J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Sep;29(Suppl 2):S117-S122. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S117.
Analysis of Correlation between 24-Hour Urinary Sodium and the Degree of Blood Pressure Control in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Non-Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2The Research Institute for Salt and Health, Seongnam, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. mednep@snubh.org
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 7Renal Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Seoul K-Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Immunology, Seoul National University Postgraduate School, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2069802
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S117
Abstract
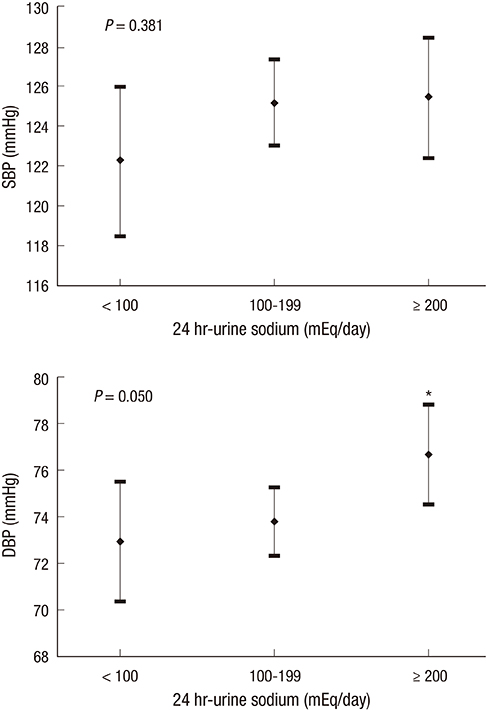
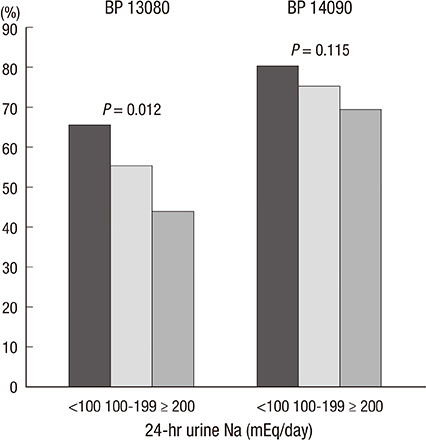
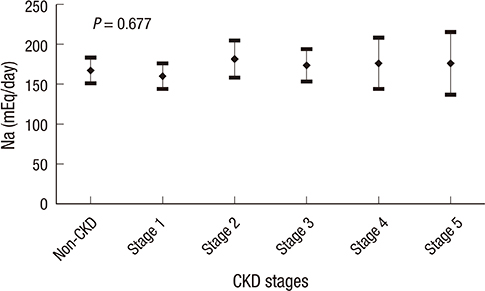
- We investigated the association between 24-hr urinary sodium (24UNA) and adequacy of blood pressure (BP) control in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and nonCKD. All data were collected retrospectively by accessing the electrical medical records in patients with 24-hr urine collection and serum creatinine. Enrolled 400 subjects were subgrouped by the amount of 24UNA, or CKD stage. The appropriate BP was defined as BP < 130/80 mmHg for subjects with proteinuria, and BP < 140/90 mmHg for subjects without proteinuria. The mean level of 24UNA was 166+/-76 mEq/day. The 24UNA group was an independently related factor to diastolic BP as a continuous variable. The rate of appropriate BP control in patients with proteinuria was highest in 24UNA <100 mEq/L (P=0.012). The odds to fail achievement of BP target in subjects with 24UNA> or =90 mEq/day was 2.441 (1.249-4.772, P=0.009) higher than that of 24UNA <90 mEq/day among participants with proteinuria. There was difference in the amount of 24UNA between CKD and non-CKD except each stage of CKD group. In conclusion, salt intake estimated by 24-hr urine sodium excretion is a risk factor to achieve appropriate BP control.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Algorithms
Blood Pressure/*physiology
Creatine/blood
Demography
Female
Humans
Hypertension/complications
Male
Middle Aged
Odds Ratio
Proteinuria/complications
Renal Insufficiency, Chronic/complications/*pathology
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Severity of Illness Index
Sodium, Dietary/*urine
Urine Specimen Collection
Creatine
Sodium, Dietary
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weir MR, Dengel DR, Behrens MT, Goldberg AP. Salt-induced increases in systolic blood pressure affect renal hemodynamics and proteinuria. Hypertension. 1995; 25:1339–1344.2. Jones-Burton C, Mishra SI, Fink JC, Brown J, Gossa W, Bakris GL, Weir MR. An in-depth review of the evidence linking dietary salt intake and progression of chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2006; 26:268–275.3. Swift PA, Markandu ND, Sagnella GA, He FJ, MacGregor GA. Modest salt reduction reduces blood pressure and urine protein excretion in black hypertensives: a randomized control trial. Hypertension. 2005; 46:308–312.4. Outcomes KDIG. KDIGO guidelines. accessed on 31 Mar 2014. Available from http://kdigo.org/home/guidelines/ckd-evaluation-management/.5. Hoffmann IS, Cubeddu LX. Increased blood pressure reactivity to dietary salt in patients with the metabolic syndrome. J Hum Hypertens. 2007; 21:438–444.6. Xu J, Wang M, Chen Y, Zhen B, Li J, Luan W, Ning F, Liu H, Ma J, Ma G. Estimation of salt intake by 24-hour urinary sodium excretion: a cross-sectional study in Yantai, China. BMC Public Health. 2014; 14:136.7. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 39:S1–266.8. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:604–612.9. Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976; 16:31–41.10. Khaw KT, Bingham S, Welch A, Luben R, O'Brien E, Wareham N, Day N. Blood pressure and urinary sodium in men and women: the Norfolk Cohort of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC-Norfolk). Am J Clin Nutr. 2004; 80:1397–1403.11. Schachter J, Harper PH, Radin ME, Caggiula AW, McDonald RH, Diven WF. Comparison of sodium and potassium intake with excretion. Hypertension. 1980; 2:695–699.12. Ljungman S, Aurell M, Hartford M, Wikstrand J, Wilhelmsen L, Berglund G. Sodium excretion and blood pressure. Hypertension. 1981; 3:318–326.13. Rhee MY, Shin SJ, Park SH, Kim SW. Sodium intake of a city population in Korea estimated by 24-h urine collection method. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013; 67:875–880.14. Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, Coresh J, Culleton B, Hamm LL, McCullough PA, Kasiske BL, Kelepouris E, Klag MJ, et al. Kidney disease as a risk factor for development of cardiovascular disease: a statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Kidney in Cardiovascular Disease, High Blood Pressure Research, Clinical Cardiology, and Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2003; 108:2154–2169.15. Jafar TH, Stark PC, Schmid CH, Landa M, Maschio G, Marcantoni C, de Jong PE, de Zeeuw D, Shahinfar S, Ruggenenti P, et al. Proteinuria as a modifiable risk factor for the progression of non-diabetic renal disease. Kidney Int. 2001; 60:1131–1140.16. Elliott P, Stamler J, Nichols R, Dyer AR, Stamler R, Kesteloot H, Marmot M. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. Intersalt revisited: further analyses of 24 hour sodium excretion and blood pressure within and across populations. BMJ. 1996; 312:1249–1253.17. Meneton P, Jeunemaitre X, de Wardener HE, MacGregor GA. Links between dietary salt intake, renal salt handling, blood pressure, and cardiovascular diseases. Physiol Rev. 2005; 85:679–715.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of urinary angiotensinogen and high-salt diet on blood pressure in patients with chronic kidney disease: results from the Korean Cohort Study for Outcome in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD)
- Altered Regulation of Renal Aquaporins and Sodium Transporters in Experimental Chronic Renal Failure
- Loop Diuretics in Clinical Practice
- Updated Guideline for Diagnosis of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: Based on 2017 ACC/AHA Hypertension Guideline
- Blood pressure control in patients with chronic kidney disease