Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Sep;8(3):202-205. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.202.
Nasalance in Cochlear Implantees
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Christian Medical College, Vellore, India. swapna_santhosh@yahoo.co.in
- 2Department of Speech Language Pathology, All India Institute of Speech & Hearing, Mysore, India.
- KMID: 2117512
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.202
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
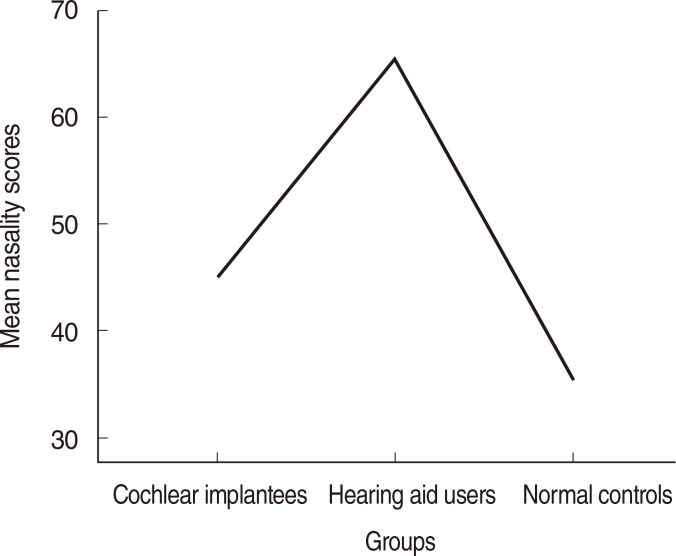
Speech intelligibility is severely affected in children with congenital profound hearing loss. Hypernasality is a problem commonly encountered in their speech. Auditory information received from cochlear implants is expected to be far superior to that from hearing aids. Our study aimed at comparing the percentages of nasality in the speech of the cochlear implantees with hearing aid users and also with children with normal hearing.
METHODS
Three groups of subjects took part in the study. Groups I and II comprised 12 children each, in the age range of 4-10 years, with prelingual bilateral profound hearing loss, using multichannel cochlear implants and digital hearing aids respectively. Both groups had received at least one year of speech therapy intervention since cochlear implant surgery and hearing aid fitting respectively. The third group consisted of age-matched and sex-matched children with normal hearing. The subjects were asked to say a sentence which consisted of only oral sounds and no nasal sounds ("Buy baby a bib"). The nasalance score as a percentage was calculated.
RESULTS
Statistical analysis revealed that the children using hearing aids showed a high percentage of nasalance in their speech. The cochlear implantees showed a lower percentage of nasalance compared to children using hearing aids, but did not match with their normal hearing peers.
CONCLUSION
The quality of speech of the cochlear implantees was superior to that of the hearing aid users, but did not match with the normal controls. The study suggests that acoustic variables still exist after cochlear implantation in children, with hearing impairments at deviant levels, which needs attention. Further research needs to be carried out to explore the effect of the age at implantation as a variable in reducing nasality in the speech and attaining normative values in cochlear implantees, and also between unilateral versus bilateral implantees.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hudgins CV, Numbers FC. An investigation of the intelligibility of the speech of the deaf. Provincetown (MA): The Journal Press;1942.2. Stevens KN, Nickerson RS, Boothroyd A, Rollins AM. Assessment of nasalization in the speech of deaf children. J Speech Hear Res. 1976; 6. 19(2):393–416. PMID: 790016.
Article3. House WF. Cochlear implants. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976; May-Jun. 85(Suppl 27):(3Pt2):1–93. PMID: 779582.
Article4. Staller SJ. Cochlear implant characteristics: a review of current technology. Semin Hear. 1985; 2. 6(1):23–32.
Article5. Hoth S. Indication for the need of flexible and frequency specific mapping functions in cochlear implant speech processors. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 2. 264(2):129–138. PMID: 17004087.
Article6. LaPine PR, Stewart MG, Tatchell J. Application of nasometry to speech samples of hearing-impaired children. Percept Mot Skills. 1991; 10. 73(2):467–475. PMID: 1766773.
Article7. Plant G, Oster AM. The effects of cochlear implantation on speech production: a case study. STL-QPSR. 1986; 27(1):65–86.8. Langereis MC, Dejonckere PH, van Olphen AF, Smoorenburg GF. Effect of cochlear implantation on nasality in post-lingually deafened adults. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 1997; 49(6):308–314. PMID: 9415736.
Article9. Mathew P, Yathiraj A. A picture test of speech perception in Malayalam [master's thesis]. Mysuru: University of Mysore;1996.10. Zimmerman-Phillips S, Osberger MJ, Robbins AM. Infant-toddler meaningful auditory integration scale. Sylmar (CA): Advanced Bionics Co.;2001.11. RukminiA P. Malayalam language test [master's thesis]. Mysuru: University of Mysore;1994.12. Robbins AM, Osberger MJ. Meaningful use of speech scale. Indianapolis: Indiana University School of Medicine Press;1991.13. Evans MK, Deliyski DD. Acoustic voice analysis of prelingually deaf adults before and after cochlear implantation. J Voice. 2007; 11. 21(6):669–682. PMID: 16952440.
Article14. Colton RH, Cooker HS. Perceived nasality in the speech of the deaf. J Speech Hear Res. 1968; 9. 11(3):553–559. PMID: 5722479.
Article15. Fletcher SG, Higgins JM. Performance of children with severe to profound auditory impairment in instrumentally guided reduction of nasal resonance. J Speech Hear Disord. 1980; 5. 45(2):181–194. PMID: 7442151.
Article16. Lock RB, Seaver EJ 3rd. Nasality and velopharyngeal function in five hearing impaired adults. J Commun Disord. 1984; 2. 17(1):47–64. PMID: 6715568.
Article17. Ysunza A, Vazquez MC. Velopharyngeal sphincter physiology in deaf individuals. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1993; 3. 30(2):141–143. PMID: 8452833.
Article18. Fletcher SG, Mahfuzh F, Hendarmin H. Nasalance in the speech of children with normal hearing and children with hearing loss. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 1999; 8. 8(3):241–248.
Article19. Leder SB, Spitzer JB. A perceptual evaluation of the speech of adventitiously deaf adult males. Ear Hear. 1990; 6. 11(3):169–175. PMID: 1967115.
Article20. LaPine PR, Stewart MG, Settle SV, Brandow M. Examining the effects of amplification on the nasalance ratios of hearing-impaired children. Folia Phoniatr (Basel). 1992; 44(5):185–193. PMID: 1490643.
Article21. Fletcher SG, Daly DA. Nasalance in utterances of hearing-impaired speakers. J Commun Disord. 1976; 3. 9(1):63–73. PMID: 965505.
Article22. Tye-Murray N. Articulatory organizational strategies and the roles of audition. Volta Rev. 1992; 7. 94(3):243–259.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acoustic Analysis of Speech of Cochlear Implantees and Its Implications
- Objective Evaluation of Surgically Corrected Velopharyngeal Insufficiency with Nasalance on Nasometer
- Educational Status in Bilateral Prelingual Deaf Children with Cochlear Implantation
- A Case of Cochlear Implantation in Otosclerosis Histologically Diagnosed
- Application of Intra-operative Neural Response Telemetry in Cochlear Implant