Korean J Schizophr Res.
2015 Oct;18(2):86-90. 10.16946/kjsr.2015.18.2.86.
A Case Report: Irbesartan and Naltrexone Treatment of Polydipsia in a Patient with Schizophrenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Korea University College of Medicine, Ansan Hospital, Ansan, Korea.
- 2Department of Psychiatry, Korea University College of Medicine, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. gurokim@gmail.com
- KMID: 2103937
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16946/kjsr.2015.18.2.86
Abstract
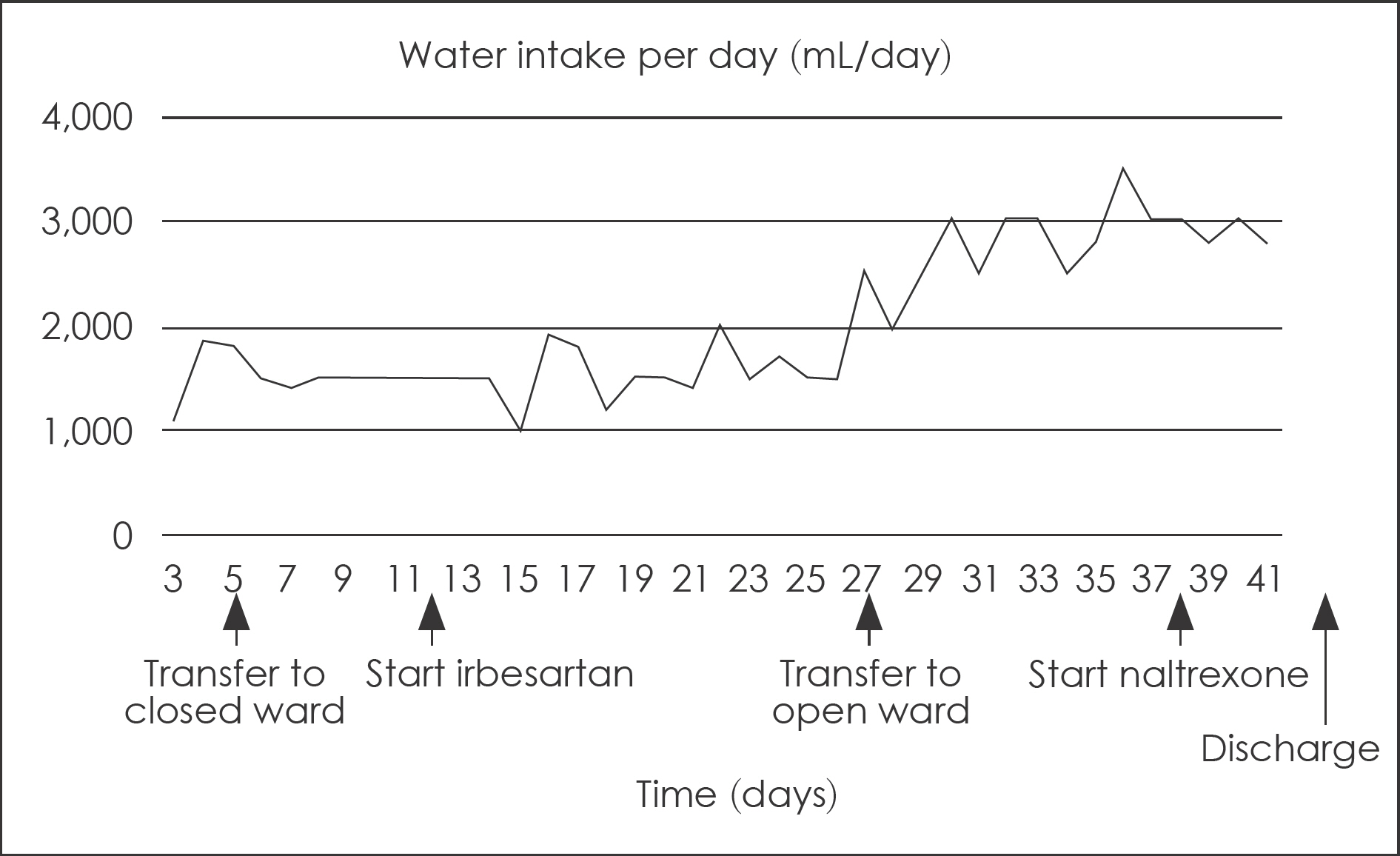
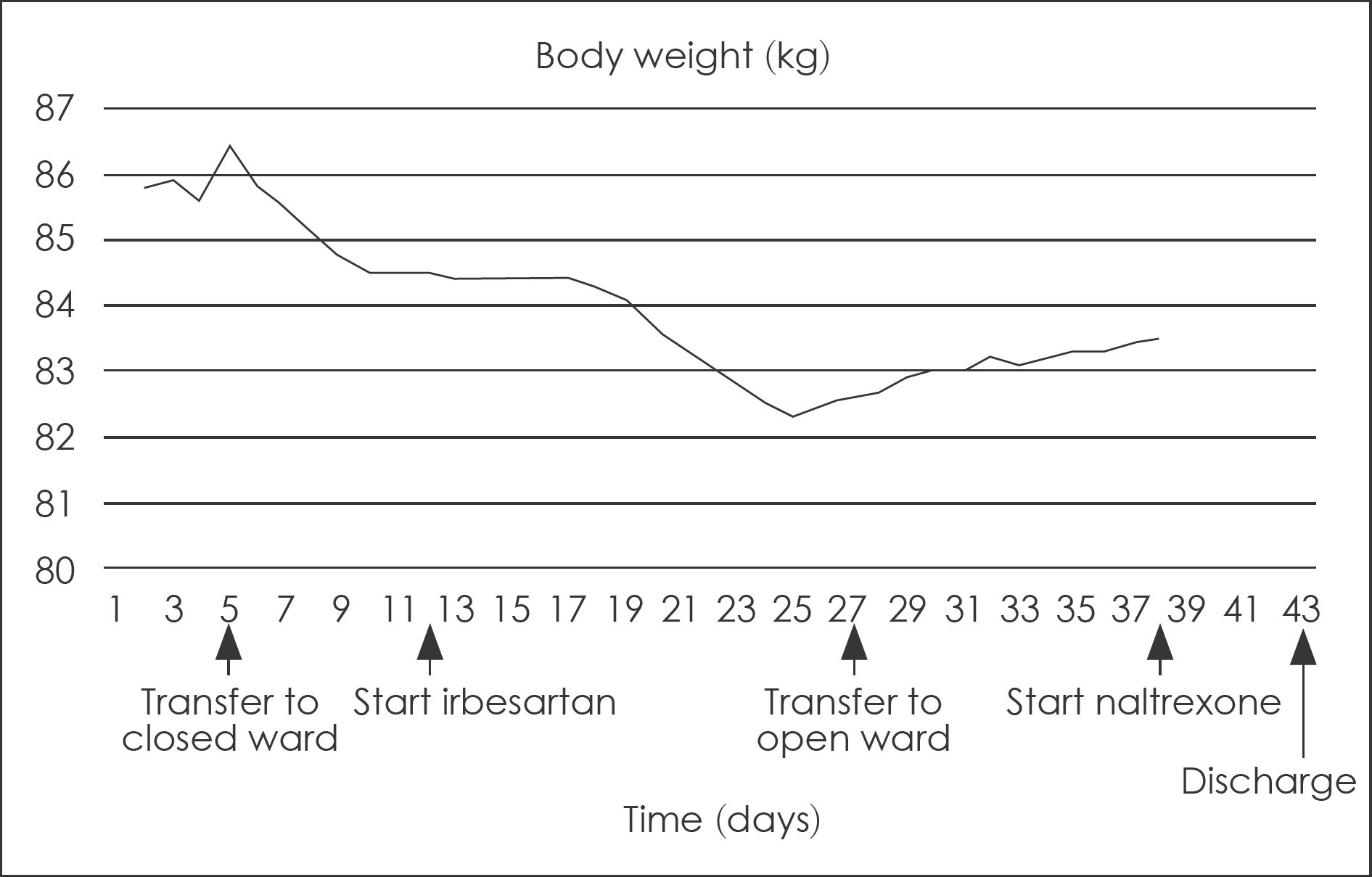
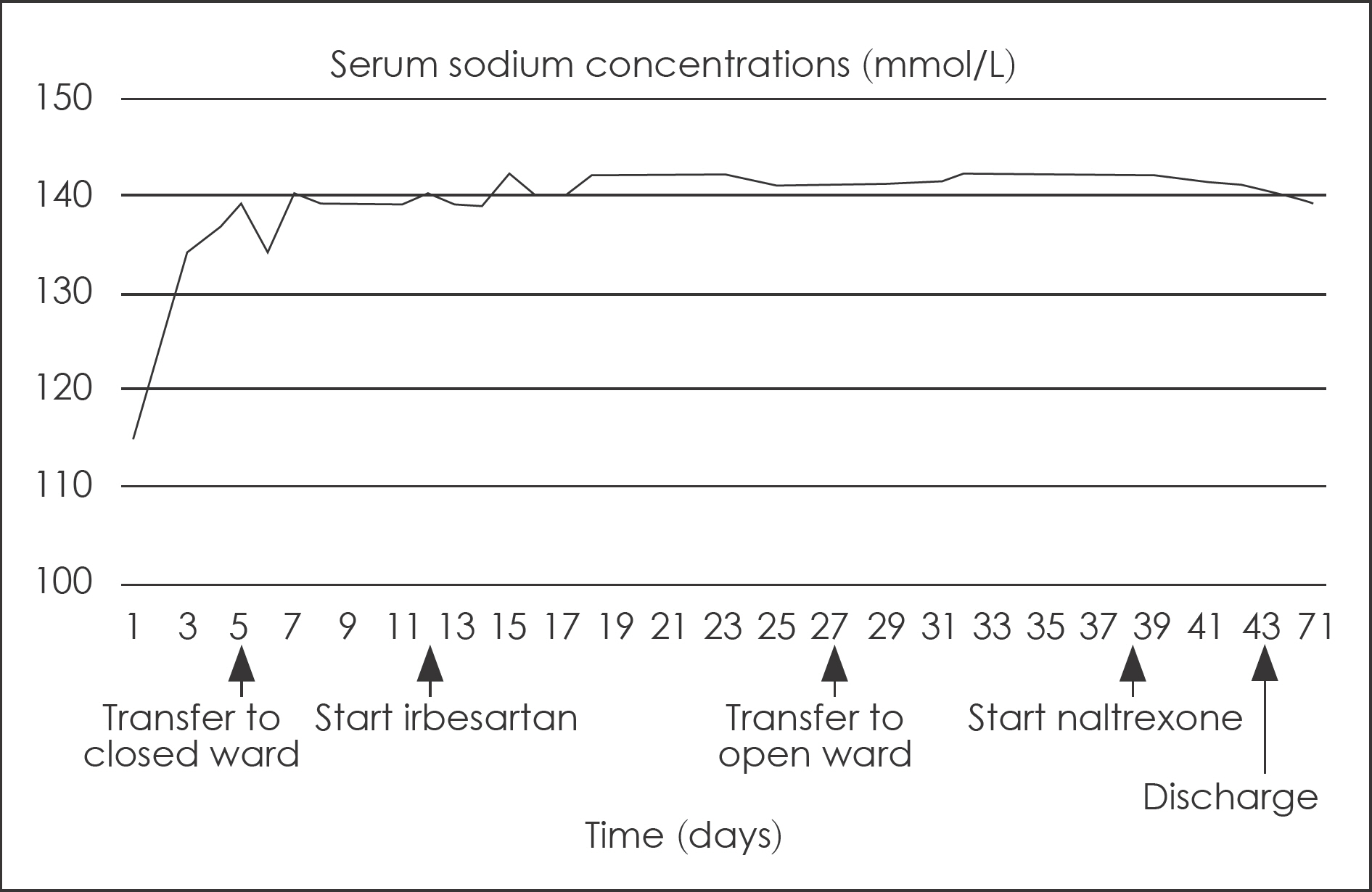
- Polydipsia in schizophrenic patients is not uncommon, but a frequently underdiagnosed condition. The etiology of polydipsia remains unclear, and its complications can be life-threatening, while often being difficult to manage it. We report a case of a successfully treated chronic schizophrenic patient with polydipsia. The patient was male, 47-year-old, suffering 27-years of residual schizophrenia who had been consuming more than 10 L of water per day, and is complicated by hyponatremia. He was treated with irbesarten 300 mg and naltrexone 50 mg in the setting of closed ward. He consumed less than 3.5 L of water per day and serum sodium levels seemed to be stable following discharge from the closed ward. We suggest that irbesartan and naltrexone may have beneficial effects for treating polydipsia, and future prospective and well-controlled studies are to be performed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Costanzo ES, Antes LM, Christensen AJ. Behavioral and medical treatment of chronic polydipsia in a patient with schizophrenia and diabetes insipidus. Psychosom Med. 2004; 66:283–286.
Article2). Goldman MB. A rational approach to disorders of water balance in psychiatric patients. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1991; 42:488–494.
Article3). Brown RP, Kocsis JH, Cohen SK. Delusional depression and inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Biol Psychiatry. 1983; 18:1059–1063.4). Raskind MA, Courtney N, Murburg MM, Backus FI, Bokan JA, Ries RK, et al. Antipsychotic drugs and plasma vasopressin in normals and acute schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry. 1987; 22:453–462.
Article5). Raskind MA, Orenstein H, Christopher TG. Acute psychosis, increased water ingestion, and inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Am J Psychiatry. 1975; 132:907–910.6). Raskind MA, Weitzman RE, Orenstein H, Fisher DA, Courtney N. Is antidiuretic hormone elevated in psychosis? A Pilot Study. Biol Psychiatry. 1978; 13:385–390.7). Goldman MB, Luchins DJ, Robertson GL. Mechanisms of altered water metabolism in psychotic patients with polydipsia and hyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 1988; 318:397–403.
Article8). de Leon J. Polydipsia–a study in a longterm psychiatric unit. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003; 253:37–39.9). Evenson RC, Jos CJ, Mallya AR. Prevalence of polydipsia among public psychiatric patients. Psychol Rep. 1987; 60:803–807.
Article10). Verghese C, de Leon J, Josiassen RC. Problems and progress in the diagnosis and treatment of polydipsia and hyponatremia. Schizophr Bull. 1996; 22:455–464.
Article11). Kwon MJ, Sim MY, Yim SJ, Lee HB, Lee JI. Polydipsia and associated factors in chronic schizophrenic patients. Korean J Schizophr Res. 2009; 12:63–68.12). Hoskins RG. Schizophrenia from the physiological point of view. Ann Intern Med. 1933; 7:445–456.
Article13). Hoskins RG. Sleeper FH. Organic functions in schizophrenia. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1933; 30:123–140.14). Barahal HS. Water intoxication in a mental case. Psychiatr Q. 1938; 12:761–771.
Article15). Bremner AJ, Regan A. Intoxicated by water. Polydipsia and water intoxication in a mental handicap hospital. Br J Psychiatry. 1991; 158:244–250.16). de Leon J, Verghese C, Tracy JI, Josiassen RC, Simpson GM. Polydipsia and water intoxication in psychiatric patients: a review of the epidemiological literature. Biol Psychiatry. 1994; 35:408–419.
Article17). Vieweg WVR. Overview of water balance in schizophrenia. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press;1996. p. 1–42.18). Illowsky BP, Kirch DG. Polydipsia and hyponatremia in psychiat ric patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1988; 145:675–683.19). Vieweg WV, David JJ, Rowe WT, Wampler GJ, Burns WJ, Spradlin WW. Death from self-induced water intoxication among patients with schizophrenic disorders. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1985; 173:161–165.
Article20). Vieweg V, Rowe W, David J, Spradlin W. Hyposthenuria as a marker for self-induced water intoxication and schizophrenic disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 1984; 141:1258–1260.21). Lee HS, Kwon KY, Alphs LD, Meltzer HY. Effect of clozapine on psychogenic polydipsia in chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1991; 11:222–223.
Article22). Spears NM, Leadbetter RA, Shutty MS Jr. Clozapine treatment in polydipsia and intermittent hyponatremia. J Clin Psychiatry. 1996; 57:123–128.23). Hirayama T, Kita T, Ogawa Y, Ohsawa H, Yamashita M, Nakashima T, et al. Effect of chronic treatment with haloperidol on vasopressin release and behavioral changes by osmotic stimulation of the supraoptic nucleus. Life Sci. 2001; 69:2147–2156.
Article24). de Leon J, Verghese C, Stanilla JK, Lawrence T, Simpson GM. Treatment of polydipsia and hyponatremia in psychiatric patients. Can clozapine be a new option? Neuropsychopharmacology. 1995; 12:133–138.
Article25). Fuller MA, Jurjus G, Kwon K, Konicki PE, Jaskiw GE. Clozapine reduces water-drinking behavior in schizophrenic patients with polydipsia. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1996; 16:329–332.
Article26). Kruse D, Pantelis C, Rudd R, Quek J, Herbert P, McKinley M. Treatment of psychogenic polydipsia: comparison of risperidone and olanzapine, and the effects of an adjunctive angiotensin-II receptor blocking drug (irbesartan). Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2001; 35:65–68.
Article27). Drew L. Clozapine and agranulocytosis: re-assessing the risks. Australas Australas Psychiatry. 2013; 21:335–337.
Article28). Fitzsimons JT, Setler PE. The relative importance of central nervous catecholaminergic and cholinergic mechanisms in drinking in response to antiotensin and other thirst stimuli. J Physiol. 1975; 250:613–631.
Article29). Goldstein JA. Captopril in the treatment of psychogenic polydipsia. J Clin Psychiatry. 1986; 47:99.30). Lawson WB, Williams B, Pasion R. Effects of captopril on psychosis and disturbed water regulation. Psychopharmacol Bull. 1988; 24:176–178.31). Blair-West JR. Thirst induced by increasing brain sodium concentration is mediated by brain angiotensin. Brain Res. 1994; 637:335–338.
Article32). Ukai M, Holtzman SG. Effects of intrahypothalamic administration of opioid peptides selective for mu-, kappa, and delta-receptors on different schedules of water intake in the rat. Brain Res. 1988; 459:275–281.33). Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Nishikawa M, Koga I, Uchida Y. Naloxone attenuates drinking behavior in a schizophrenic patient displaying self-induced water intoxication. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1992; 15:310–314.
Article34). Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Nishikawa M, Koga I, Uchida Y. Decreased polydipsia in schizophrenic patients treated with naloxone. Am J Psychiatry. 1994a; 151:947.35). Nishikawa T, Tsuda A, Tanaka M, Nishikawa M, Koga I, Uchida Y. Naloxone attenuates drinking behavior in psychiatric patients displaying self-induced water intoxication. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1994b; 18:149–153.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Clozapine on Schizophrenia with Polydipsia: Two Cases Experience
- Naltrexone-associated Visual Hallucinations: A Case Report
- Hyponatremia with Neurological Symptom in Patients with Chronic Schizophrenia : Five Cases
- Thiazide-induced Electrolyte Disturbance with Altered Mental Status
- A Case of Prurigo Nodularis Treated with Narrow-band UVB and Naltrexone