Korean J Urol.
2014 Dec;55(12):814-820. 10.4111/kju.2014.55.12.814.
Impact of Metabolic Syndrome on Response to Medical Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran.
- 2Minimally Invasive Surgery Research Center, Iran University of Medical Sciences, and Department of Epidemiology, Faculty of Public Health, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. aikabir@yahoo.com
- 3Department of Endocrinology, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran.
- 4Asadabad Health and Treatment Network, Hamedan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, and Department of Epidemiology, Faculty of Public Health, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 5Department of Statistics, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran.
- 6Department of Surgery, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
- 7Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran.
- KMID: 2070096
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.12.814
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the effect of metabolic syndrome (MetS) on the response to medical therapy of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) after a 3-month period of treatment.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
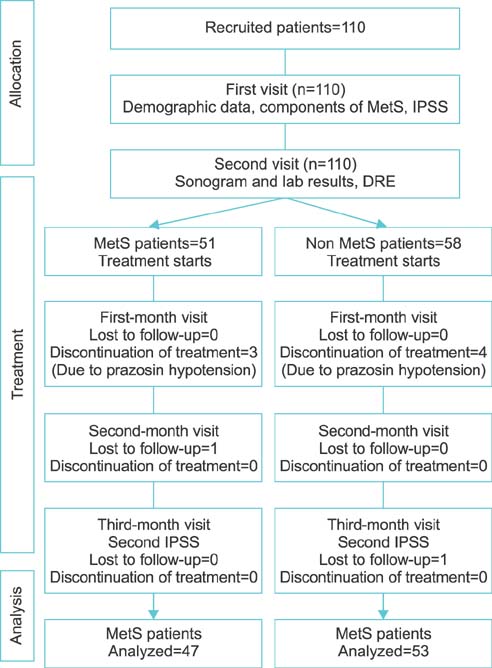
This was a cohort study of 100 patients, 47 with MetS and 53 without MetS, referred to either the primary care unit or referral hospital with BPH who had moderate lower urinary tract symptoms of prostate involvement and were candidates for medical treatment. Our main outcome was response to medical treatment with prazosin 1 mg twice a day and finasteride 5 mg daily in patients with BPH on the basis of International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS). Multivariate analysis of covariance was used to compare BPH treatment response in patients with and without MetS before and after receiving treatment.
RESULTS
The mean volume of the prostate was significantly higher in MetS patients than in patients without MetS (57+/-32.65 mL compared with 46.00+/-20.19 mL, p=0.036). The control group demonstrated an 11-unit reduction in IPSS, whereas those with MetS showed a reduction in the symptom score of only 6 units (p<0.001). Regarding the components of MetS separately, triglyceride (p<0.001), fasting blood sugar (p=0.001), and waist circumference (p=0.028) significantly affected the clinical progression of BPH. The observational nature of this study may be a limitation in comparison with an interventional study.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of the present study showed that MetS can negatively affect the response to medical treatment of BPH. Therefore, it is necessary to consider MetS in selecting patients with BPH for drug therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Case-Control Studies
Finasteride/*therapeutic use
Humans
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms/etiology
Male
Metabolic Syndrome X/*complications
Middle Aged
Patient Selection
Prazosin/*therapeutic use
Prostatic Hyperplasia/complications/*drug therapy/pathology
Treatment Outcome
Urological Agents/*therapeutic use
Finasteride
Prazosin
Urological Agents
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Correlation between Body Mass Index and Routine Parameters in Men Over Fifty
Deok Ha Seo, Sol Yoon, Jae Hwi Choi, Jungmo Do, Sin Woo Lee, Chunwoo Lee, Seong Uk Jeh, See Min Choi, Sung Chul Kam, Jeong Seok Hwa, Ky Hyun Chung, Sung Won Kwon, Sae Chul Kim, Dong Soo Park, Jae Mann Song, Kyung Seop Lee, Jae Seog Hyun
World J Mens Health. 2017;35(3):178-185. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.16032.
Reference
-
1. Tanagho EA, McAninch JW. Smith's general urology. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical;2008.2. Cruz F, Desgrandchamps F. New concepts and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract symptoms in men. Eur Urol Suppl. 2010; 9:472–476.3. Parsons JK, Bergstrom J, Barrett-Connor E. Lipids, lipoproteins and the risk of benign prostatic hyperplasia in community-dwelling men. BJU Int. 2008; 101:313–318.4. Ozden C, Ozdal OL, Urgancioglu G, Koyuncu H, Gokkaya S, Memis A. The correlation between metabolic syndrome and prostatic growth in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2007; 51:199–203.5. Parsons JK, Sarma AV, McVary K, Wei JT. Obesity and benign prostatic hyperplasia: clinical connections, emerging etiological paradigms and future directions. J Urol. 2013; 189:1 Suppl. S102–S106.6. Yim SJ, Cho YS, Joo KJ. Relationship between metabolic syndrome and prostate volume in Korean men under 50 years of age. Korean J Urol. 2011; 52:390–395.7. Sarma AV, Wei JT, Jacobson DJ, Dunn RL, Roberts RO, Girman CJ, et al. Comparison of lower urinary tract symptom severity and associated bother between community-dwelling black and white men: the Olmsted County Study of Urinary Symptoms and Health Status and the Flint Men's Health Study. Urology. 2003; 61:1086–1091.8. De Nunzio C, Aronson W, Freedland SJ, Giovannucci E, Parsons JK. The correlation between metabolic syndrome and prostatic diseases. Eur Urol. 2012; 61:560–570.9. Tewari R, Prabhat P, Natu S, Dalela D, Goel A, Goel M, et al. Association of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) with the metabolic syndrome (MS) and its components: a growing dilemma. J Mens Health. 2011; 8:66–71.10. Gogia A, Agarwal PK. Metabolic syndrome. Indian J Med Sci. 2006; 60:72–81.11. Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2002; 287:356–359.12. Wallner LP, Morgenstern H, McGree ME, Jacobson DJ, St Sauver JL, Jacobsen SJ, et al. The effects of metabolic conditions on prostate cancer incidence over 15 years of follow-up: results from the Olmsted County Study. BJU Int. 2011; 107:929–935.13. Park HS, Oh SW, Cho SI, Choi WH, Kim YS. The metabolic syndrome and associated lifestyle factors among South Korean adults. Int J Epidemiol. 2004; 33:328–336.14. Rohrmann S, Smit E, Giovannucci E, Platz EA. Association between markers of the metabolic syndrome and lower urinary tract symptoms in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). Int J Obes (Lond). 2005; 29:310–316.15. Kupelian V, McVary KT, Kaplan SA, Hall SA, Link CL, Aiyer LP, et al. Association of lower urinary tract symptoms and the metabolic syndrome: results from the Boston area community health survey. J Urol. 2013; 189:1 Suppl. S107–S114.16. Han JH, Chang IH, Ahn SH, Kwon OJ, Bang SH, Choi NY, et al. Association between serum prostate-specific antigen level, liver function tests and lipid profile in healthy men. BJU Int. 2008; 102:1097–1101.17. Mehrdad M, Hosainpanah F, Azizi F. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome among 3-9 years old children inTehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Pejouhesh. 2006; 30:337–346.18. Sadrbafoghi SM, Salari M, Rafiee M, Namayandeh SM, Abdoli AM, Karimi M, et al. Prevalence and criteria of metabolic syndrome in an urban population:Yazd Healthy Heart Project. Tehran Univ Med J. 2006; 64:90–96.19. Park SB, Kim JK, Choi SH, Noh HN, Ji EK, Cho KS. Prostate volume measurement by TRUS using heights obtained by transaxial and midsagittal scanning: comparison with specimen volume following radical prostatectomy. Korean J Radiol. 2000; 1:110–113.20. Jeong IG, Hwang SS, Kim HK, Ahn H, Kim CS. The association of metabolic syndrome and its components with serum prostate-specific antigen levels in a Korean-screened population. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010; 19:371–380.21. Parekh N, Lin Y, Marcella S, Kant AK, Lu-Yao G. Associations of lifestyle and physiologic factors with prostate-specific antigen concentrations: evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2001-2004). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008; 17:2467–2472.22. Park YW, Min SK, Lee JH. Relationship between lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia and metabolic syndrome in Korean men. World J Mens Health. 2012; 30:183–188.23. Jang TH, Son JH, Kim JI, Jang SH. Metabolic Syndrome and benign prostatic hyperplasia: a study focused on the correlation between metabolic syndrome factors and prostate volume and prostate-specific antigen. Korean J Urol. 2008; 49:986–991.24. Koo KC, Cho KS, Kang EM, Kwon SW, Hong SJ. The relationship between metabolic syndrome and prostate volume in men over sixties who underwent prostate health check-up. Korean J Urol. 2008; 49:813–817.25. Nandeesha H, Koner BC, Dorairajan LN, Sen SK. Hyperinsulinemia and dyslipidemia in non-diabetic benign prostatic hyperplasia. Clin Chim Acta. 2006; 370:89–93.26. Martin RM, Vatten L, Gunnell D, Romundstad P, Nilsen TI. Components of the metabolic syndrome and risk of prostate cancer: the HUNT 2 cohort, Norway. Cancer Causes Control. 2009; 20:1181–1192.27. Kim WT, Yun SJ, Choi YD, Kim GY, Moon SK, Choi YH, et al. Prostate size correlates with fasting blood glucose in non-diabetic benign prostatic hyperplasia patients with normal testosterone levels. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:1214–1218.28. Laukkanen JA, Laaksonen DE, Niskanen L, Pukkala E, Hakkarainen A, Salonen JT. Metabolic syndrome and the risk of prostate cancer in Finnish men: a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004; 13:1646–1650.29. Baldeweg SE, Golay A, Natali A, Balkau B, Del Prato S, Coppack SW. Insulin resistance, lipid and fatty acid concentrations in 867 healthy Europeans. European Group for the Study of Insulin Resistance (EGIR). Eur J Clin Invest. 2000; 30:45–52.30. Tan CE, Ma S, Wai D, Chew SK, Tai ES. Can we apply the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel definition of the metabolic syndrome to Asians. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1182–1186.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter to the editor: Impact of metabolic syndrome on response to medical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- The authors reply: Impact of metabolic syndrome on response to medical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- The Correlation between Metabolic Syndrome and the Prostate Volume
- A Prominently Large Glans penis as a Possible sign of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- The Relating Factors of Metabolic Syndrome to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia