Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Sep;8(3):194-197. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.194.
Relationship Between Otorhinolaryngologic Diseases and Obesity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yeo2park@gmail.com
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2117510
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.3.194
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Obesity rates have been increasing for all population groups worldwide, leading to the increased development of various diseases. This study was designed is to identify the relationships between obesity and several important otorhinolaryngologic diseases, including chronic otitis media (COM), chronic rhinosinusitis, and chronic tonsillitis.
METHODS
Mean body mass index (BMI) was compared in patients with COM, rhinosinusitis, and tonsillitis and in a control group. The relationships among the prevalence rates of overweight and obesity, morbidity period, and BMI were assessed in each group.
RESULTS
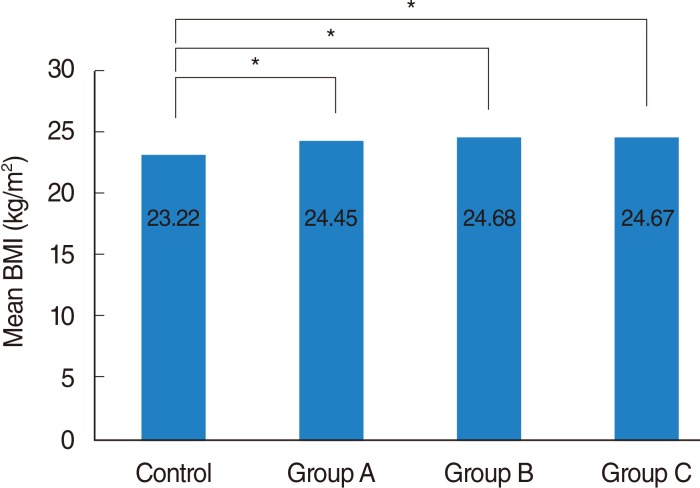
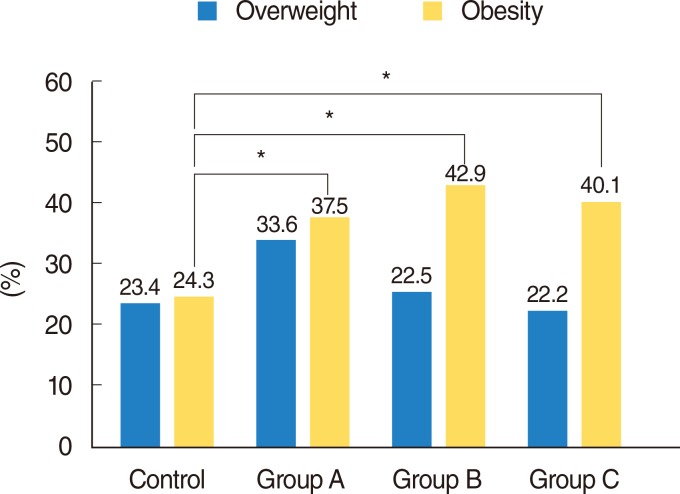
Mean BMIs in the COM, rhinosinusitis, and tonsillitis groups were 24.45+/-2.72 kg/m2, 24.68+/-3.25 kg/m2, and 24.67+/-3.82 kg/m2, respectively, with each significantly higher than in the control group (23.22+/-3.01 kg/m2, P<0.05). The rates of obesity in the COM, rhinosinusitis, and tonsillitis groups were 37.5%, 42.9%, and 40.1%, respectively, each significantly higher than in the control group (24.3%, P<0.05). However, the rates of overweight did not differ significantly in the COM, rhinosinusitis, and tonsillitis compared with the control group (P>0.05 each).
CONCLUSION
Mean BMI and the prevalence of obesity were elevated in the three groups of patients with representative otorhinolaryngologic inflammatory diseases, including COM, chronic rhinosinusitis, and chronic tonsillitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Geneva: World Health Organization;2006.2. Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH. Cause-specific excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA. 2007; 11. 298(17):2028–2037. PMID: 17986696.
Article3. Kim JB, Park DC, Cha CI, Yeo SG. Relationship between pediatric obesity and otitis media with effusion. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 4. 133(4):379–382. PMID: 17438253.
Article4. Wang CC, Goalstone ML, Draznin B. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance that impact cardiovascular biology. Diabetes. 2004; 11. 53(11):2735–2740. PMID: 15504952.
Article5. World Health Organization Western Pacific Region. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Sydney: Health Communications Australia Pty Ltd;2000.6. Kaplan MS, Huguet N, Newsom JT, McFarland BH, Lindsay J. Prevalence and correlates of overweight and obesity among older adults: findings from the Canadian National Population Health Survey. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2003; 11. 58(11):1018–1030. PMID: 14630884.
Article7. Fantuzzi G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 5. 115(5):911–919. PMID: 15867843.
Article8. Esposito K, Pontillo A, Ciotola M, Di Palo C, Grella E, Nicoletti G, et al. Weight loss reduces interleukin-18 levels in obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 8. 87(8):3864–3866. PMID: 12161523.
Article9. Juge-Aubry CE, Somm E, Giusti V, Pernin A, Chicheportiche R, Verdumo C, et al. Adipose tissue is a major source of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: upregulation in obesity and inflammation. Diabetes. 2003; 5. 52(5):1104–1110. PMID: 12716739.10. Cottam DR, Mattar SG, Barinas-Mitchell E, Eid G, Kuller L, Kelley DE, et al. The chronic inflammatory hypothesis for the morbidity associated with morbid obesity: implications and effects of weight loss. Obes Surg. 2004; 5. 14(5):589–600. PMID: 15186624.
Article11. Lee SK, Yeo SG. Relationship between pediatric obesity and otitis media with effusion. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009; 11. 9(6):465–472. PMID: 19814920.
Article12. Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993; 4. 328(17):1230–1235. PMID: 8464434.
Article13. Schwartz AR, Patil SP, Laffan AM, Polotsky V, Schneider H, Smith PL. Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2008; 2. 5(2):185–192. PMID: 18250211.
Article14. Camargo CA Jr, Weiss ST, Zhang S, Willett WC, Speizer FE. Prospective study of body mass index, weight change, and risk of adult-onset asthma in women. Arch Intern Med. 1999; 11. 159(21):2582–2588. PMID: 10573048.
Article15. Taylor B, Mannino D, Brown C, Crocker D, Twum-Baah N, Holguin F. Body mass index and asthma severity in the National Asthma Survey. Thorax. 2008; 1. 63(1):14–20. PMID: 18156567.
Article16. Shore SA. Obesity and asthma: possible mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 5. 121(5):1087–1093. PMID: 18405959.
Article17. MacArthur CJ, Pillers DA, Pang J, Kempton JB, Trune DR. Altered expression of middle and inner ear cytokines in mouse otitis media. Laryngoscope. 2011; 2. 121(2):365–371. PMID: 21271590.
Article