J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2008 Feb;43(1):43-49. 10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.43.
Operative Treatment for Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcer: Usefulness of V-Y Advancement Flap for Unhealing Plantar Ulcer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea. kjyos@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2106415
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.43
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: This study examined the results of a single or double V-Y advancement flap, which was found to be technically simple for the management of chronic plantar ulcer in patients with neuropathic diabetic foot.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2004 to December 2005, 29 patients who were hospitalized for the management of a neuropathic diabetic foot plantar ulcer were examined. All patients underwent single- or double-V-Y advancement flap for the management of the ulceration. Hematological, hemodynamic, diabetic, bacteriologic, and radiological tests wereperformed prior to surgery. The condition of the wound was checked during surgery, and the healing rate, healing time and recurrence during the follow-up examinations were evaluated after surgery.
RESULTS
The mean age of the patients was 53.4 years (36-69). The plantar ulcers were the most commonly found in the forefoot area (12 cases). Nine cases showed ulcers in the hindfoot area, 6 cases were found are in the lateral foot area, and 2 cases were identified in the medial foot area. The area covered with the V-Y advancement flap averaged 2.05 cm(2) (0.8-3.9). The mean healing time of the wound was 4.7 weeks (3-8). One day after surgery, there were 7 cases of partial circulation disturbance that were managed with a partial stitch out and secondary intension wound healing. There were 5 cases of recurrence of the wound.
CONCLUSION
A V-Y advancement flap to manage chronic diabetic plantar ulcers can produce excellent or good results. However, a high incidence of delay in healing of the surgical wound can be expected, and a longer period is needed to protect the wound comparing with normal patients.
MeSH Terms
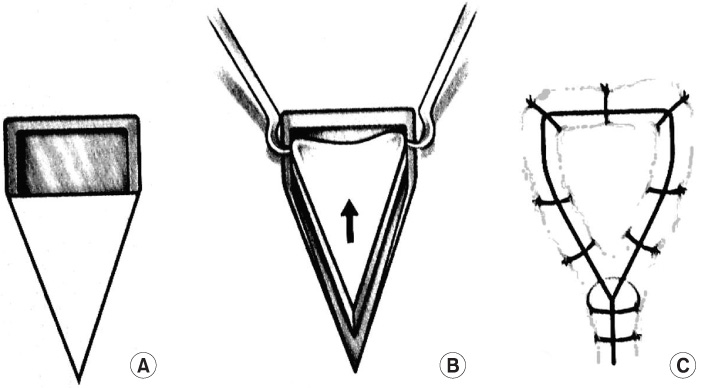
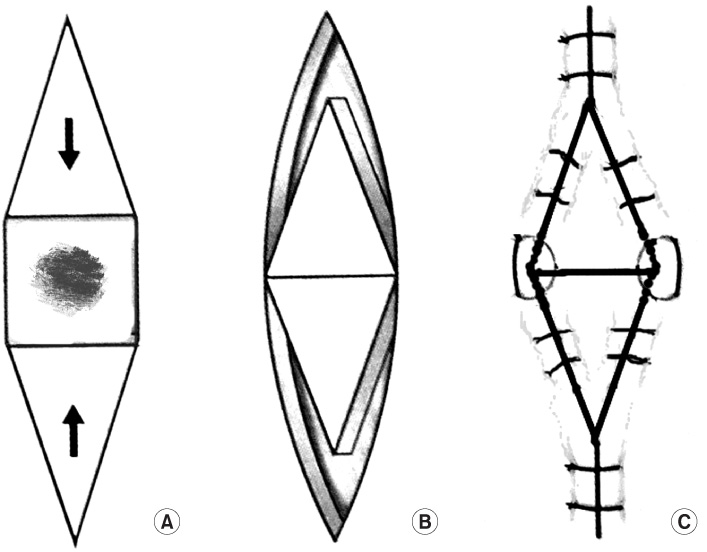
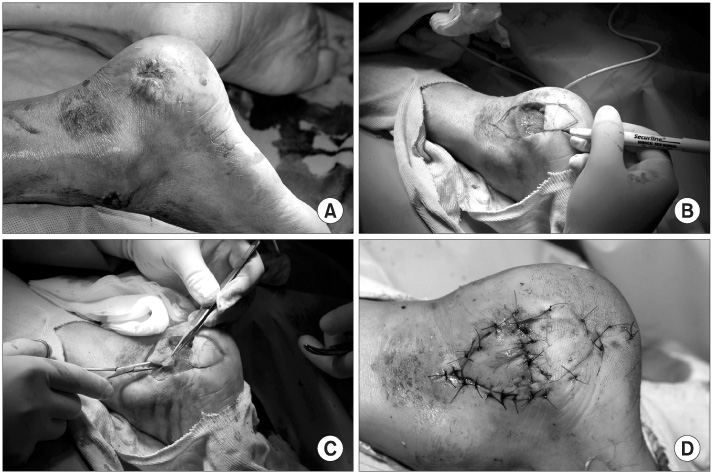
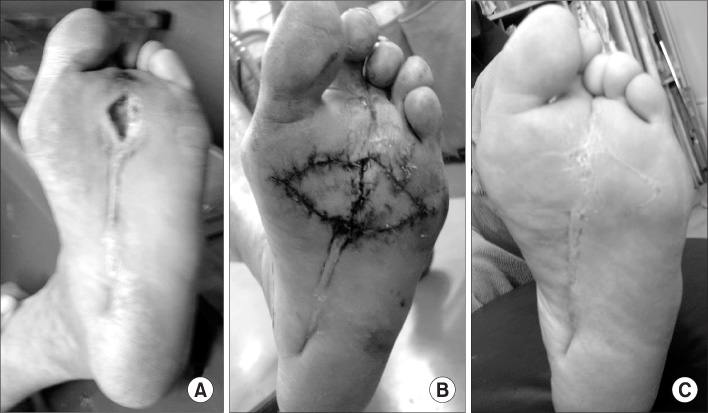
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abbott CA, Garrow AP, Carrington AL, et al. Foot ulcer risk is lower in South-Asian and African-Caribbean compared with European diabetic patients in the U.K.: the North-West diabetes foot care study. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1869–1875.2. American Diabetic Association. Consensus Development Conference on Diabetic Foot Wound Care: 7-8 April 1999, Boston, Massachusetts. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:1354–1360.3. Armstrong DG, Nguyen HC, Lavery LA, van Schie CH, Boulton AJ, Harkless LB. Off-loading the diabetic foot wound: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2001. 24:1019–1022.4. Armstrong DG, Lavery LA, Kimbriel HR, Nixon BP, Boulton AJ. Activity patterns of patients with diabetic foot ulceration: patients with active ulceration may not adhere to a standard pressure off-loading regimen. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:2595–2597.5. Atasoy E, IoaKimidis E, Kasdan ML, Kutz JE, Kleinert HE. Reconstruction of the amputated finger tip with a triangular volar flap. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970. 52:921–926.
Article6. Attinger C. soft tissue coverage for lower-extremity trauma. Orthop Clin North Am. 1995. 26:295–334.7. Bergin SM, Wraight P. Silver based wound dressings and topical agents for treating diabetic foot ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006. 25:CD005082.
Article8. Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, Stensel V, Forsberg RC, Davignon DR, Smith DG. A prospective study of risk factors for diabetic foot ulcer The Seattle Diabetic Foot Study. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:1036–1042.
Article9. Brodsky JW. Mann RA, Coughlin MJ, editors. The diabetic foot. Surgery of the foot and ankle. 1993. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby, Inc;877–958.10. Cavanagh PR, Lipsky BA, Bradbury AW, Botek G. Treatment for diabetic foot ulcers. Lancet. 2005. 366:1725–1735.
Article11. Colen LB, Replogle SL, Mathes SJ. The V-Y plantar flap for reconstruction of the forefoot. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1988. 81:220–228.
Article12. Dockery GL, Christensen JC. Principle and descriptions of design of skin flaps for use on the lower extremity. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 1986. 3:563–577.13. Hong JP, Jung HD, Kim YW. Recombinant human epidermal growth factor (EGF) to enhance healing for diabetic foot ulcers. Ann Plast Surg. 2006. 56:394–398.
Article14. Ledoux WR, Shofer JB, Smith DG, et al. Relationship between foot type, foot deformity, and ulcer occurrence in the high-risk diabetic foot. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2005. 42:665–672.
Article15. Manson PN, Anthenelli RM, Im MJ, Bulkley GB, Hoopes JE. The role of oxygen-free radicals in ischemic tissue injury in island skin flaps. Ann Surg. 1983. 198:87–90.
Article16. Maruyama Y, Iwahira Y, Ebihara H. V-Y advancement flaps in the reconstruction of skin defect of the posterior heel and ankle. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990. 85:759–764.17. Mueller MJ, Diamond JE, Sinacore DR, et al. Total contact casting in treatment of diabetic plantar ulcers. Controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 1989. 12:384–388.
Article18. Myerson M, Papa J, Eaton K, Wilson K. The total-contact cast for management of neuropathic plantar ulceration of the foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:261–269.
Article19. Pua BB, Muhs BE, Maldonado T, Ben-Arie E, Sheehan P, Gagne PJ. Total-contact casting as an adjunct to promote healing of pressure ulcers in amputees. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2006. 40:135–140.
Article20. Roeckl-Wiedmann I, Bennett M, Kranke P. Systematic review of hyperbaric oxygen in the management of chronic wounds. Br J Surg. 2005. 92:24–32.
Article21. Saap LJ, Donohue K, Falanga V. Clinical classification of bioengineered skin use and its correlation with healing of diabetic and venous ulcers. Dermatol Surg. 2004. 30:1095–1100.
Article22. Singh N, Armstrong DG, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA. 2005. 293:217–228.
Article23. Townsand CM, Beauchamp RD, Evans BM, et al. Sabiston text book of surgery. 2004. 17th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders, Inc;2184.24. Willrich A, Pinzur M, McNeil M, Juknelis D, Lavery L. Health related quality of life, cognitive function, and depression in diabetic patients with foot ulcer or amputation. A preliminary study. Foot Ankle Int. 2005. 26:128–134.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Significance of Plantar Pressure Measurement in Diabetic Patients
- Surgical Treatment of Diabetic Foot Disease
- Clinical Application of Digital Infrared Thermographic Imaging for the Prediction of Foot Ulcer Development in Diabetic Patients
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer Recording Form Incorporating the Concepts of Wound Care and Treatment Plan
- Reconstruction of Diabetic Foot Ulcers by Regional Flap Surgery