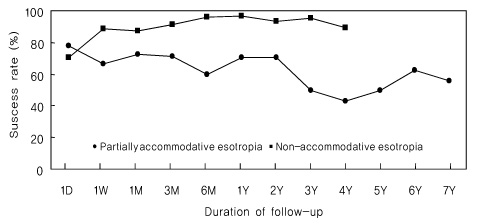
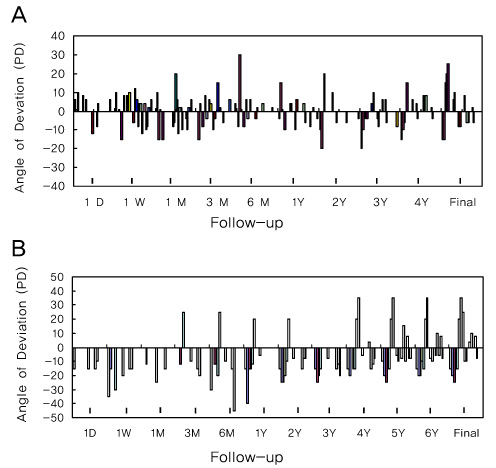
Twenty-nine patients belonged to the PAE group, and 18 patients belonged to the NAE group. The age at surgery in the PAE group was higher than that of the NAE group, and the deviated angle for surgical correction was smaller in the PAE group than in the NAE group. No statistically significant difference in the frequency of amblyopia presentation was found between the two groups. The surgical success rates were much higher in the PAE group at postoperative two years and at the final visit compared to those of the NAE group.
CONCLUSIONS
In esotropic children who underwent surgery, the long-term surgical success rate was highest in the cases in which the esotropic angle was decreased by hyperopic correction.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Changes in Hypermetropic Spectacle Correction after Surgery in Partially Accommodative Esotropia
Sin Woo Bae, Moses Kim, Mi Young Choi
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2014;55(5):719-725. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2014.55.5.719.
Reference
-
1. Mohney BG. Common forms of childhood strasbismus in an incidence Cohort. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007. 144:465–467.2. von Noorden GK. . Binocular vision and ocular motility. 2002. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;311–355. 3.3. Scheiman M, Ciner E. Surgical success rates in acquired, comitant, partially accommodative and nonaccommodative esotropia. J Am Optom Assoc. 1987. 58:556–561.4. Braddick O. Binocularity in infancy. Eye. 1996. 10:182–188.5. Kim SJ, Kim OJ, Lee WS. Surgical results in nonaccommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalomol Soc. 1994. 35:442–447.6. Archer SM, Sondhi N, Helveston EM. Strabismus in infancy. Ophthalmology. 1989. 96:133–137.7. von Noorden GK. Current concepts of infantile esotropia. Eye. 1988. 2:343–357.8. Robb RM, Rodier DW. The variable clinical characteristics and course of early infantile esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1987. 24:276–281.9. Ing MR. Early surgical alignment for congenital esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1983. 20:11–18.10. Fisher NF, Folm MC, Jampolsky A. Early surgical alignment of congenital esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968. 18:19–22.11. von Noorden GK, Isaza A, Parks ME. Surgical treatment of congenital esotropia. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1972. 76:1465–1478.12. Cho YA, Roh KH. Early surgery for infantile esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1993. 34:1251–1256.13. Kim EJ, Cho YA. Clinical assessment of partially accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1993. 34:447–451.14. Haynes H, White BL, Held R. Visual accommodation in human infants. Science. 1965. 148:528–530.15. Baker JD, Parks MM. Early-onset accommodative esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980. 90:11–20.16. Marge E, Freeman D, Peltaman P, Goldstein P. Visual acuity development in human infants, evoked potential measurement. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1976. 15:150–153.17. Havertape SA, Whitfill CR, Cruz OA. Early-onset accommodative esotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1999. 36:69–73.18. Dickey CF, Scott WE. The deterioration of accommodative esotropia: Frequency, characteristics, and predictive factors. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1988. 25:172–175.19. von Noorden GK. Binocular vision and ocular motility. 2002. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;256–272.20. Kim JC, Park SC, Park C. The clinical effect of augmented surgery for partially accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1995. 36:505–509.21. Hiles DA, Waston BA, Biglan AW. Characteristics of infantile esotropia. Surv Ophthalmol. 1987. 31:363–383.22. Costenbader FD. Infantile esotropia. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1961. 59:397–429.23. Abrahamsson M, Fabian G, Sjostrand J. A longitudinal study of a population based sample of astigmatic children. II. The changeability of anisometropia. Acta Ophthalmol. 1990. 68:435–440.24. De Vries J. Anisometropia in children: analysis of a hospital population. Br J Ophthalmol. 1985. 69:504–507.25. Jotterand VH, Isenberg SJ. Enhancing surgery for acquired esotropia. Ophthalmic Surg. 1988. 19:263–266.26. Wright KW, Bruce-Lyle L. Augmented surgery for esotropia associated with high hypermetropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993. 30:167–170.27. Lee JY, Kim JK, Cho YA. The long-term postoperative alignment and binocularity of partially accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000. 41:1974–1982.28. Song JH, Seong YS, Chang YH, Lee JB. The long-term surgical outcome after bilateral medial rectus muscle recession in partially accommodative esotropia. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004. 45:462–467.29. Shauly Y, Prager TC, Mazow ML. Clinical characteristics and long-term postoperative result of infantile esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994. 117:183–189.30. Bateman JB, Parks MM, Wheeler N. Discriminant analysis of congenital esotropia surgery. Predictor variables for short and long-term outcomes. Ophthalmology. 1983. 90:1146–1153.31. Choi AH, Park SE, O SY. Long-term outcome of patients with partially accommodative esotropia who had augmented surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003. 44:1833–1838.32. Plenty JV. Increased incidence of dissociated vertical deviation in congenital infantile esotropia undergoing surgical correction in the first year of life. Binoc Vis. 1989. 4:76–80.33. Wilson ME, Parks MM. Primary inferior oblique overaction in congenital esotropia, accommodative esotropia and intermittent exotropia. Ophthalmology. 1989. 96:950–957.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Assessment of Partially Accommodative Esotropia
- Clinical Features of Refractive Accommodative Esotropia and Partially Accommodative Esotropia
- The Ratio of Accommodative-Convergence to Accommodation in Patients with Nonrefractive Accommodative Esotropia
- Clinical Studies on Accormmodative Esotropia
- Surgical Outcome of Esotropia Considering the Functional Equator