Korean J Pain.
2011 Dec;24(4):235-238. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.235.
Spontaneous Height Restoration of Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hiitsme@snubh.org
- KMID: 2074020
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.235
Abstract
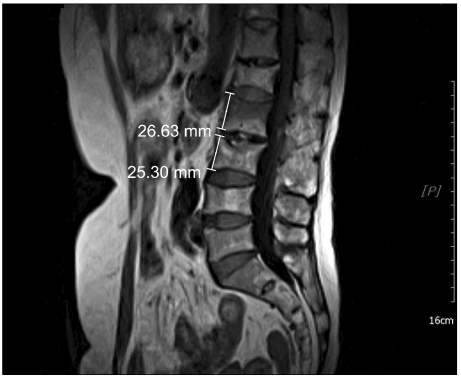
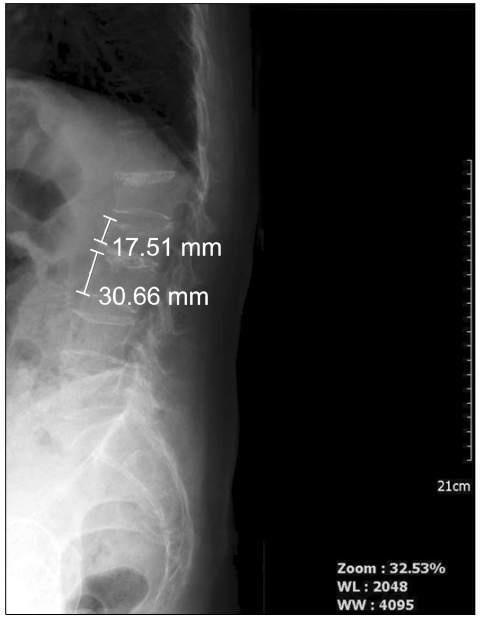
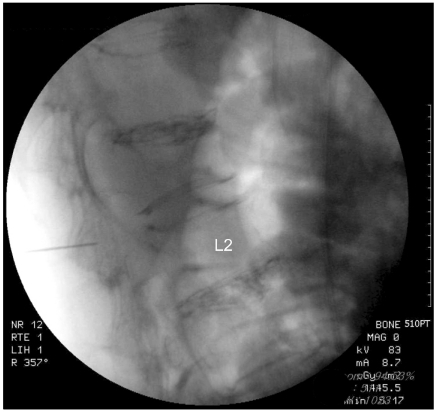
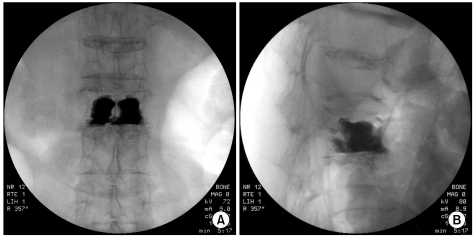
- Vertebral compression fractures result in vertebral height loss and alter sagittal spinal alignment, which in turn can lead to increased morbidity and mortality. Acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures are known to increase mobility and instability of the spine. There are limited published data correlating the degree of dynamic mobility and the efficacy of kyphoplasty on vertebral compression fractures. Here we report a 73-year-old female with a severe acute osteoporotic L2 compression fracture who obtained total vertebral height restoration following kyphoplasty, with resolution of back pain.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shindle MK, Gardner MJ, Koob J, Bukata S, Cabin JA, Lane JM. Vertebral height restoration in osteoporotic compression fractures: kyphoplasty balloon tamp is superior to postural correction alone. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17:1815–1819. PMID: 16983458.
Article2. McKiernan F, Jensen R, Faciszewski T. The dynamic mobility of vertebral compression fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2003; 18:24–29. PMID: 12510802.
Article3. McKiernan F, Faciszewski T, Jensen R. Reporting height restoration in vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:2517–2521. PMID: 14624087.
Article4. Rao RD, Singrakhia MD. Painful osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Pathogenesis, evaluation, and roles of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in its management. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85-A:2010–2022. PMID: 14563813.5. Silverman SL. The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fracture. Bone. 1992; 13(Suppl 2):S27–S31. PMID: 1627411.
Article6. Han KR, Kim C, Yang JY, Han ST, Kim YS. Balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Korean J Pain. 2006; 19:56–62.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
- Risk Factors of New Compression Fractures in Adjacent Vertebrae after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
- Early Onset Subsequent Vertebral Compression Fracture after Percutaneous Verteroplasty
- Vertebral Body Height Restoration after Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture
- Comparisons of Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures