Ann Surg Treat Res.
2015 Nov;89(5):240-246. 10.4174/astr.2015.89.5.240.
Choledochoduodenal fistula in Mainland China: a review of epidemiology, etiology, diagnosis and management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, the Second Hospital of Chongqing New North Zone, Chongqing, China.
- 2Chongqing Key Laboratory of Hepatobiliary Surgery and Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China. gjp_cqmu@yeah.net
- 3Department of Infectious Diseases, Institute for Viral Hepatitis, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Infectious Diseases, Ministry of Education, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China.
- KMID: 2095529
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2015.89.5.240
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Choledochoduodenal fistula (CDF) is an extremely rare condition even in the most populous nations. However, diagnostic tools are inadequate for the young surgeon to be made aware of such a rare condition before surgery. Hence, basic understanding of the epidemiology, etiology, and management for this unusual but discoverable condition are necessary and essential.
METHODS
The exclusive case reports of CDF, which were published from 1983 to 2014 concerning mainland Chinese people, were performed to review the epidemiology, etiology, and management.
RESULTS
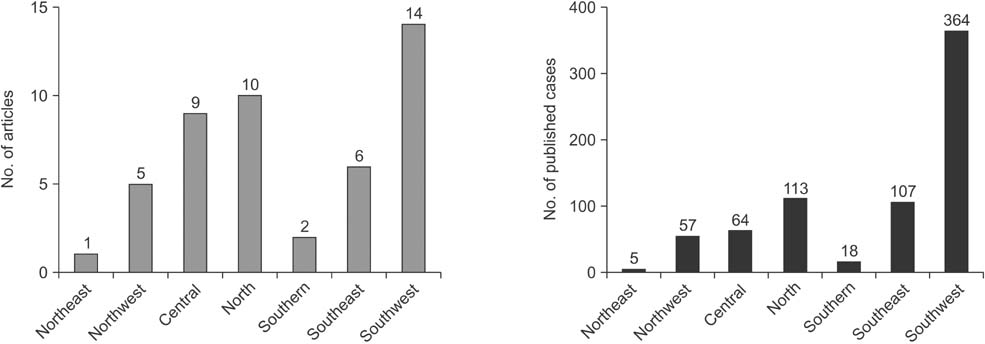
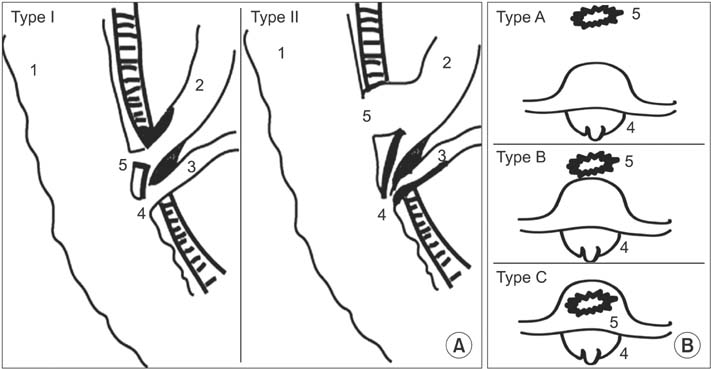
A total of 728 cases were incorporated into this review among 48 papers. More than half of the CDF cases were female (416) with an average age of 57.3 years. CDF was usually caused by cholelithiasis (573 of 728). Epigastric pain (589 of 728) and cholangitis (395 of 728) were the most common symptoms of CDF. CDF was usually detected and confirmed by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) (475 of 728) in Mainland China. The fistulas larger than 1 cm (82 of 654) were recommended for surgical biliary reconstruction. Fistulas between 0.5 cm and 1.0 cm (467 of 654) which were followed frequently by cholangitis attacks also required surgery; the rest were recommended to have stone removal and/or the application of an effective biliary drainage. Fistulas less than 0.5 cm (105 of 654) were usually received conservative therapy.
CONCLUSION
CDF should be considered in differential diagnosis of recurrent epigastric pain and cholangitis. A possible ERCP should be arranged to investigate carefully. Depending on the size of fistula and clinical presentation, different programs for CDF are indicated, ranging from drug therapy to choledochojejunostomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Double Duodenal Major Papilla
Huapyong Kang
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2021;78(6):359-361. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2021.162.A reinforced suture method for stapled gastrointestinal anastomosis to reduce gastrointestinal hemorrhage during Whipple operation in laparoscopy
La Zhang, Ning Jiang, Liujun Jiang, Rui Liao, Lei Xiang, Baoyong Zhou, Dewei Li
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2022;102(2):110-116. doi: 10.4174/astr.2022.102.2.110.
Reference
-
1. Marshall T, Kamalvand K, Cairns SR. Endoscopic treatment of biliary enteric fistula. BMJ. 1990; 300:1176.2. Liu TM, Chiu HH. Images in clinical medicine. Gallstone ileus. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:345.3. Lin CT, Hsu KF, Yu JC, Chu HC, Hsieh CB, Fu CY, et al. Choledochoduodenal fistula caused by cholangiocarcinoma of the distal common bile duct. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:Suppl 2. E319–E320.4. Luu MB, Deziel DJ. Unusual complications of gallstones. Surg Clin North Am. 2014; 94:377–394.5. Cao JY, Fang Z, Guo WT, Dai LH. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula. Tianjin Yi Yao. 1983; 6:978–980.6. Xu RN. Parapapillary choledochoduodenal fistula: diagnosis and treatment. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1984; 22:672–673. 7017. He SL, Tang RS. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula. Lichuang Fangshexue Za Zhi. 1984; 3:120–121.8. Jiao TY. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula. Shanghai Med J. 1985; 5:420–421.9. Dai XZ, Chen MZ. Clinical assessment of para-ampulla choledocho-duodenal fistulae in 27 cases. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 1986; 25:655–657. 700–701.10. Li XC. Two case reports of choledochoduodenal fistula. Beijing Med J. 1987; 4:251–252.11. Gu GH. Choledochoduodenal fistula: a long-term complication of T tuber drainage. J Third Mil Med Univ. 1987; 4:443.12. Li Z. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula after T tuber drainage. J Chin Pract Surg. 1991; 4:201.13. Wang ZL, Lu Qide. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula secondary penetrated duodenal peptic ulcer. J Pract Radiol. 1993; 3:507.14. Fei X. Pedical A case report of omentum repairing the choledochoduodenal fistula. J Hepatobiliary Surg. 1995; 4:216.15. Li YC. 2 Cases of choledochoduodenal fistula. Hainan Yi Xue. 1995; 2:135.16. Zhu JR, Kai GW, Zhang YC. X-ray analysis for choledochoduodenal fistula. J Pract Radiol. 1995; 3:183–184.17. Hu MX. 13 Cases of choledochoduodenal fistula after T tuber drainage. Curr Physician. 1996; 12:34.18. Shen WS, Zhao P. 4 Cases of choledochoduodenal fistula. J Chin Pract Surg. 1996; 8:486–487.19. Zhao DL, You L. Cardiac cancer implicated with choledochoduodenal fistula. Chin J Clin Gastroenterol. 1996; 2:82.20. Li WM. Surgical treatment for choledochoduodenal fistula: 11 cases report. J Mod Oper Surg. 1997; 4:286.21. Fan XJ, Geng XQ. 4 Rare cases of choledochoduodenal fistula. Yunnan Yi Yao. 1997; 5:398–399.22. Li NF, Zhang YD, Liu S. 69 Cases of choledochoduodenal fistula: a retrospective study of ERCP. Chin J Endosc. 1999; 4:34–35.23. Gong JP, Zhou YB, Han BL. Diagnosis and classification of choledochoduodenal fistula. Chin J Digest Endosc. 1999; 2:42–43.24. Gong JP, Zhou YB, Han BL. Diagnosis and surgical management of choledochoduodenal fistula. J Third Mil Med Univ. 2000; 22:287–289.25. Wang XX, Tao F. Choledochoduodenal fistula induced by the partially prolapsed T tube: two cases report. Zhejiang Pract Med. 2001; 6:57–58.26. Tian ZL, Wu DX. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula. J Hebei Med Uni. 2001; 22:106.27. Li ZH, Zhou YB, Chen M, Liu JK, Chen K. Clinical analysis of juxtapapillary choledochoduodenal fistula: report of 47 cases. Chin J Gen Surg. 2001; 16:331–333.28. Ku RX, Chen F, Liu SL, Wei NR, Ge XH, Ablet . Diagnosis of choledochoduodenal fistula by barium meal analysis: a case report. Xinjiang Med J. 2001; 1:65.29. Xie J. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula after T tuber drainage. J Clin Surg. 2002; 10:10.30. Yu HZ, Li FY, Du Y, Geng XP, Xiong QR. Diagnosis and treatment of choledochoduodenal fistul. J Clin Surg. 2002; 10:88–89.31. Gu J, Li JS, Ren J AN. Discussion of the suitable management and preventive methods for distal choledochoduodenal fistula. Chin J Gen Surg. 2002; 17:725–726.32. Hou YL, Chen ZW, Cheng H, Fu G. Analysis of 7 cases of postoperative distal choleo-duodonum fistulas. Fu Bu Wai Ke. 2004; 17:230–231.33. Hao RR, Yu L, Wang HJ. A case report of gallstone ileus induced by choledochoduodenal fistul. Beijing Med. 2005; 27:719.34. Lan XH, Xu L, Wang LY, Wang YZ. Diagnosis and treatment for peripapillary choledo-choduodenal fistula. Clin Med Chin. 2005; 1:71–72.35. Li ZH, Ding J, Ye Y, Cai L, Liu X, Liu J, et al. New strategy to prevent ascending cholangitis in larger choledochoduodenal fistula. ANZ J Surg. 2006; 76:796–800.36. Zhao DP, Sun W, Xu HM, Ma YW. 7 Cases of choledochoduodenal fistula after T tuber drainage. Acta Acad Med Weifang. 2006; 28:76.37. Lin D, Zhang LH, Jiang TR, Lan SQ, Yang LK. 16 Cases reports of choledochoduodenal fistula diagnosed by ERCP. Fujian Med J. 2006; 28:118–119.38. Peng B, Du JP, Deng B, Cun BY, Jiang LL, Zhang SF. A case report of primary pleomorphic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma complicated with choledochoduodenal fistula. J Sichuan Univ. 2006; 3:455.39. Sheng W, Zhao J, Luo HY, Liu ZB. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula. J Clin Radiol. 2007; 26:87.40. Chen HP, Bai L, Li WB, Liang C, Han SX. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula induced by foreign bodies on the border of duodenum ball drop. Chin J Endosc. 2007; 13:1341–1342.41. Xu ZY, Liu L, Zhang CQ, Li F, Li QQ. Clinic analysis 0f 9 cases with choledochoduodenal fistula associated with pancreatic carcinoma. Chin J Mod Med. 2007; 17:1386–1388. 139242. Wang An G. 5 Cases of choledochoduodenal fistula after T tuber drainage. J Liaoning Med Univ. 2010; 31:73–74.43. Chen RB. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula. J Yangtze Univ. 2010; 1:107–108.44. Wang WZ, He CH, Yi HF. 2 Cases of spontaneous chronic choledochoduodenal fistula. J Pract Med. 2010; 26:4050.45. Zong KC, You HB, Gong JP, Tu B. Diagnosis and management of choledochoduodenal fistula. Am Surg. 2011; 77:348–350.46. Li SW, Tian CP, Feng MH. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula complicated cholecystolithiasis and choledocholithiasis. Public Med Forum Mag. 2012; 34:4632.47. Yi XL, Li XH, Wang J. Management of choledochoduodenal fistula. For All Health. 2012; 18:66–67.48. Ding CL, Ma D. Management of choledochoduodenal fistula. Chin J Aesthet Med. 2012; 21:84–85.49. Liu Q, Lu MX, Zhang TH, Feng CL. 78 Cases report of choledochoduodenal fistula. Chin J Gerontol. 2012; 32:3534–3535.50. Li CS, Yuan D, Zhang J, Yuan YS. A case report of choledochoduodenal fistula diagnosed by ERCP. J Chin Physician. 2012; 14:718.51. Zhao S, Wang J, Ge J, Zhang X, Liu J, Zhang A, et al. Implantation of covered selfexpandable metal stent in the common bile duct for the treatment of choledochoduodenal fistula. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014; 48:383–384.52. Zhang YL, Xu JG, Zhu YY. Analysis of diagnosis and surgical treatment of the choledochoduodenal fistula. Chin J Mod Med. 2014; 29:103–105.53. Halabi WJ, Kang CY, Ketana N, Lafaro KJ, Nguyen VQ, Stamos MJ, et al. Surgery for gallstone ileus: a nationwide comparison of trends and outcomes. Ann Surg. 2014; 259:329–335.54. Chang WT, Lin NC, Hsia CY, Liu CS, Tsai HL, Loong CC. Liver transplantation for a renal transplantation recipient with secondary sclerosing cholangitis by choledochoduodenal fistula. Asian J Surg. 2012; 35:49–52.55. Neumann H, Nagel A, Bernatik T, Wickles N, Neurath MF, Raithel M. Endoscopic closure of large, spontaneous, choledochoduodenal fistula by using an overthe-scope clip. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:200–202.56. Hong T, Xu XQ, He XD, Qu Q, Li BL, Zheng CJ. Choledochoduodenal fistula caused by migration of endoclip after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20:4827–4829.57. Moghaddam JA, Amini M, Adibnejad S. Development of bile duct bezoars following cholecystectomy caused by choledochoduodenal fistula formation: a case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006; 6:1.58. Williamson JB, Draganov PV. Choledochoduodenal fistula after biliary metallic stent placement for pancreatic cancer. Dig Endosc. 2014; 26:292.59. Chaudhari D, Saleem A, Murthy R, Baron T, Young M. Choledochoduodenal fistula after biliary placement of a selfexpanding metallic stent for palliation of pancreatic cancer. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:Suppl 2 UCTN. E77.60. Okabe Y, Kaji R, Ishida Y, Noda T, Sasaki Y, Tsuruta O, et al. Successful endoscopic extraction of a large impacted choledocholithiasis in the ampulla of vater: two interesting cases. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22:Suppl 1. S103–S106.61. Song TJ, Hyun YS, Lee SS, Park do H, Seo DW, Lee SK, et al. Endoscopic ultrasoundguided choledochoduodenostomies with fully covered self-expandable metallic stents. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:4435–4440.62. Chikamori F, Okumiya K, Inoue A, Kuniyoshi N. Laparoscopic cholecystofistulectomy for preoperatively diagnosed cholecystoduodenal fistula. J Gastroenterol. 2001; 36:125–128.63. Karincaoglu M, Yildirim B, Kantarceken B, Aladag M, Hilmioglu F. Association of peripapillary fistula with common bile duct stones and cholangitis. ANZ J Surg. 2003; 73:884–886.64. Ikeda S, Okada Y. Classification of choledochoduodenal fistula diagnosed by duodenal fiberscopy and its etiological significance. Gastroenterology. 1975; 69:130–137.65. Yang D, Wang Z, Duan ZJ, Jin S. Laparoscopic treatment of an upper gastrointestinal obstruction due to Bouveret's syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:6943–6946.66. Mohammed N, Godfrey EM, Subramanian V. Cholecysto-duodenal fistula as the source of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Endoscopy. 2013; 45:Suppl 2 UCTN. E250–E251.67. Miyamoto S, Furuse J, Maru Y, Tajiri H, Muto M, Yoshino M. Duodenal tuberculosis with a choledocho-duodenal fistula. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 16:235–238.68. Jaballah S, Sabri Y, Karim S. Choledochoduodenal fistula due to duodenal peptic ulcer. Dig Dis Sci. 2001; 46:2475–2479.69. Mueller XM, Tevaearai HT, Stumpe F, Hurni M, Ruchat P, Fischer AP, et al. Gastrointestinal disease following heart transplantation. World J Surg. 1999; 23:650–655.70. Povoski S, Shamma'a J. Fistula involving portal vein and duodenum at the site of a duodenal ulcer in a patient after previous extrahepatic bile duct resection and brachytherapy. Dig Surg. 2003; 20:53–55.71. Choi D, Lim HK, Kim MJ, Kim SJ, Kim SH, Lee WJ, et al. Liver abscess after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinomas: frequency and risk factors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1860–1867.72. Ohtsuka T, Tanaka M, Inoue K, Nabae T, Takahata S, Yokohata K, et al. Is peripapillary choledochoduodenal fistula an indication for endoscopic sphincterotomy? Gastrointest Endosc. 2001; 53:313–317.73. Dwivedi AN, Kumar S, Rana S, Maurya B. Transmural invasion of hepatic flexure of colon causing cholecystocolic fistula by aggressive gallbladder carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2013; 11:86.74. Agarwal N, Sharma BC, Garg S, Kumar R, Sarin SK. Endoscopic management of postoperative bile leaks. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2006; 5:273–277.75. Periselneris N, Bong JJ. Choledocho-duodenal fistula encountered during emergency laparotomy for upper gastro-intestinal haemorrhage: what should be the surgical strategy? Clin Ter. 2011; 162:547–548.76. Lee JH, Han HS, Min SK, Lee HK. Laparoscopic repair of various types of biliaryenteric fistula: three cases. Surg Endosc. 2004; 18:349.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Duodenal Diverticulum Accompanied with Choledochoduodenal and Pancreaticoduodenal Fistulas
- Avian Influenza: Should China Be Alarmed?
- Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Bile Ducts Accompanied by a Choledochoduodenal Fistula
- Spontaneous Choledochoduodenal Fistula after Metallic Biliary Stent Placement in a Patient with Ampulla of Vater Carcinoma
- Pelvic Fistulas Complicating Pelvic Surgery or Diseases: Spectrum of Imaging Findings