Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2013 Nov;17(4):181-185. 10.14701/kjhbps.2013.17.4.181.
Case report of a pancreatic squamoid cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shwang@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2083345
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/kjhbps.2013.17.4.181
Abstract
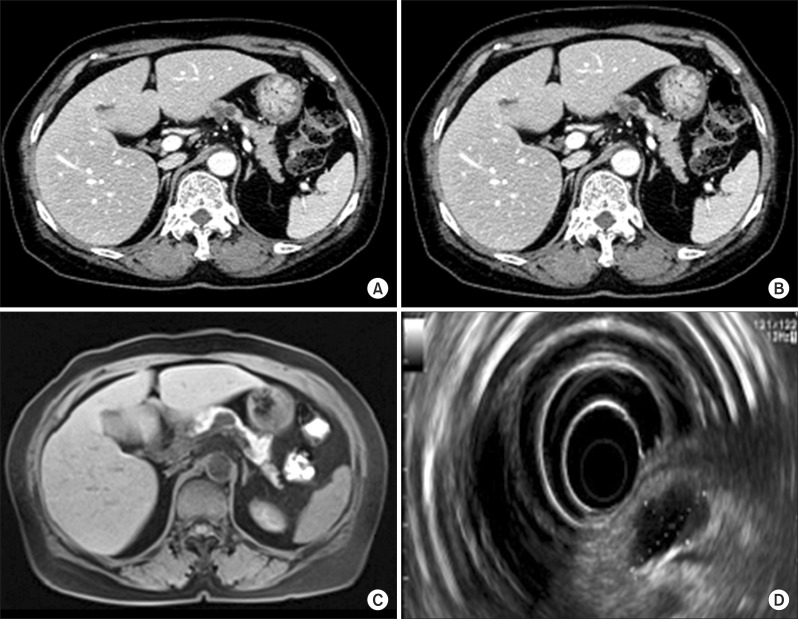
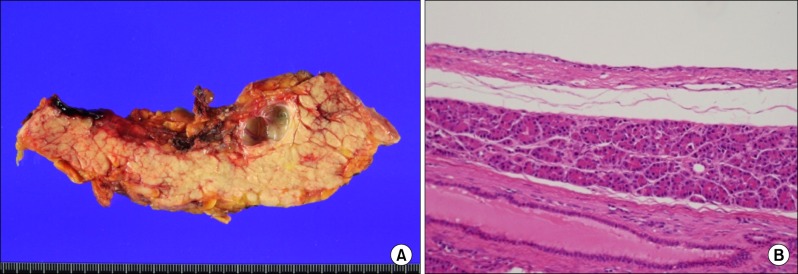
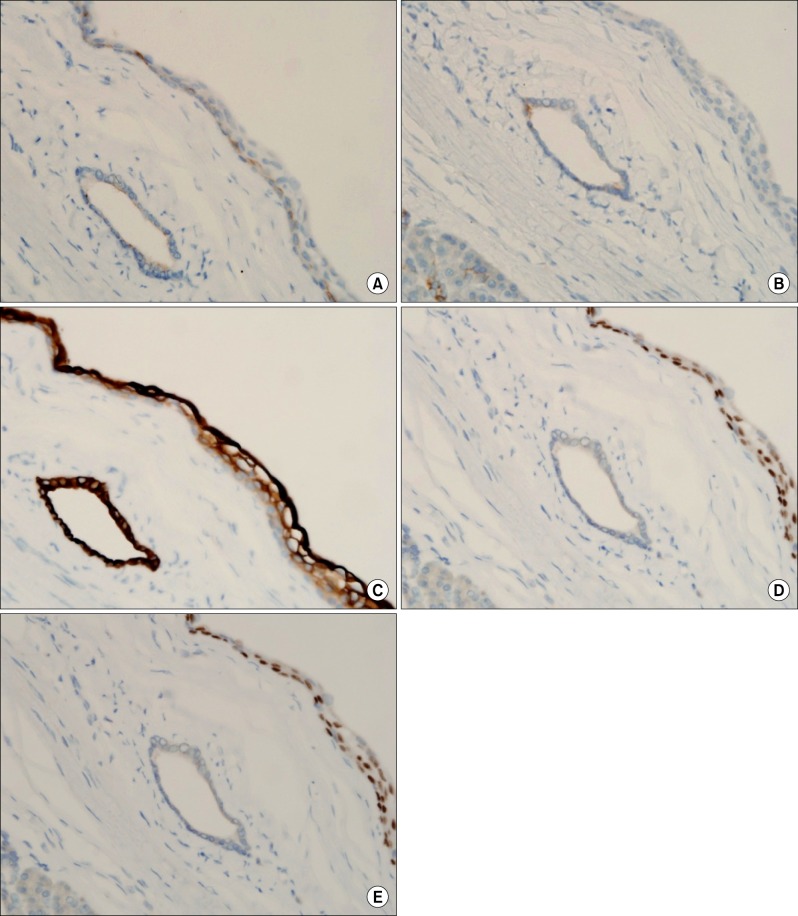
- Squamoid cyst of the pancreas is a very rare disease and it has been proposed only recently as a distinct pathologic lesion. We herein present a case of pancreatic squamoid cyst in a patient who underwent laparoscopic resection. A 60-year-old woman had an abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan for a routine check-up, and a multi-cystic lesion of 1.8-cm in size was incidentally found in the tail of the pancreas. Biochemical laboratory tests were within normal limits. At first, we presumed that the most likely diagnosis of the cystic lesion was an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. To treat this lesion, we performed laparoscopic spleen-saving distal pancreatectomy. The patient showed the usual routine postoperative course and she was discharged 10 days after surgery. On examination of the resected specimen, a well-defined, oligolocular cystic mass was found in the pancreatic tail, without a solid portion. Histologic examination revealed that the cysts had linings ranging from flat squamoid cells to transitional cells with non-keratinization. After immunohistochemical staining, the final diagnosis was confirmed to be squamoid cyst of the pancreas. This lesion appears to be regarded as a benign entity, thus an extended operation should be avoided and resection of the lesion can be performed minimally.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Squamoid cyst of pancreatic ducts: A case report
Jeong-Ik Park
Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2021;25(2):293-298. doi: 10.14701/ahbps.2021.25.2.293.
Reference
-
1. Kurahara H, Shinchi H, Mataki Y, et al. A case of squamoid cyst of pancreatic ducts. Pancreas. 2009; 38:349–351. PMID: 19307935.
Article2. Othman M, Basturk O, Groisman G, et al. Squamoid cyst of pancreatic ducts: A distinct type of cystic lesion in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:291–297. PMID: 17255775.
Article3. Brugge WR. The use of EUS to diagnose cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69(2 Suppl):S203–S209. PMID: 19179158.
Article4. Adsay NV, Klimstra DS, Compton CC. Cystic lesions of the pancreas. Introduction. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000; 17:1–6. PMID: 10721802.5. Kanazawa H, Kamiya J, Nagino M, et al. Epidermoid cyst in an intrapancreatic accessory spleen: a case report. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2004; 11:61–63. PMID: 15754048.
Article6. Adsay NV, Hasteh F, Cheng JD, et al. Lymphoepithelial cysts of the pancreas: a report of 12 cases and a review of the literature. Mod Pathol. 2002; 15:492–501. PMID: 12011254.
Article7. Fernandez-Cebrian JM, Carda P, Morales V, et al. Dermoid cyst of the pancreas: a rare cystic neoplasm. Hepatogastroenterology. 1998; 45:1874–1876. PMID: 9840167.8. Klein WM, Hruban RH, Klein-Szanto AJ, et al. Direct correlation between proliferative activity and dysplasia in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN): additional evidence for a recently proposed model of progression. Mod Pathol. 2002; 15:441–447. PMID: 11950919.
Article