Chonnam Med J.
2010 Dec;46(3):163-169. 10.4068/cmj.2010.46.3.163.
Altered Renal Expression of Acid-base Transporters in Rats with Glycerol-induced Tubular Injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. skimw@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2116770
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2010.46.3.163
Abstract
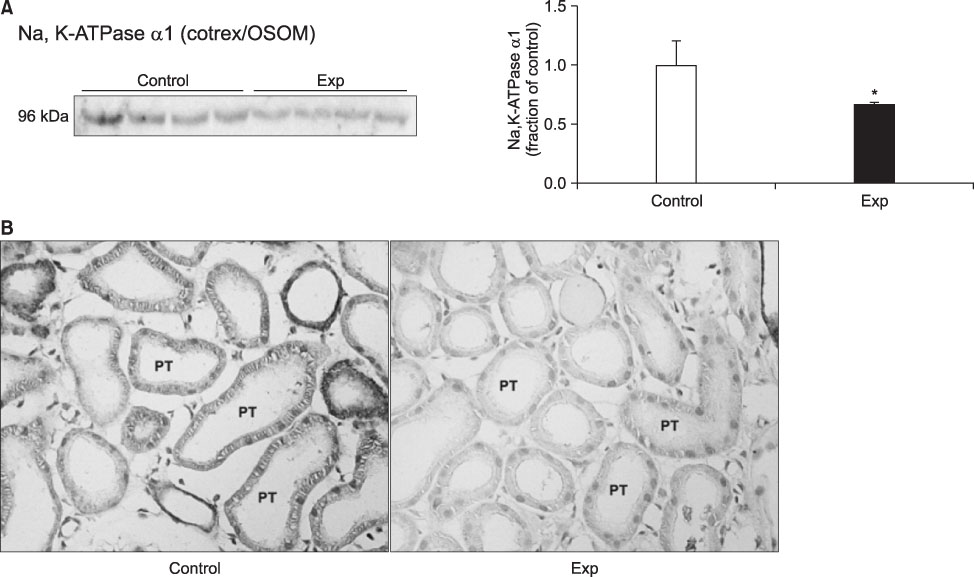
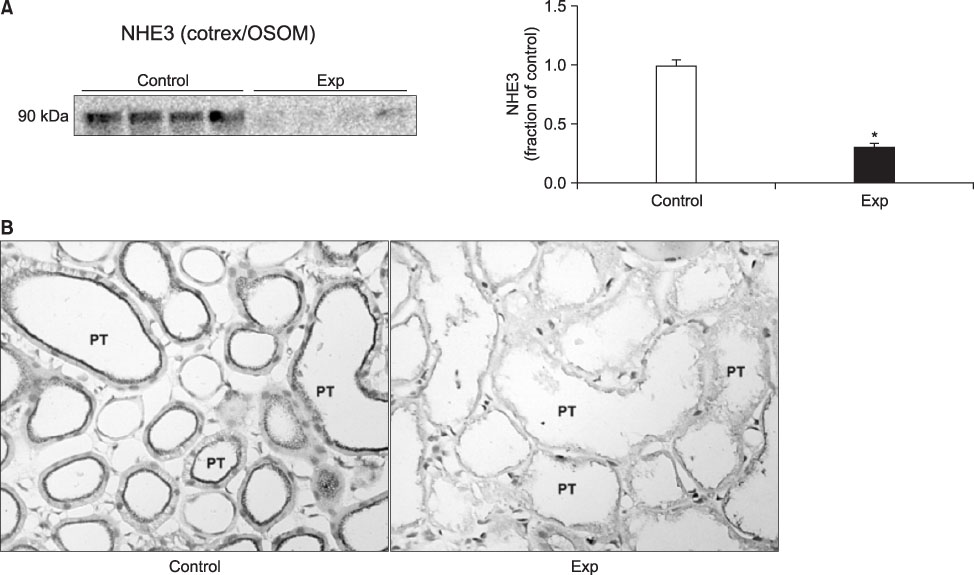
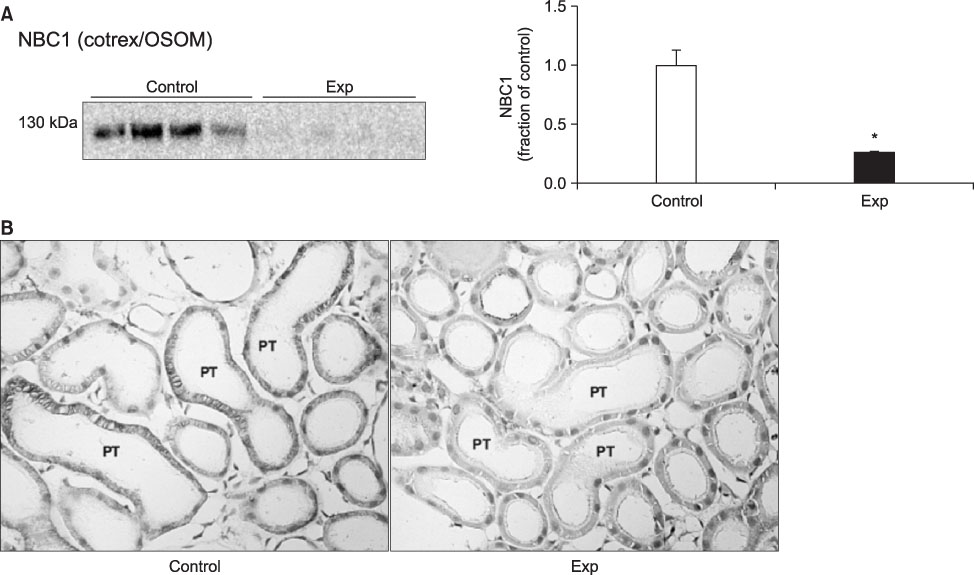
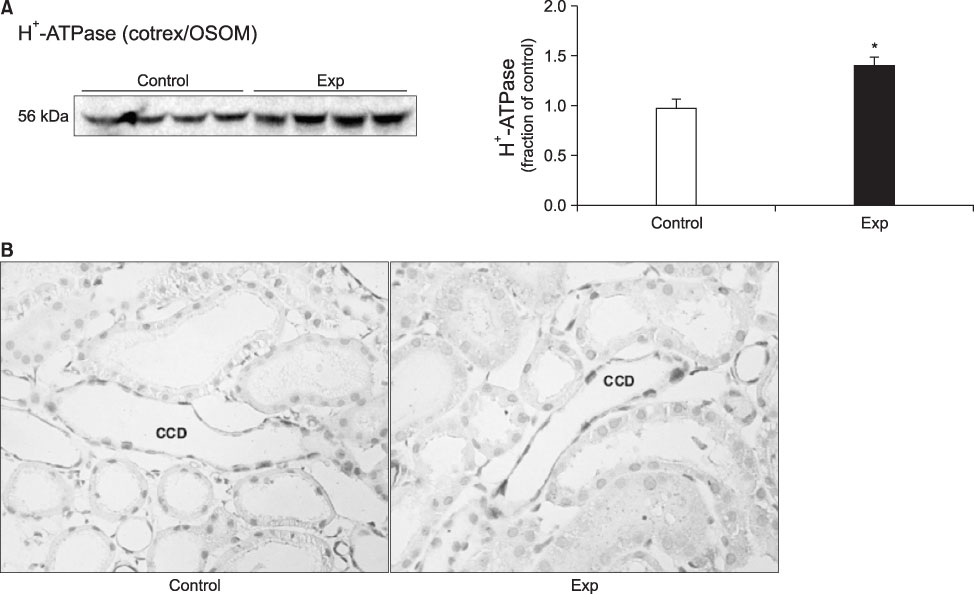
- The present study aimed to investigate the altered regulation of renal tubular acid-base transporters in rats with glycerol-induced tubular injury. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were used. Rats were injected with 50% glycerol in normal saline (7 mL/kg, i.m.) after water deprivation for 12 hours and were then sacrificed at 24 hours after the glycerol injection. The expression of Na,K-ATPase alpha1-subunit, type 3 Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE3), type 1 Na+:HCO3 - (NBC1), and B1-subunit of apical H+-ATPase was determined in the kidney by semiquantitative immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. In the experimental rats, creatinine clearance was decreased, whereas fractional sodium excretion was not changed. Urine pH and bicarbonate concentrations were decreased, although plasma pH and bicarbonate concentrations were not changed. In the experimental group, the protein expression of Na,K-ATPase alpha1-subunit was decreased in the cortex and outer stripe of outer medulla (cortex/OSOM) and inner stripe of outer medulla (ISOM) but increased in the inner medulla. The expression of NHE3 was decreased in the cortex/OSOM and ISOM, and that of NBC1 was decreased in the cortex/OSOM. By contrast, the expression of H+-ATPase was increased in the cortex/OSOM and inner medulla but was unchanged in the ISOM. Immunohistochemical analyses confirmed the immunoblotting data. In glycerol-induced tubular injury, the down-regulation of Na,K-ATPase alpha1-subunit, NHE3, and NBC1 may contribute to impaired tubular reabsorption of sodium and bicarbonate. The upregulation of H+-ATPase may play a preventive role against the development of metabolic acidosis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kashgarian M, Biemesderfer D, Caplan M, Forbush B 3rd. Monoclonal antibody to Na,K-ATPase: immunocytochemical localization along nephron segments. Kidney Int. 1985. 28:899–913.
Article2. Amemiya M, Loffing J, Lötscher M, Kaissling B, Alpern RJ, Moe OW. Expression of NHE-3 in the apical membrane of rat renal proximal tubule and thick ascending limb. Kidney Int. 1995. 48:1206–1215.
Article3. Mahnensmith RL, Aronson PS. The plasma membrane sodium-hydrogen exchanger and its role in physiological and pathophysiological processes. Circ Res. 1985. 56:773–788.
Article4. Preisig PA, Ives HE, Cragoe EJ Jr, Alpern RJ, Rector FC Jr. Role of the Na+/H+ antiporter in rat proximal tubule bicarbonate absorption. J Clin Invest. 1987. 80:970–978.
Article5. Soleimani M, Grassi SM, Aronson PS. Stoichiometry of Na+-HCO-3 cotransport in basolateral membrane vesicles isolated from rabbit renal cortex. J Clin Invest. 1987. 79:1276–1280.
Article6. Preisig PA, Alpern RJ. Chronic metabolic acidosis causes an adaptation in the apical membrane Na/H antiporter and basolateral membrane Na(HCO3)3 symporter in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1988. 82:1445–1453.
Article7. Eladari D, Leviel F, Pezy F, Paillard M, Chambrey R. Rat proximal NHE3 adapts to chronic acid-base disorders but not to chronic changes in dietary NaCl intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002. 282:F835–F843.
Article8. Amlal H, Chen Q, Greeley T, Pavelic L, Soleimani M. Coordinated down-regulation of NBC-1 and NHE-3 in sodium and bicarbonate loading. Kidney Int. 2001. 60:1824–1836.
Article9. Nicoletta JA, Schwartz GJ. Distal renal tubular acidosis. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004. 16:194–198.
Article10. Wall SM. Recent advances in our understanding of intercalated cells. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2005. 14:480–484.
Article11. Brown D, Hirsch S, Gluck S. Localization of a proton-pumping ATPase in rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1988. 82:2114–2126.
Article12. Alper SL, Natale J, Gluck S, Lodish HF, Brown D. Subtypes of intercalated cells in rat kidney collecting duct defined by antibodies against erythroid band 3 and renal vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989. 86:5429–5433.
Article13. Kim J, Kim YH, Cha JH, Tisher CC, Madsen KM. Intercalated cell subtypes in connecting tubule and cortical collecting duct of rat and mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. 10:1–12.
Article14. Royaux IE, Wall SM, Karniski LP, Everett LA, Suzuki K, Knepper MA, et al. Pendrin, encoded by the Pendred syndrome gene, resides in the apical region of renal intercalated cells and mediates bicarbonate secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001. 98:4221–4226.
Article15. Kim YH, Kwon TH, Frische S, Kim J, Tisher CC, Madsen KM, et al. Immunocytochemical localization of pendrin in intercalated cell subtypes in rat and mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002. 283:F744–F754.
Article16. Kim YH, Kwon TH, Christensen BM, Nielsen J, Wall SM, Madsen KM, et al. Altered expression of renal acid-base transporters in rats with lithium-induced NDI. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. 285:F1244–F1257.
Article17. Wang G, Ring T, Li C, Kim SW, Wen J, Djurhuus JC, et al. Unilateral ureteral obstruction alters expression of acid-base transporters in rat kidney. J Urol. 2009. 182:2964–2973.
Article18. Wang G, Li C, Kim SW, Ring T, Wen J, Djurhuus JC, et al. Ureter obstruction alters expression of renal acid-base transport proteins in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008. 295:F497–F506.
Article19. Zager RA, Burkhart KM, Conrad DS, Gmur DJ. Iron, heme oxygenase, and glutathione: effects on myohemoglobinuric proximal tubular injury. Kidney Int. 1995. 48:1624–1634.
Article20. Homsi E, Janino P, de Faria JB. Role of caspases on cell death, inflammation, and cell cycle in glycerol-induced acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2006. 69:1385–1392.
Article21. Rodrigo R, Bosco C, Herrera P, Rivera G. Amelioration of myoglobinuric renal damage in rats by chronic exposure to flavonol-rich red wine. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004. 19:2237–2244.
Article22. Ma SK, Bae EH, Lee JU, Kim SY, Kim SZ, Choi KC, et al. Altered regulation of type 3 Na+/H+ exchanger, type 1 Na+/HCO3- cotransporter, and Na+,K+-ATPase in the Kidney of Rats with experimental rhabdomyolysis. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2007. 5:55–61.
Article23. Karet FE, Finberg KE, Nelson RD, Nayir A, Mocan H, Sanjad SA, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding B1 subunit of H+-ATPase cause renal tubular acidosis with sensorineural deafness. Nat Genet. 1999. 21:84–90.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Altered Regulation of Renal Acid Base Transporters in Response to Ammonium Chloride Loading in Rats
- Effects of Antioxidant Drugs in Rats with Acute Renal Injury
- Expression of Fas Ligand (FasL) in Normal Kidney and Experimental Acute Tubular Necrosis
- Pathophysiological Implications of Sodium Transporters and Water Channels in the Kidney
- A Case of Exercise-induced Acute Renal Failure with G774A Mutation in SCL22A12 Causing Renal Hypouricemia