Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Sep;8(3):237-242. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.237.
Benefit From Directional Microphone Hearing Aids: Objective and Subjective Evaluations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Hearing Research Laboratory, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. moonij@skku.edu
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2117518
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.237
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aims of this study were to find and compare the effect of directional (DIR) processing of two different hearing aids via both subjective and objective methods, to determine the association between the results of the subjective and objective evaluations, and to find out individual predictive factors influencing the DIR benefit.
METHODS
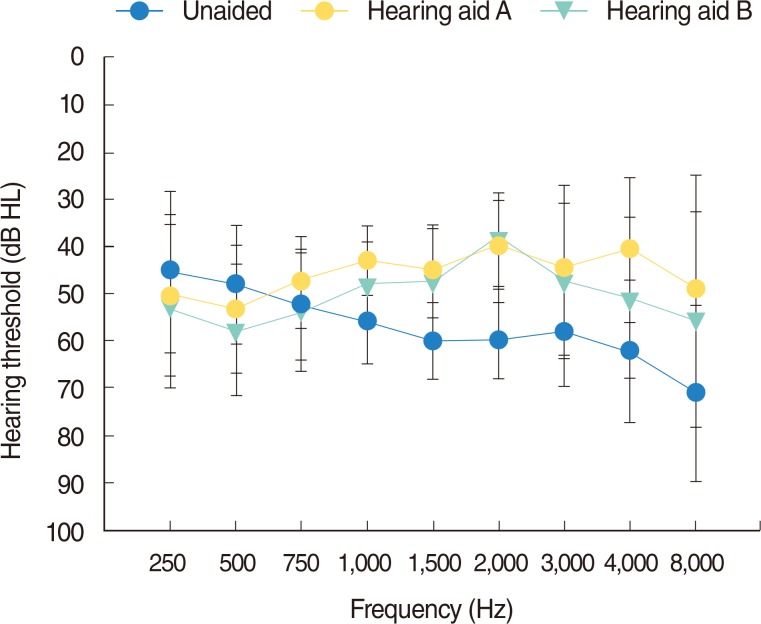
Twenty-six hearing aid users fitted unilaterally with each two different experimental hearing aid performed modified Korean Hearing in Noise Test (K-HINT) in three DIR conditions; omnidirectional (OMNI) mode, OMNI plus noise reduction feature, fixed DIR mode. In order to determine benefits from DIR benefit within a hearing aid and compare performance of the DIR processing between hearing aids, a subjective questionnaire was administrated on speech quality (SQ) and discomfort in noise (DN) domain. Correlation analysis of factors influencing DIR benefit was accomplished.
RESULTS
Benefits from switching OMNI mode to DIR mode within both hearing aids in K-HINT were about 2.8 (standard deviation, 3.5) and 2.1 dB SNR (signal to ratio; SD, 2.5), but significant difference in K-HINT results between OMNI and OMNI plus noise reduction algorithm was not shown. The subjective evaluation resulted in the better SQ and DN scores in DIR mode than those in OMNI mode. However, the difference of scores on both SQ and DN between the two hearing aids with DIR mode was not statistically significant. Any individual factors did not significantly affect subjective and objective DIR benefits.
CONCLUSION
DIR benefit was found not only in the objective measurement performed in the laboratory but also in the subjective questionnaires, but the subjective results was failed to have significant correlation with the DIR benefit obtained in the K-HINT. Factors influencing individual variation in perceptual DIR benefit were still hard to explain.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ricketts TA. Directional hearing aids: then and now. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2005; Jul-Aug. 42(4 Suppl 2):133–144. PMID: 16470469.
Article2. Bentler RA. Effectiveness of directional microphones and noise reduction schemes in hearing aids: a systematic review of the evidence. J Am Acad Audiol. 2005; Jul-Aug. 16(7):473–484. PMID: 16295234.
Article3. Ricketts TA. Directional hearing AIDS. Trends Amplif. 2001; 12. 5(4):139–176. PMID: 25425906.
Article4. Klemp EJ, Dhar S. Speech perception in noise using directional microphones in open-canal hearing aids. J Am Acad Audiol. 2008; Jul-Aug. 19(7):571–578. PMID: 19248734.
Article5. Valente M, Mispagel KM, Tchorz J, Fabry D. Effect of type of noise and loudspeaker array on the performance of omnidirectional and directional microphones. J Am Acad Audiol. 2006; 6. 17(6):398–412. PMID: 16866004.
Article6. Ricketts TA, Hornsby BW. Directional hearing aid benefit in listeners with severe hearing loss. Int J Audiol. 2006; 3. 45(3):190–197. PMID: 16579494.
Article7. Walden BE, Surr RK, Grant KW, Van Summers W, Cord MT, Dyrlund O. Effect of signal-to-noise ratio on directional microphone benefit and preference. J Am Acad Audiol. 2005; 10. 16(9):662–676. PMID: 16515138.
Article8. Kuk F, Keenan D, Lau CC, Ludvigsen C. Performance of a fully adaptive directional microphone to signals presented from various azimuths. J Am Acad Audiol. 2005; 6. 16(6):333–347. PMID: 16178405.
Article9. Cord MT, Surr RK, Walden BE, Dyrlund O. Relationship between laboratory measures of directional advantage and everyday success with directional microphone hearing aids. J Am Acad Audiol. 2004; 5. 15(5):353–364. PMID: 15506497.
Article10. Wu YH, Bentler RA. Impact of visual cues on directional benefit and preference. Part II. field tests. Ear Hear. 2010; 2. 31(1):35–46. PMID: 19773657.11. Gnewikow D, Ricketts T, Bratt GW, Mutchler LC. Real-world benefit from directional microphone hearing aids. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2009; 46(5):603–618. PMID: 19882494.
Article12. Festen JM, Plomp R. Effects of fluctuating noise and interfering speech on the speech-reception threshold for impaired and normal hearing. J Acoust Soc Am. 1990; 10. 88(4):1725–1736. PMID: 2262629.
Article13. Palmer C, Bentler R, Mueller HG. Evaluation of a second-order directional microphone hearing aid: II. Self-report outcomes. J Am Acad Audiol. 2006; 3. 17(3):190–201. PMID: 16646279.
Article14. Keidser G, Dillon H, Convery E, Mejia J. Factors influencing individual variation in perceptual directional microphone benefit. J Am Acad Audiol. 2013; Nov-Dec. 24(10):955–968. PMID: 24384081.
Article15. Wu YH, Bentler RA. Impact of visual cues on directional benefit and preference. Part I. laboratory tests. Ear Hear. 2010; 2. 31(1):22–34. PMID: 19864954.16. Wu YH. Effect of age on directional microphone hearing aid benefit and preference. J Am Acad Audiol. 2010; 2. 21(2):78–89. PMID: 20166310.
Article17. Ricketts T, Mueller HG. Predicting directional hearing aid benefit for individual listeners. J Am Acad Audiol. 2000; Nov-Dec. 11(10):561–569. PMID: 11198073.18. Keidser G, Dillon H, Carter L, O'Brien A. NAL-NL2 empirical adjustments. Trends Amplif. 2012; 12. 16(4):211–223. PMID: 23203416.
Article19. Jang HS, Lee JH, Lim DH, Lee KW, Jeon AR, Jung EJ. Development of Korean standard sentence lists for sentence recognition tests. Audiology. 2008; 10. 4(2):161–177.
Article20. Moon SK, Hee Kim S, Mun HA, Jung HK, Lee JH, Choung YH, et al. The Korean hearing in noise test. Int J Audiol. 2008; 6. 47(6):375–376. PMID: 18569115.
Article21. Nilsson M, Soli SD, Sullivan JA. Development of the Hearing in Noise Test for the measurement of speech reception thresholds in quiet and in noise. J Acoust Soc Am. 1994; 2. 95(2):1085–1099. PMID: 8132902.
Article22. Ricketts TA. How fitting, patient, and environmental factors affect directional benefit. Hear J. 2003; 11. 56(11):31–39.
Article23. Brons I, Houben R, Dreschler WA. Effects of noise reduction on speech intelligibility, perceived listening effort, and personal preference in hearing-impaired listeners. Trends Hear. 2014; 10. 18:pii: 2331216514553924.
Article24. Alcantara JL, Moore BC, Kuhnel V, Launer S. Evaluation of the noise reduction system in a commercial digital hearing aid. Int J Audiol. 2003; 1. 42(1):34–42. PMID: 12564514.25. Nordrum S, Erler S, Garstecki D, Dhar S. Comparison of performance on the hearing in noise test using directional microphones and digital noise reduction algorithms. Am J Audiol. 2006; 6. 15(1):81–91. PMID: 16803795.
Article26. Chung K. Challenges and recent developments in hearing aids. Part I. Speech understanding in noise, microphone technologies and noise reduction algorithms. Trends Amplif. 2004; 8(3):83–124. PMID: 15678225.
Article27. Ricketts T. The impact of head angle on monaural and binaural performance with directional and omnidirectional hearing aids. Ear Hear. 2000; 8. 21(4):318–328. PMID: 10981608.
Article28. Wu YH, Bentler RA. A method to measure hearing aid directivity index and polar pattern in small and reverberant enclosures. Int J Audiol. 2011; 6. 50(6):405–416. PMID: 21309640.
Article29. Cox RM, Alexander GC, Taylor IM, Gray GA. Benefit acclimatization in elderly hearing aid users. J Am Acad Audiol. 1996; 12. 7(6):428–441. PMID: 8972444.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Acceptable Noise Level Benefit From Directionality for Listeners With Severe Hearing Loss
- Advantages of Binaural Amplification to Acceptable Noise Level of Directional Hearing Aid Users
- Hearing Performance Benefits of a Programmable Power Baha(R) Sound Processor with a Directional Microphone for Patients with a Mixed Hearing Loss
- Subjective Satisfaction in Hearing Aid Users by APHAB
- Comparative Analysis of Subjective Satisfaction Between Hearing Aid Users With Insurance Payment and General Payment