J Adv Prosthodont.
2014 Jun;6(3):165-170. 10.4047/jap.2014.6.3.165.
The effect of a desensitizer and CO2 laser irradiation on bond performance between eroded dentin and resin composite
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Esthetic Restorative Dentistry, Graduate School of Clinical Dentistry, Korea University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. koprosth@unitel.co.kr
- 2Department of Advanced Prosthodontics, Institute for Clinical Dental Research, Korea University Medical Center, Korea University, Seoul, Republic of Korea. wddc@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2118226
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2014.6.3.165
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was aimed to evaluate effect of the desensitizing pretreatments on the micro-tensile bond strengths (microTBS) to eroded dentin and sound dentin.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
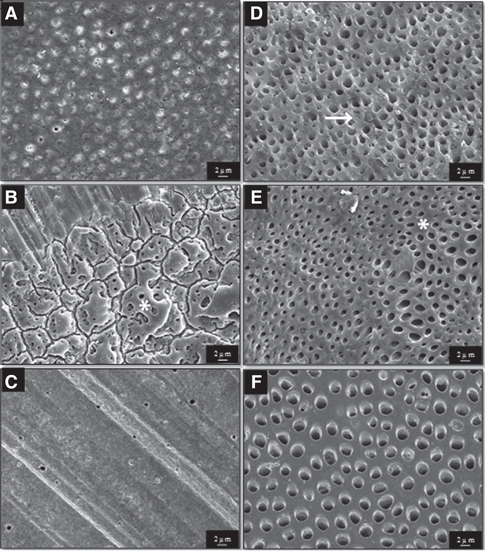
Forty-two extracted molars were prepared to form a flat dentin surface, and then they were divided into two groups. Group I was stored in distilled water while group II was subjected to a pH cycling. Each group was then subdivided into three subgroups according to desensitizing pretreatment used: a) pretreatment with desensitizer (Gluma); b) pretreatment with CO2 Laser (Ultra Dream Pluse); c) without any pretreatment. All prepared surfaces were bonded with Single Bond 2 and built up with resin composite (Filtek Z250). The micro-tensile bond test was performed. Fracture modes were evaluated by stereomicroscopy. Pretreated surfaces and bonded interfaces were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The data obtained was analyzed by two-way ANOVA (alpha=0.05).
RESULTS
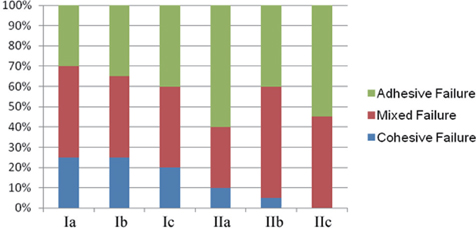
For both sound and eroded dentin, samples treated with desensitizer showed the greatest microTBS, followed by samples without any treatment. And samples treated with CO2 laser showed the lowest microTBS. SEM study indicated that teeth with eroded dentin appeared prone to debonding, as demonstrated by existence of large gaps between adhesive layers and dentin.
CONCLUSION
Pretreatment with Gluma increased the microTBS of Single Bond 2 for eroded and sound teeth. CO2 laser irradiation weakened bond performance for sound teeth but had no effect on eroded teeth.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Murakami C, Oliveira LB, Sheiham A, Nahás Pires Corrêa MS, Haddad AE, Bönecker M. Risk indicators for erosive tooth wear in Brazilian preschool children. Caries Res. 2011; 45:121–129.2. Kazoullis S, Seow WK, Holcombe T, Newman B, Ford D. Common dental conditions associated with dental erosion in schoolchildren in Australia. Pediatr Dent. 2007; 29:33–39.3. Braga RR, Meira JB, Boaro LC, Xavier TA. Adhesion to tooth structure: a critical review of "macro" test methods. Dent Mater. 2010; 26:e38–e49.4. Federlin M, Thonemann B, Schmalz G, Urlinger T. Clinical evaluation of different adhesive systems for restoring teeth with erosion lesions. Clin Oral Investig. 1998; 2:58–66.5. Brackett WW, Brackett MG, Dib A, Franco G, Estudillo H. Eighteen-month clinical performance of a self-etching primer in unprepared class V resin restorations. Oper Dent. 2005; 30:424–429.6. Bartlett D, Sundaram G. An up to 3-year randomized clinical study comparing indirect and direct resin composites used to restore worn posterior teeth. Int J Prosthodont. 2006; 19:613–617.7. Zimmerli B, De Munck J, Lussi A, Lambrechts P, Van Meerbeek B. Long-term bonding to eroded dentin requires superficial bur preparation. Clin Oral Investig. 2012; 16:1451–1461.8. Flury S, Koch T, Peutzfeldt A, Lussi A, Ganss C. The effect of a tin-containing fluoride mouth rinse on the bond between resin composite and erosively demineralised dentin. Clin Oral Investig. 2013; 17:217–225.9. Gerrard WA, Winter PJ. Evaluation of toothpastes by their ability to assist rehardening of enamel in vitro. Caries Res. 1986; 20:209–216.10. Shono Y, Ogawa T, Terashita M, Carvalho RM, Pashley EL, Pashley DH. Regional measurement of resin-dentin bonding as an array. J Dent Res. 1999; 78:699–705.11. Rees JS, Jin LJ, Lam S, Kudanowska I, Vowles R. The prevalence of dentine hypersensitivity in a hospital clinic population in Hong Kong. J Dent. 2003; 31:453–461.12. Udoye CI. Pattern and distribution of cervical dentine hypersensitivity in a Nigerian tertiary hospital. Odontostomatol Trop. 2006; 29:19–22.13. Scheutzel P. Etiology of dental erosion-intrinsic factors. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996; 104:178–190.14. Lussi A, Schlueter N, Rakhmatullina E, Ganss C. Dental erosion-an overview with emphasis on chemical and histopathological aspects. Caries Res. 2011; 45:2–12.15. Waterhouse PJ, Auad SM, Nunn JH, Steen IN, Moynihan PJ. Diet and dental erosion in young people in south-east Brazil. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2008; 18:353–360.16. Lussi A, Jaeggi T. Erosion-diagnosis and risk factors. Clin Oral Investig. 2008; 12:S5–S13.17. Ganss C, Schlechtriemen M, Klimek J. Dental erosions in subjects living on a raw food diet. Caries Res. 1999; 33:74–80.18. Schlueter N, Neutard L, von Hinckeldey J, Klimek J, Ganss C. Tin and fluoride as anti-erosive agents in enamel and dentine in vitro. Acta Odontol Scand. 2010; 68:180–184.19. Schreiner RF, Chappell RP, Glaros AG, Eick JD. Microtensile testing of dentin adhesives. Dent Mater. 1998; 14:194–201.20. Armstrong S, Geraldeli S, Maia R, Raposo LH, Soares CJ, Yamagawa J. Adhesion to tooth structure: a critical review of "micro" bond strength test methods. Dent Mater. 2010; 26:e50–e62.21. Neelima L, Sathish ES, Kandaswamy D. Bupesh. Evaluation of microtensile bond strength of total-etch, self-etch, and glass ionomer adhesive to human dentin: an in vitro study. Indian J Dent Res. 2008; 19:129–133.22. Schmidlin PR, Siebenmann J, Kocher P, Seemann R, Attin T, Bindl A. Effects of de- and remineralization of dentin on bond strengths yielded by one-, three-, and four-step adhesives. J Adhes Dent. 2008; 10:119–126.23. Sattabanasuk V, Vachiramon V, Qian F, Armstrong SR. Resin-dentin bond strength as related to different surface preparation methods. J Dent. 2007; 35:467–475.24. Armstrong SR, Boyer DB, Keller JC. Microtensile bond strength testing and failure analysis of two dentin adhesives. Dent Mater. 1998; 14:44–50.25. Moritz A, Gutknecht N, Schoop U, Goharkhay K, Ebrahim D, Wernisch J, Sperr W. The advantage of CO2-treated dental necks, in comparison with a standard method: results of an in vivo study. J Clin Laser Med Surg. 1996; 14:27–32.26. Cakar G, Kuru B, Ipci SD, Aksoy ZM, Okar I, Yilmaz S. Effect of Er:YAG and CO2 lasers with and without sodium fluoride gel on dentinal tubules: a scanning electron microscope examination. Photomed Laser Surg. 2008; 26:565–571.27. Apel C, Meister J, Götz H, Duschner H, Gutknecht N. Structural changes in human dental enamel after subablative erbium laser irradiation and its potential use for caries prevention. Caries Res. 2005; 39:65–70.28. Omae M, Inoue M, Itota T, Finger WJ, Inoue M, Tanaka K, Yamamoto K, Yoshiyama M. Effect of a desensitizing agent containing glutaraldehyde and HEMA on bond strength to Er:YAG laser-irradiated dentine. J Dent. 2007; 35:398–402.29. Sengun A, Koyuturk AE, Sener Y, Ozer F. Effect of desensitizers on the bond strength of a self-etching adhesive system to caries-affected dentin on the gingival wall. Oper Dent. 2005; 30:430–435.30. Ravikumar N, Shankar P, Indira R. Shear bond strengths of two dentin bonding agents with two desensitizers: An in vitro study. J Conserv Dent. 2011; 14:247–251.31. Stawarczyk B, Hartmann R, Hartmann L, Roos M, Ozcan M, Sailer I, Hämmerle CH. The effect of dentin desensitizer on shear bond strength of conventional and self-adhesive resin luting cements after aging. Oper Dent. 2011; 36:492–501.32. Munksgaard EC, Asmussen E. Bond strength between dentin and restorative resins mediated by mixtures of HEMA and glutaraldehyde. J Dent Res. 1984; 63:1087–1089.33. Van Landuyt KL, Snauwaert J, De Munck J, Peumans M, Yoshida Y, Poitevin A, Coutinho E, Suzuki K, Lambrechts P, Van Meerbeek B. Systematic review of the chemical composition of contemporary dental adhesives. Biomaterials. 2007; 28:3757–3785.34. Van Landuyt KL, De Munck J, Snauwaert J, Coutinho E, Poitevin A, Yoshida Y, Inoue S, Peumans M, Suzuki K, Lambrechts P, Van Meerbeek B. Monomer-solvent phase separation in one-step self-etch adhesives. J Dent Res. 2005; 84:183–188.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect Of Dentin Desensitizers On Shear Bond Strength Of Resin Cements
- The effect of Er,Cr:YSGG irradiation on microtensile bond strength of composite resin restoration
- The Effect Of Temporary Cement And Desensitizer On The Bond Strength Of Luting Cements
- Effect of a desensitizer on dentinal bond strength in cementation of composite resin inlay
- The effect of bonding resin on bond strength of dual-cure resin cements