J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Jun;80(Suppl 1):S17-S20. 10.4174/jkss.2011.80.Suppl1.S17.
Pneumomediastinum caused by colonic diverticulitis perforation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. eacechoi@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2096643
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.80.Suppl1.S17
Abstract
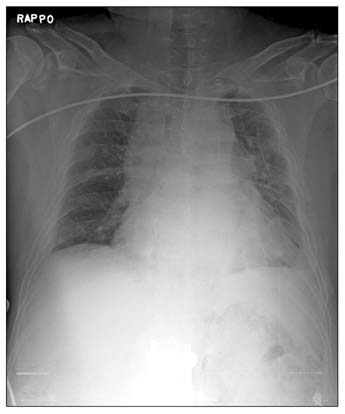
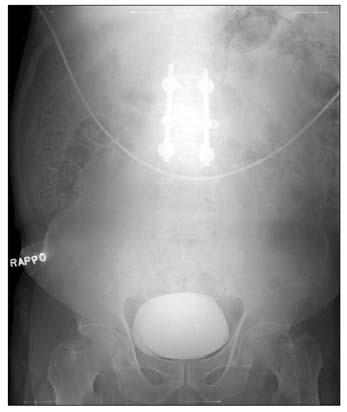
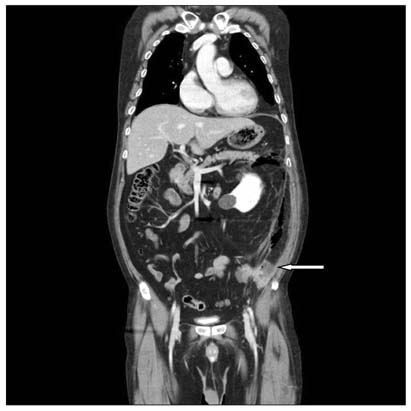
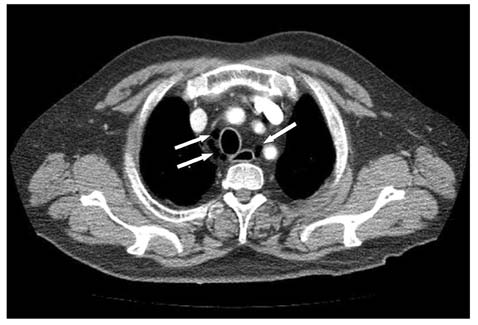
- A 59-year-old man presented with abdominal and left flank pain. The symptom had started 30 days before as an acute nephrolithiasis, which had worsened despite conservative management. The abdomen was slightly distended and tender over the lower abdomen, without signs of generalized peritoneal irritation. A computed tomography (CT) scan showed an abscess in left para-renal space up to the subphrenic space and an unexpected pneumomediastinum. An emergency operation was performed, which showed retroperitoneal diverticulitis perforation of the sigmoid descending junction with abscess formation. A segmental resection of the diseased colon and end-colostomy was performed (Hartmann's procedure). However, the patient's condition progressively deteriorated, and he died of sepsis and multi-organ failure on the 5th postoperative day. Although pneumomediastinum caused by colonic diverticulitis perforation is extremely rare, it could be a life-threatening condition in patients without signs of peritonitis because of delayed diagnosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ravo B, Khan SA, Ger R, Mishrick A, Soroff HS. Unusual extraperitoneal presentations of diverticulitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1985. 80:346–351.2. Caceres M, Ali SZ, Braud R, Weiman D, Garrett HE Jr. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a comparative study and review of the literature. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008. 86:962–966.3. Hur T, Chen Y, Shu GH, Chang JM, Cheng KC. Spontaneous cervical subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema secondary to occult sigmoid diverticulitis. Eur Respir J. 1995. 8:2188–2190.4. Suros J, Lee RA. Pneumoretroperitoneum, pneumomediastinum, and subcutaneous emphysema. Complications of acute, perforated diverticulitis. Minn Med. 1973. 56:747–749.5. van Oers JA, Ponssen HH, Hesp WL. Pneumopericardium, pneumomediastinum, pericarditis and mediastinal abscess secondary to diverticulitis of the sigmoid. Intensive Care Med. 2000. 26:1867–1868.6. Besic N, Zgajnar J, Kocijancic I. Pneumomediastinum, pneumopericardium, and pneumoperitoneum caused by peridiverticulitis of the colon: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004. 47:766–768.7. Bordeianou L, Hodin R. Controversies in the surgical management of sigmoid diverticulitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007. 11:542–548.8. Krukowski ZH, Matheson NA. Emergency surgery for diverticular disease complicated by generalized and faecal peritonitis: a review. Br J Surg. 1984. 71:921–927.9. Meyers MA. Radiological features of the spread and localization of extraperitoneal gas and their relationship to its source: an anatomical approach. Radiology. 1974. 111:17–26.10. Maunder RJ, Pierson DJ, Hudson LD. Subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Arch Intern Med. 1984. 144:1447–1453.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Colon Cancer with Ovarian Metastasis Mimicking Acute Diverticulitis
- Clinical characteristics of right versus left colonic diverticulitis
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Colon Diverticulitis
- Clinical Characteristics of Colonic Diverticulitis in Koreans
- What is the Difference Between Right- and Left-Sided Colonic Diverticulitis?