J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Mar;64(3):285-288. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.3.285.
A Child Case of a Bilateral Hydatid of Morgagni with Unilateral Torsion Occurred
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital Bucheon, Korea. rad1995@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University Hospital Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2097952
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.3.285
Abstract
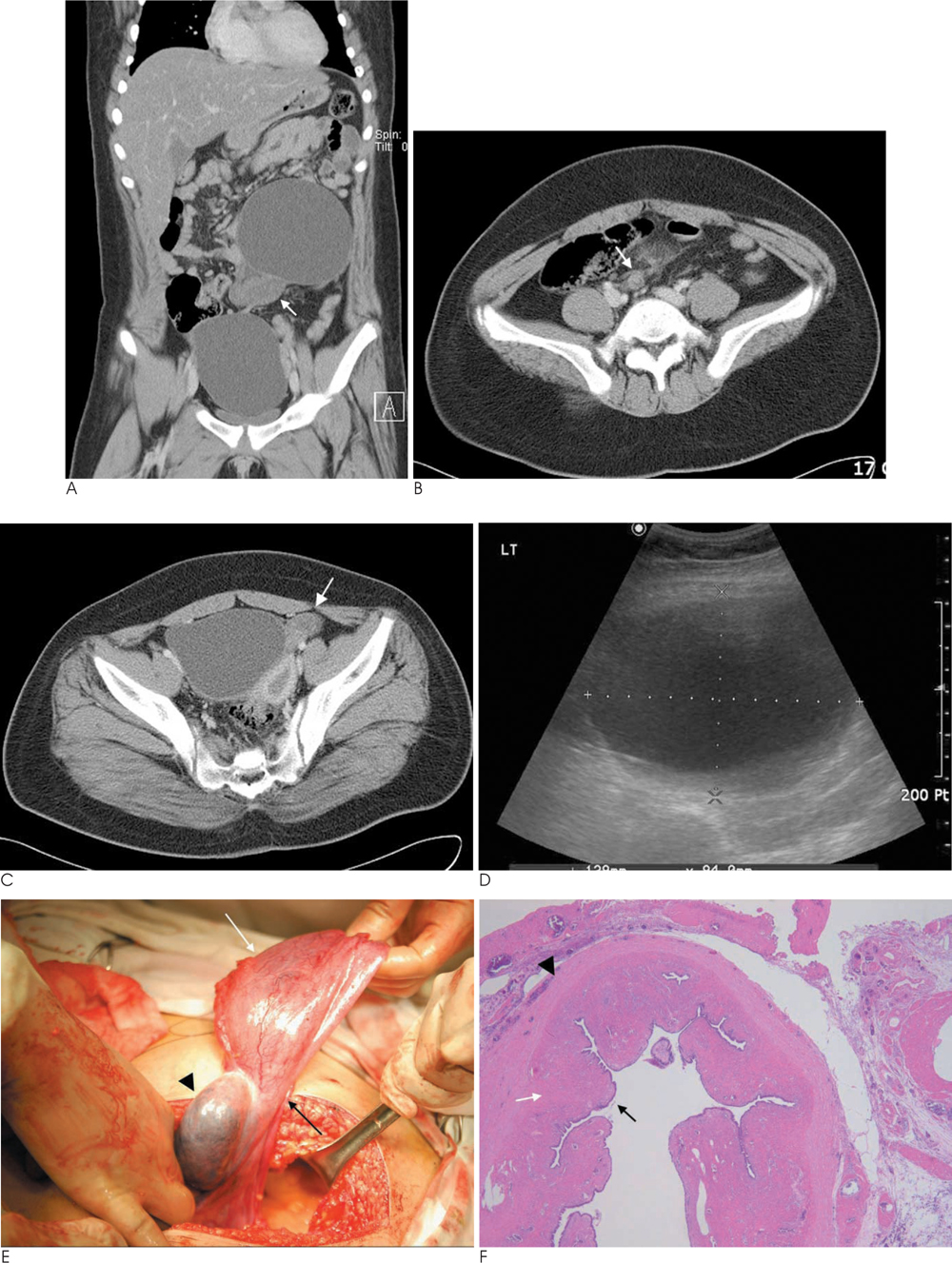
- Hydatids of Morgagni are benign, pedunculated cystic structures which originate from mullerian vestiges in the inferior aspect of the fallopian tube. They are usually asymptomatic unless torsion or ischemia occurs, which is rare. We report on a child case of a bilateral Hydatid of Morgagni with torsion.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Samaha M, Woodruff JD. Paratubal cysts: frequency, histogenesis, and associated clinical features. Obstet Gynecol. 1985; 65:691–694.2. Kern IB. Torsion of the hydatid of Morgagni in the female. Aust N Z J Surg. 1969; 38:338–342.3. Okada T, Yoshida H, Matsunaga T, Kouchi K, Ohtsuka Y, Takano H, et al. Paraovarian cyst with torsion in children. J Pediatr Surg. 2002; 37:937–940.4. Darwish AM, Amin AF, Mohammad SA. Laparoscopic management of paratubal and paraovarian cysts. JSLS. 2003; 7:101–106.5. Genadry R, Parmley T, Woodruff JD. The origin and clinical behavior of the paraovarian tumor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977; 129:873–880.6. Stein AL, Koonings PP, Schlaerth JB, Grimes DA, d'Ablaing G 3rd. Relative frequency of malignant paraovarian tumors: should paraovarian tumors be aspirated? Obstet Gynecol. 1990; 75:1029–1031.7. Fujii T, Kozuma S, Kikuchi A, Hanada N, Sakamaki K, Yasugi T, et al. Paraovarian cystadenoma: sonographic features associated with magnetic resonance and histopathologic findings. J Clin Ultrasound. 2004; 32:149–153.8. Crum CP, Lee KR. Diagnostic gynecologic & obstetric pathology. Philadelphia: Saunders;2006. p. 679–681.9. Rizk DE, Lakshminarasimha B, Joshi S. Torsion of the fallopian tube in an adolescent female: a case report. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2002; 15:159–161.10. Dieminger HJ, Friebel L, Bethmann R. Primary cancer of a Morgagni hydatid. Zentralbl Gynakol. 1985; 107:442–445.