Lab Anim Res.
2010 Dec;26(4):369-375. 10.5625/lar.2010.26.4.369.
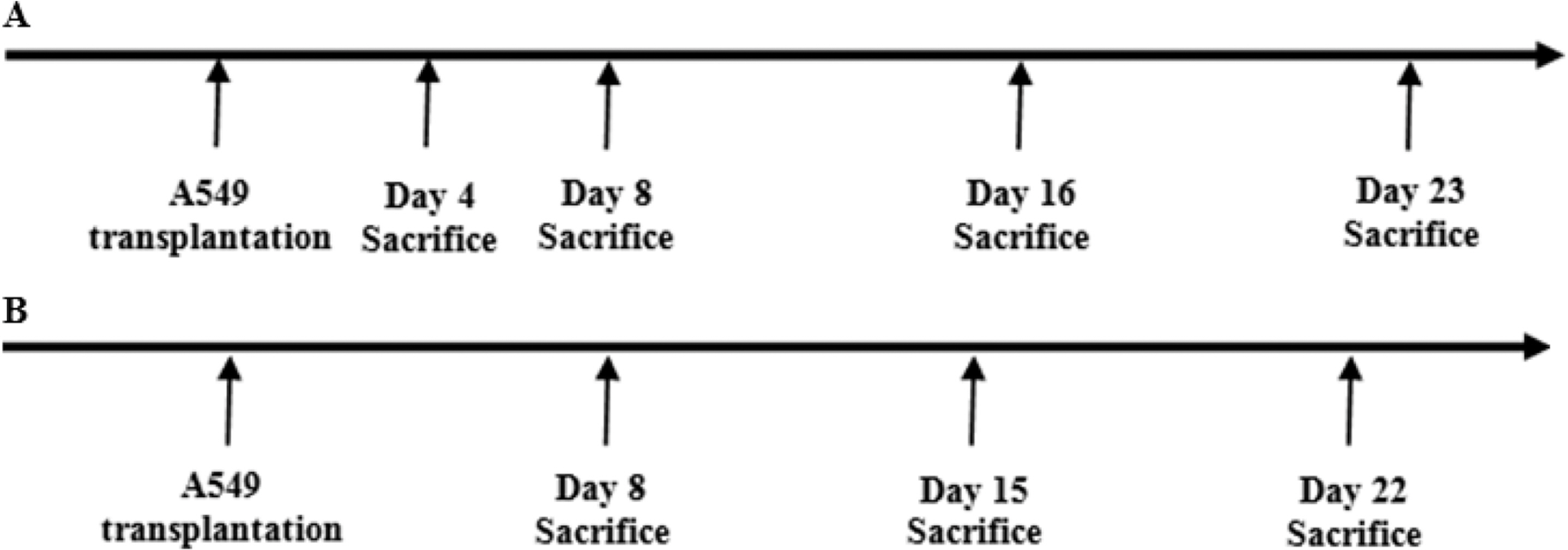
The Incidence Rate and Severity of Orthotopic Lung Cancer in an Animal Model Depends on the Number of A549 Cells and Transplantation Period
- Affiliations
-
- 1Inhalation Toxicology Center, Korea Institute of Toxicology Jeongeup Campus, Jeongeup, Korea. cwsong@kitox.re.kr
- 2Major of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Science and Technology, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2114705
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2010.26.4.369
Abstract
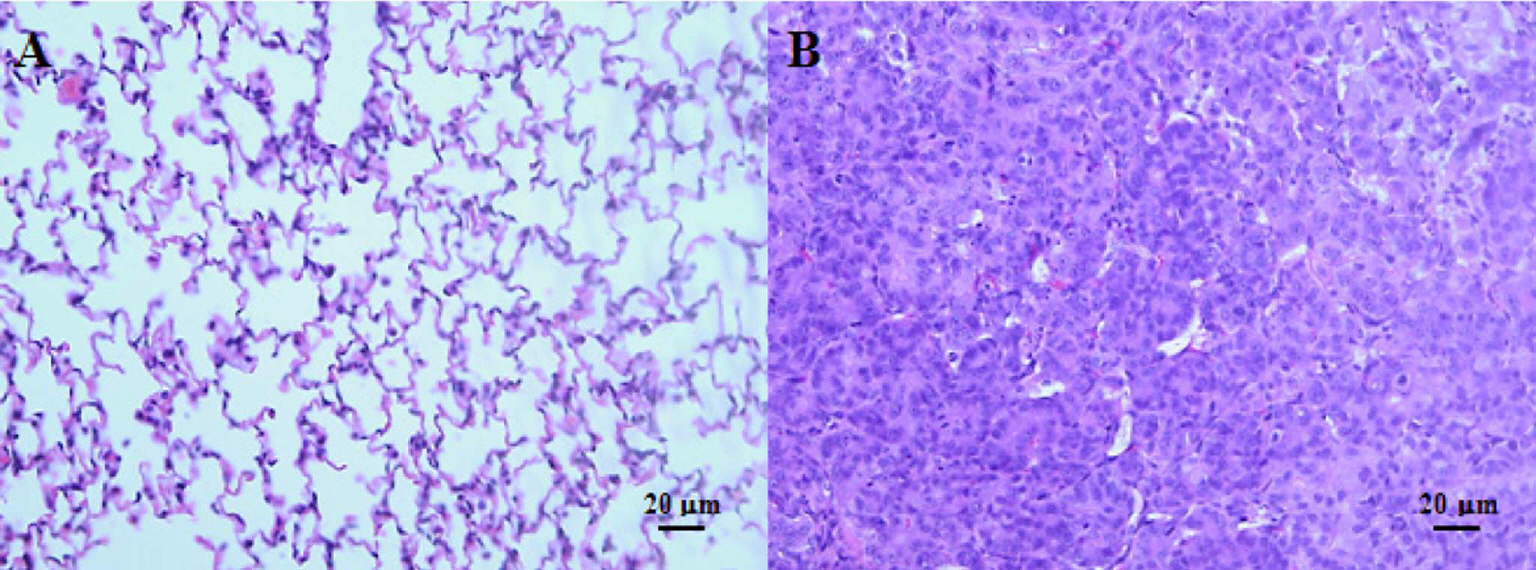
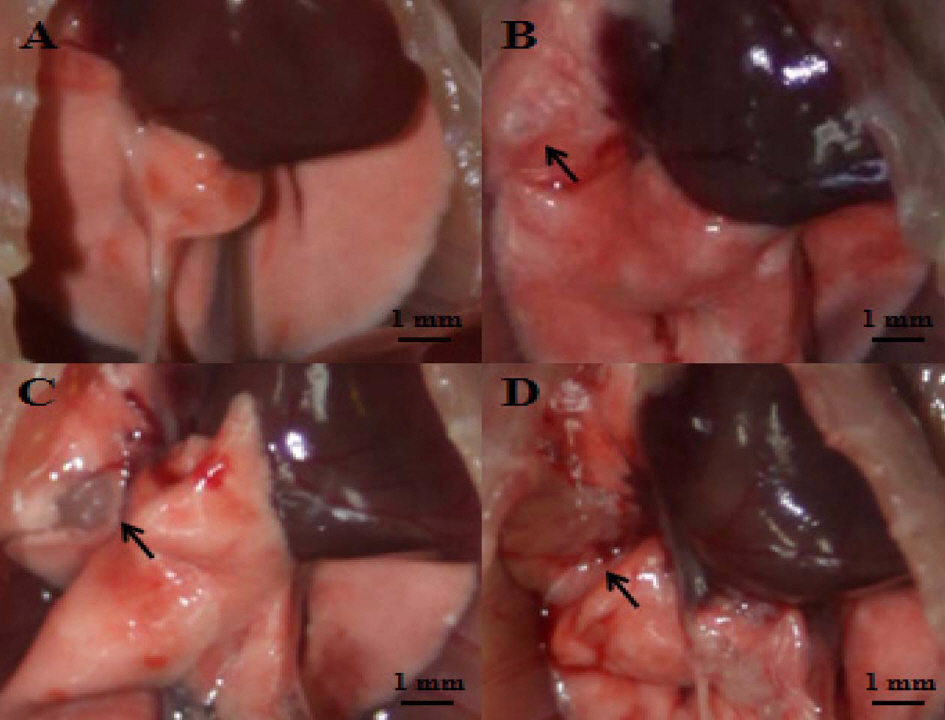
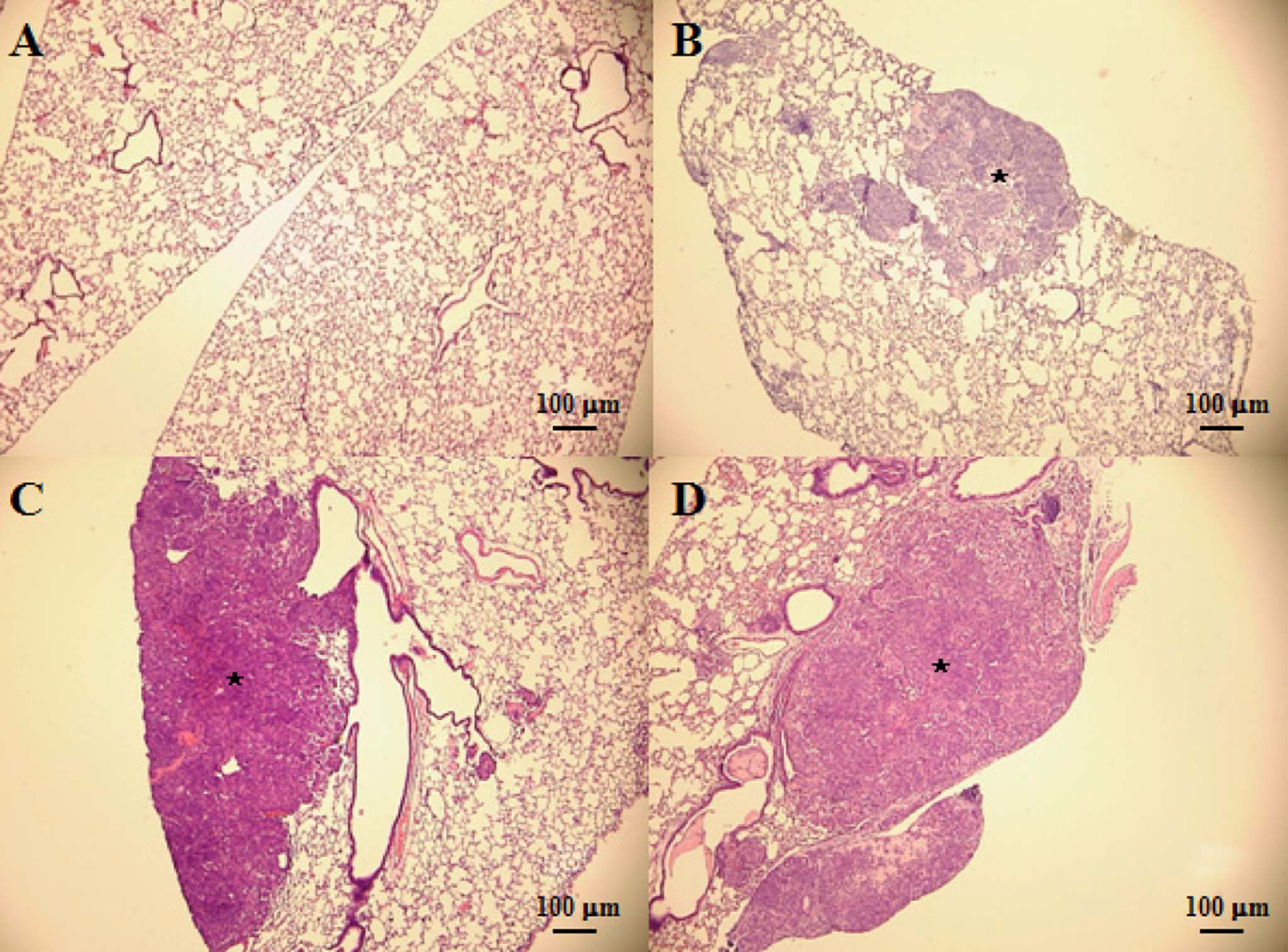
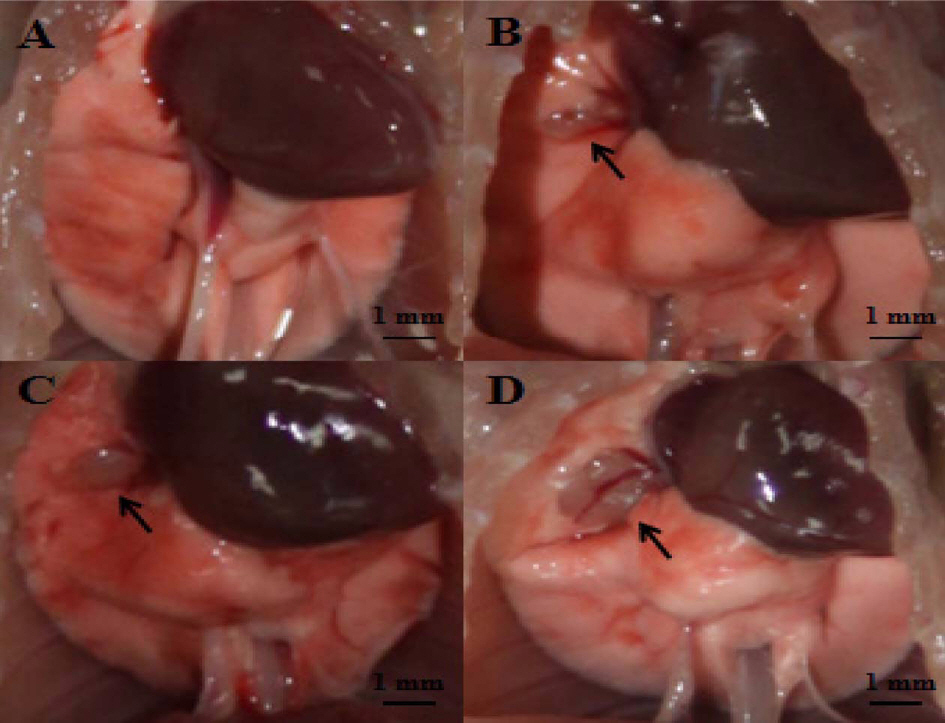
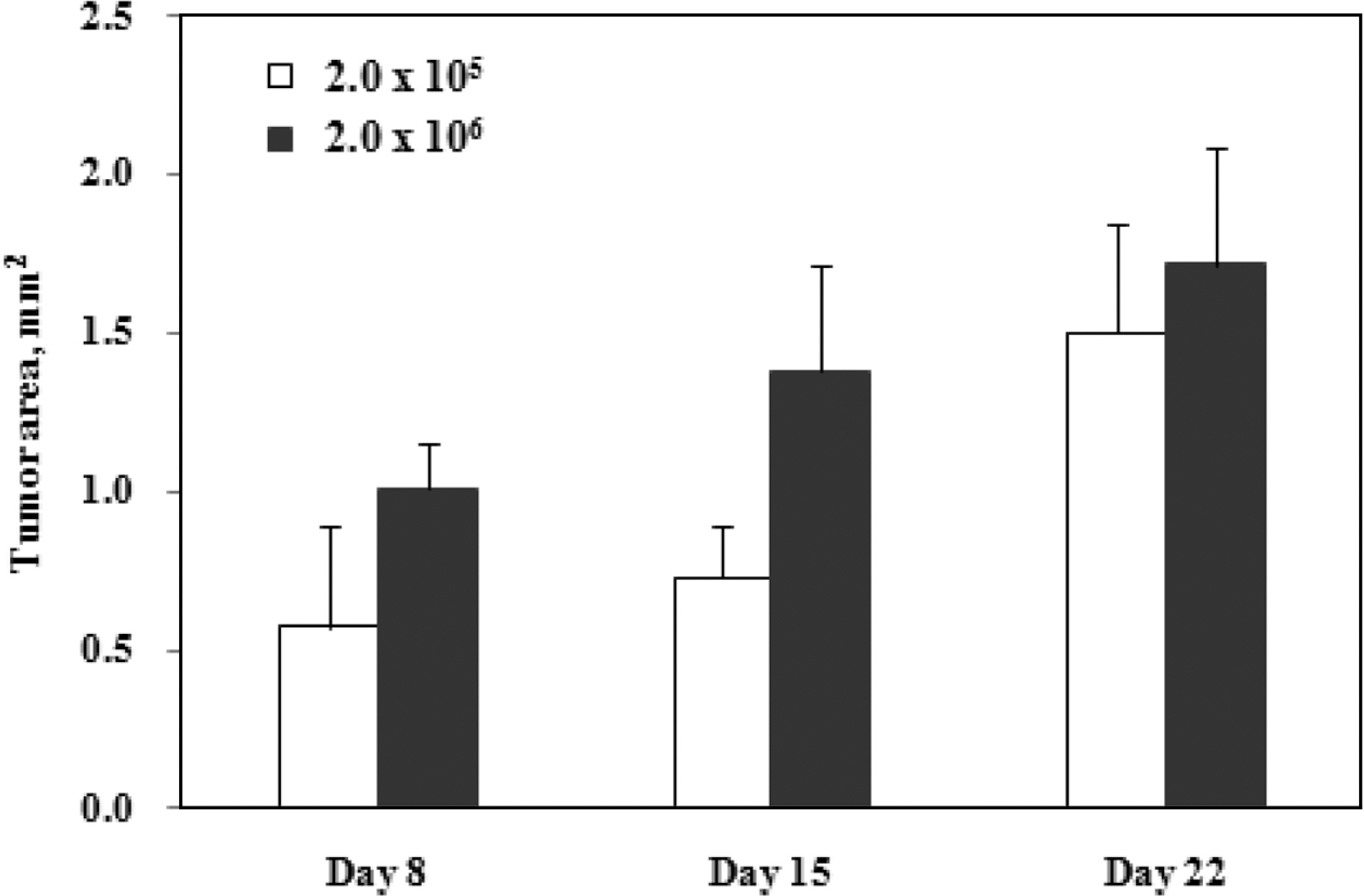
- The incidence rate of lung cancer is continually increasing, and lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Nevertheless, few therapeutic methods are available for lung cancer. Therefore, establishing appropriate lung cancer animal models is important to investigate mechanisms and to evaluate new drugs for lung cancer. In the present study, we transplanted non-small cell lung cancer A549 human adenocarcinoma cells (2x10(4), 2.0x10(5), and 2.0x10(6) cells) into the right lobe of BALB/c nude mice via the intercostal space to develop an orthotopic lung cancer animal model that is minimally invasive and similar to human lung cancer. We then investigated the incidence rate and severity of lung cancer according to the A549 cell number (2x10(4), 2.0x10(5), and 2.0x10(6) cells) and transplantation periods (4~23 days). Lung cancer development was confirmed with gross examination, which was supported by histopathological examination. These results indicate that the incidence rate and severity of lung cancer was increased depending on the number of transplanted cells and transplantation period which the cell number and duration are increasing risk of lung cancer. Thus, this study can provide appropriate reference data to develop an orthotopic lung cancer animal model using the non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell line for researching mechanisms and evaluating candidate drugs, including various approaches for treating lung cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
Cai, K.X., Tse, L.Y., Leung, C., Tam, P.K., Xu, R. and Sham, M.H. (. 2008. ). Suppression of lung tumor growth and metastasis in mice by adeno-associated virus-mediated expression of vasostatin. Clin. Cancer Res. 14(3):939–949.Colon, J., Basha, M.R., Madero-Visbal, R., Konduri, S., Baker, C.H., Herrera, L.J., Safe, S., Sheikh-Hamad, D., Abudayyeh, A., Alvarado, B. and Abdelrahim, M. (. 2009. ). Tolfenamic acid decreases c-Met expression through Sp proteins degradation and inhibits lung cancer cells growth and tumor formation in orthotopic mice. Invest. New Drugs. Epub ahead of print Cui, Z.Y., Ahn, J.S., Lee, J.Y., Kim, W.S., Lim, H.Y., Jeon, H.J., Suh, S.W., Kim, J.H., Kong, W.H., Kang, J.M., Nam, H. and Park, K. (2006) Mouse orthotopic lung cancer model induced by PC14PE6. Cancer Res. Treat. 38(4):234–239.Doki, Y., Murakami, K., Yamaura, T., Sugiyama, S., Misaki, T. and Saiki, I. (. 1999. ). Mediastinal lymph node metastasis model by orthotopic intrapulmonary implantation of Lewis lung carcinoma cells in mice. Br. J. Cancer. 79(7–8):1121–1126.Goto, H., Yano, S., Zhang, H., Matsumori, Y., Ogawa, H., Blakey, D.C. and Sone, S. (. 2002. ). Activity of a new vascular targeting agent, ZD6126, in pulmonary metastases by human lung adenocarcinoma in nude mice. Cancer Res. 62(13):3711–3715.Hassid, Y., Furman-Haran, E., Margalit, R., Eilam, R. and Degani, H. (. 2006. ). Noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging of transport and interstitial fluid pressure in ectopic human lung tumors. Cancer Res. 66(8):4159–4166.Hoffman, P.C., Mauer, A.M. and Vokes, E.E. (. 2000. ). Lung cancer. Lancet. 355(9202):479–485.Jemal, A., Siegel, R., Ward, E., Murray, T., Xu, J., Smigal, C. and Thun, M.J. (. 2006. ). Cancer statistics. CA Cancer. J. Clin. 56:106–130.Kang, Y., Omura, M., Suzuki, A., Oka, T., Nakagami, Y., Cheng, C., Nagashima, Y. and Inoue, T. (. 2006. ). Development of an orthotopic transplantation model in nude mice that simulates the clinical features of human lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 97(10):996–1001.Koizumi, K., Kozawa, Y., Ohashi, Y., Nakamura, E.S., Aozuka, Y., Sakurai, H., Ichiki, K., Doki, Y., Misaki, T. and Saiki, I. (. 2007. ). CCL21 promotes the migration and adhesion of highly lymph node metastatic human non-small cell lung cancer Lu-99 in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 17(6):1511–1516.Korea National Statistical Office. (. 2008. ). 2007 Death and the cause of death statistical result. pp.13–14. Korea Development Institute, Seoul.Kraus-Berthier, L., Jan, M., Guilbaud, N., Naze, M., Pierré, A. and Atassi, G. (. 2000. ). Histology and sensitivity to anticancer drugs of two human non-small cell lung carcinomas implanted in the pleural cavity of nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 6(1):297–304.Määttä, A.M., Mäkinen, K., Ketola, A., Liimatainen, T., Yongabi, F.N., Vähä-Koskela, M., Pirinen, R., Rautsi, O., Pellinen, R., Hinkkanen, A. and Wahlfors, J. (. 2008. ). Replication competent Semliki Forest virus prolongs survival in experimental lung cancer. In.t. J. Cancer. 123(7):1704–1711.Manzotti, C., Audisio, R.A. and Pratesi, G. (. 1993. ). Importance of orthotopic implantation for human tumors as model systems: relevance to metastasis and invasion. Clin Exp Metastasis. 11(1):5–14.Mathieu, A., Remmelink, M., D'Haene, N., Penant, S., Gaussin, J.F., Van Ginckel, R., Darro, F., Kiss, R. and Salmon, I. (. 2004. ). Development of a chemoresistant orthotopic human nonsmall cell lung carcinoma model in nude mice: analyses of tumor heterogenity in relation to the immunohistochemical levels of expression of cyclooxygenase-2, ornithine decarboxylase, lung-related resistance protein, prostaglandin E synthetase, and glutathione-S-transferase-alpha (GST)-alpha, GST-mu, and GST-pi. Cancer. 101(8):1908–18.Mazieres, J., Antonia, T., Daste, G., Muro-Cacho, C., Berchery, D., Tillement, V., Pradines, A., Sebti, S. and Favre, G. (. 2004. ). Loss of RhoB expression in human lung cancer progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 10(8):2742–2750.McLemore, T.L., Liu, M.C., Blacker, P.C., Gregg, M., Alley, M.C., Abbott, B.J., Shoemaker, R.H., Bohlman, M.E., Litterst, C.C. and Hubbard, W.C. (. 1987. ). Novel intrapulmonary model for orthotopic propagation of human lung cancers in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 47(19):5132–5140.Mijatovic, T., Mathieu, V., Gaussin, J.F., De Nève, N., Ribaucour, F., Van Quaquebeke, E., Dumont, P., Darro, F. and Kiss, R. (. 2006. ). Solitary lung tumors and their spontaneous metastasis in athymic nude mice orthotopically implanted with human non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia. 8(5):402–412.Mijatovic, T., Op De Beeck, A., Van Quaquebeke, E., Dewelle, J., Darro, F., de Launoit, Y. and Kiss, R. (. 2006. ). The cardenolide UNBS1450 is able to deactivate nuclear factor kappaB-mediated cytoprotective effects in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5(2):391–399.Ministry of Health and Welfare. (. 2009. ). Annual report of national cancer registration project; 2007 cancer incidence, 2007 cancer prevalence, 1993–2007 present condition of cancer survival. pp.17–20.Onn, A., Isobe, T., Itasaka, S., Wu, W., O'Reilly, M.S., Ki Hong, W., Fidler, I.J. and Herbst, R.S. (. 2003. ). Development of an orthotopic model to study the biology and therapy of primary human lung cancer in nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 9(15):5532–5539.Stathopoulos, G.T., Sherrill, T.P., Cheng, D.S., Scoggins, R.M., Han, W., Polosukhin, V.V., Connelly, L., Yull, F.E., Fingleton, B. and Blackwell, T.S. (. 2007. ). Epithelial NF-kappaB activation promotes urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 104(47):18514–18519.Tian, Y., Klegerman, M.E. and Hickey, A.J. (. 2004. ). Evaluation of microparticles containing doxorubicin suitable for aerosol delivery to the lungs. PDA. J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 58(5):266–275.Wakelee, H.A., Bernardo, P., Johnson, D.H. and Schiller, J.H. (. 2006. ). Changes in the natural history of nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC)–comparison of outcomes and characteristics in patients with advanced NSCLC entered in Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trials before and after 1990. Cancer. 106(10):2208–2217.Yamaura, T., Murakami, K., Doki, Y., Sugiyama, S., Misaki, T., Yamada, Y. and Saiki, I. (. 2000. ). Solitary lung tumors and their spontaneous metastasis in athymic nude mice orthotopically implanted with human non-small cell lung cancer. Neoplasia. 2(4):315–324.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mouse Orthotopic Lung Cancer Model Induced by PC14PE6
- Metastatic Model of Human Gastric Cancer by Orthotopic Transplantation
- An orthotopic nude mouse model of tongue carcinoma
- Development of Animal Model for Orthotopic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Nude Rat
- Maspin Suppresses Survival of Lung Cancer Cells through Modulation of Akt Pathway