J Korean Soc Hypertens.
2011 Mar;17(1):28-36. 10.5646/jksh.2011.17.1.28.
Effects of Bosentan Treatment on Angiotensin Converting Enzyme in Monocrotaline Induced Pulmonary Hypertension Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Deparment of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hongym@chollian.net
- KMID: 2099899
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5646/jksh.2011.17.1.28
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pulmonary artery hypertension is characterized by persistent increase of vascular resistance, and is associated with right ventricle failure. We investigated changes of plasma renin, serum aldosterone, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) concentrations, ACE gene expressions and protein contents after bosentan treatment.
METHODS
Six-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups: control (C) group, monocrotaline (M) group, and bosentan (B) group. Groups M and B were subcutaneously administered with 60 mg/kg of monocrotaline. In group B, 20 mg/kg/day of bosentan was administered by gavage twice a day. The rats were sacrificed after 1, 5, 7, 14, and 28 days. Changes of ACE gene expressions were analyzed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Also, plasma renin, serum aldosterone, and ACE levels were measured.
RESULTS
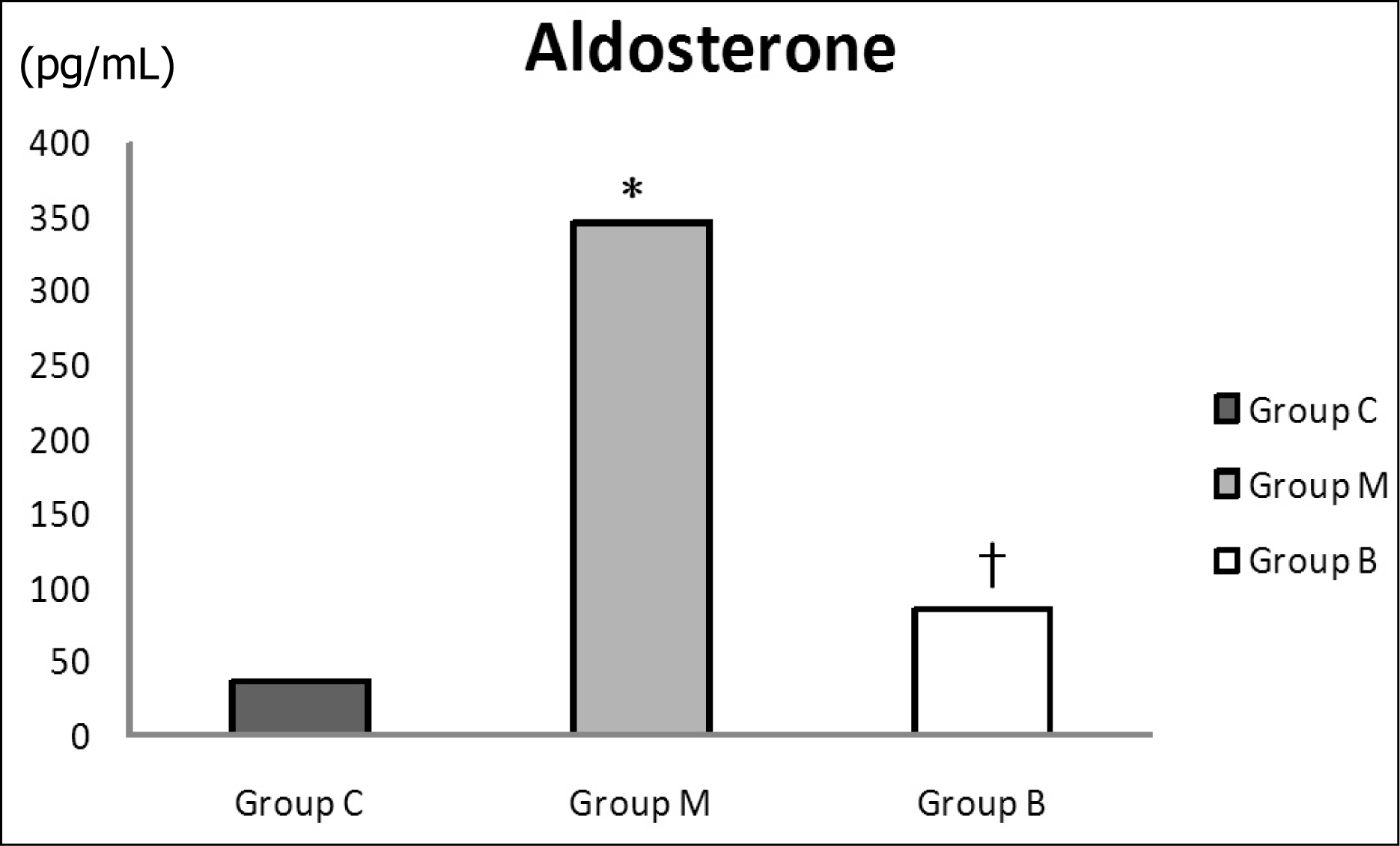
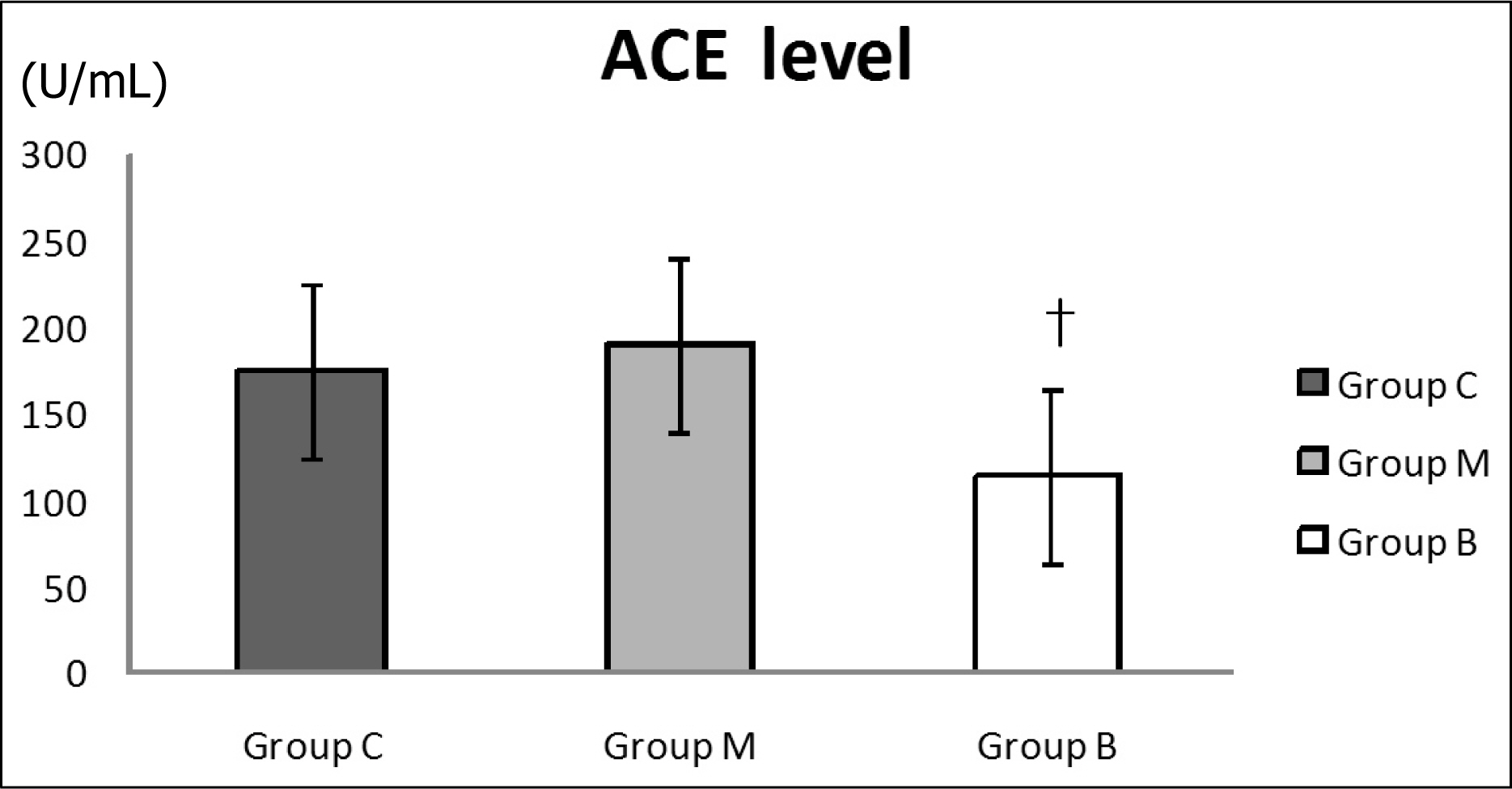
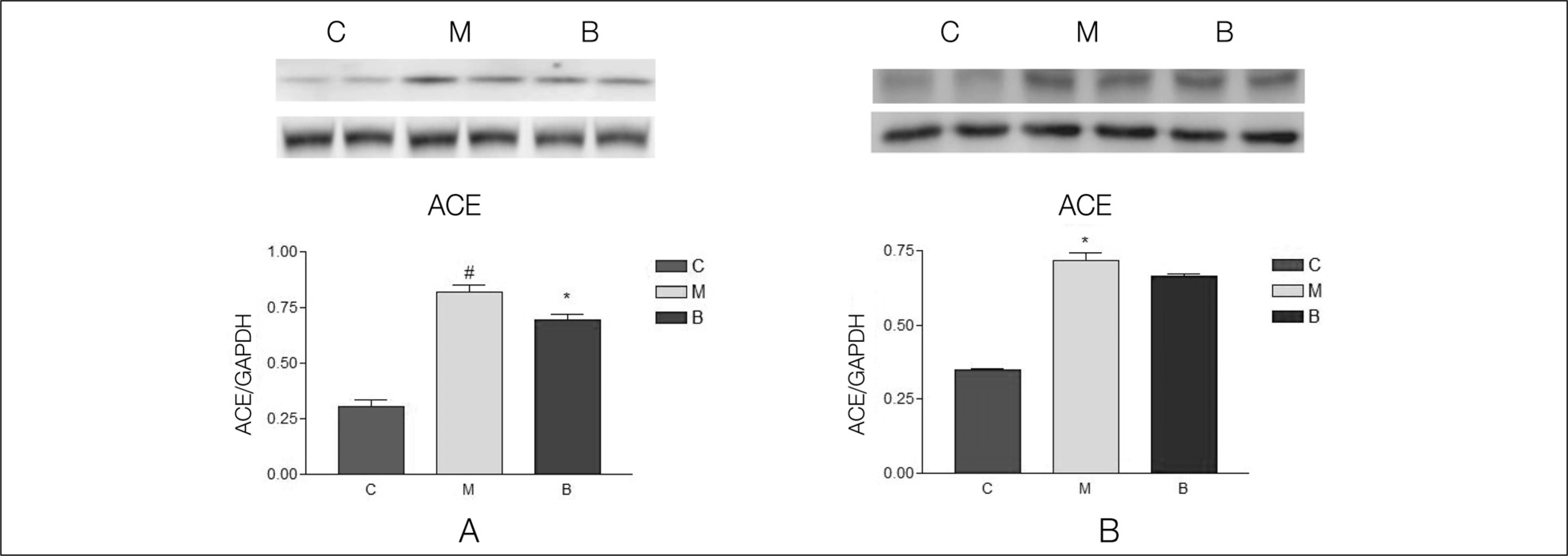
Serum aldosterone levels were significantly increased in group M compared with group C and significantly decreased after bosentan treatment on day 28. Serum ACE concentrations were significantly decreased compared with group M after bosentan treatment on day 28. Gene expressions of ACE were significantly increased in group M compared with group C on day 5 and significantly decreased after bosentan treatment on day 7 and 14. ACE protein contents significantly increased in group M compared with group C in week 2 and 4. It significantly decreased after bosentan treatment in week 2.
CONCLUSIONS
The renin-angiotensin system is associated with pulmonary artery hypertension. To investigate the effects of bosentan on the renin-angiotensin system in pulmonary artery hypertension, further studies on the effects of bosentan according to different doses are required in the future.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aldosterone
Angiotensins
Animals
Gene Expression
Heart Ventricles
Humans
Hypertension
Hypertension, Pulmonary
Male
Monocrotaline
Peptidyl-Dipeptidase A
Plasma
Pulmonary Artery
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Renin
Renin-Angiotensin System
Sulfonamides
Vascular Resistance
Aldosterone
Angiotensins
Monocrotaline
Peptidyl-Dipeptidase A
Renin
Sulfonamides
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Successful Delivery of a Woman with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Under Close Observation and without Medications
Ji Hoon Yang, Ji Yeon Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Dong Jin Song, Cheol Yoon Jeong, Hyun Ho Shin
J Korean Soc Hypertens. 2013;19(3):90-97. doi: 10.5646/jksh.2013.19.3.90.
Reference
-
References
1. Runo JR, Loyd JE. Primary pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 2003; 361:1533–44.
Article2. Chan SY, Loscalzo J. Pathogenic mechanisms of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008; 44:14–30.
Article3. Minamino T, Christou H, Hsieh CM, Liu Y, Dhawan V, Abraham NG, et al. Targeted expression of heme oxygenase-1 prevents the pulmonary inflammatory and vascular responses to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001; 98:8798–803.
Article4. Skeggs LT, Dorer FE, Levine M, Lentz KE, Kahn JR. The biochemistry of the renin-angiotensin system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1980; 130:1–27.
Article5. Turner AJ, Hooper NM. The angiotensin-converting enzyme gene family: genomics and pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2002; 23:177–83.
Article6. Studdy PR, Lapworth R, Bird R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme and its clinical significance–a review. J Clin Pathol. 1983; 36:938–47.
Article7. Orte C, Polak JM, Haworth SG, Yacoub MH, Morrell NW. Expression of pulmonary vascular angiotensin-converting enzyme in primary and secondary plexiform pulmonary hypertension. J Pathol. 2000; 192:379–84.
Article8. Cargill RI, Lipworth BJ. The role of the renin-angiotensin and natriuretic peptide systems in the pulmonary vasculature. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995; 40:11–8.
Article9. Dezso B, Nielsen AH, Poulsen K. Identification of renin in resident alveolar macrophages and monocytes: HPLC and immunohistochemical study. J Cell Sci. 1988; 91(Pt 1):155–9.
Article10. Ohkubo H, Nakayama K, Tanaka T, Nakanishi S. Tissue distribution of rat angiotensinogen mRNA and structural analysis of its heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1986; 261:319–23.
Article11. Andersen K. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in the elderly: rational use of aliskiren in managing hypertension. Clin Interv Aging. 2009; 4:137–51.
Article12. Ferreira AJ, Shenoy V, Yamazato Y, Sriramula S, Francis J, Yuan L, et al. Evidence for angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a therapeutic target for the prevention of pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 179:1048–54.
Article13. Wilson DW, Segall HJ, Pan LC, Lame MW, Estep JE.Morin D. Mechanisms and pathology of monocrotaline pulmonary toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1992. 22:307–25.14. Todd L, Mullen M, Olley PM, Rabinovitch M. Pulmonary toxicity of monocrotaline differs at critical periods of lung development. Pediatr Res. 1985; 19:731–7.
Article15. Weber C, Schmitt R, Birnboeck H, Hopfgartner G. van Marle SP, Peeters PA, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan in healthy human subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996; 60:124–37.16. Lim KA, Shim JY, Cho SH, Kim KC, Han JJ, Hong YM. Effect of endothelin receptor blockade on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:689–95.
Article17. Lim KA, Kim KC, Cho MS, Lee BE, Kim HS, Hong YM. Gene expression of endothelin-1 and endothelin receptor A on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats after bosentan treatment. Korean Circ J. 2010; 40:459–64.
Article18. Koo HS, Kim KC, Hong YM. Gene expressions of nitric oxide synthase and matrix metalloproteinase-2 in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats after bosentan treatment. Korean Circ J. 2011; 41:83–90.
Article19. Kuba K, Imai Y, Penninger JM. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in lung diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2006; 6:271–6.
Article20. Morrell NW, Morris KG, Stenmark KR. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin II in development of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1995; 269:H1186–94.
Article21. Kanazawa H, Okamoto T, Hirata K, Yoshikawa J. Deletion polymorphisms in the angiotensin converting enzyme gene are associated with pulmonary hypertension evoked by exercise challenge in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 162:1235–8.
Article22. RJ van Suylen, EF Wouters, HJ Pennings, EC Cheriex, PE van Pol, AW Ambergen, et al. The DD genotype of the angiotensin converting enzyme gene is negatively associated with right ventricular hypertrophy in male patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999; 159:1791–5.23. Kay JM, Keane PM, Suyama KL, Gauthier D. Angiotensin converting enzyme activity and evolution of pulmonary vascular disease in rats with monocrotaline pulmonary hypertension. Thorax. 1982; 37:88–96.
Article24. Lafranconi WM, Huxtable RJ. Changes in angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in lungs damaged by the pyrrolizidine alkaloid monocrotaline. Thorax. 1983; 38:307–9.
Article25. Molteni A, Ward WF, Ts’ao CH, Port CD, Solliday NH. Monocrotaline-induced pulmonary endothelial dysfunction in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984; 176:88–94.26. Cassis L, Shenoy U, Lipke D, Baughn J, Fettinger M, Gillespie M. Lung angiotensin receptor binding characteristics during the development of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997; 54:27–31.
Article27. Yamazato Y, Ferreira AJ, Hong KH, Sriramula S, Francis J, Yamazato M, et al. Prevention of pulmonary hypertension by Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 gene transfer. Hypertension. 2009; 54:365–71.
Article28. Jeffery TK, Wanstall JC. Pulmonary vascular remodeling: a target for therapeutic intervention in pulmonary hypertension. Pharmacol Ther. 2001; 92:1–20.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of endothelin receptor blockade on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats
- Gene Expression of Endothelin-1 and Endothelin Receptor A on Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats After Bosentan Treatment
- Angiotensin-(1-9) ameliorates pulmonary arterial hypertension via angiotensin type II receptor
- Effect of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors on Induced Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Activity in Rat Intestine
- Gene Expressions of Nitric Oxide Synthase and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats After Bosentan Treatment