Korean J Urol.
2014 Oct;55(10):643-649. 10.4111/kju.2014.55.10.643.
Predicting Recurrence and Progression of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in Korean Patients: A Comparison of the EORTC and CUETO Models
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. alse3025@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2069786
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.10.643
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to confirm the utility of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) and the Spanish Urological Club for Oncological Treatment (CUETO) scoring systems and to determine which model is preferred as a prognostic model in Korean patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between 1985 and 2011, 531 patients who were treated by transurethral resection of bladder cancer were retrospectively analyzed by use of the EORTC and CUETO models. Statistically, we performed Kaplan-Meier survival analysis; calculated Harrell's concordance index, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and cutoff values; and performed univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analyses.
RESULTS
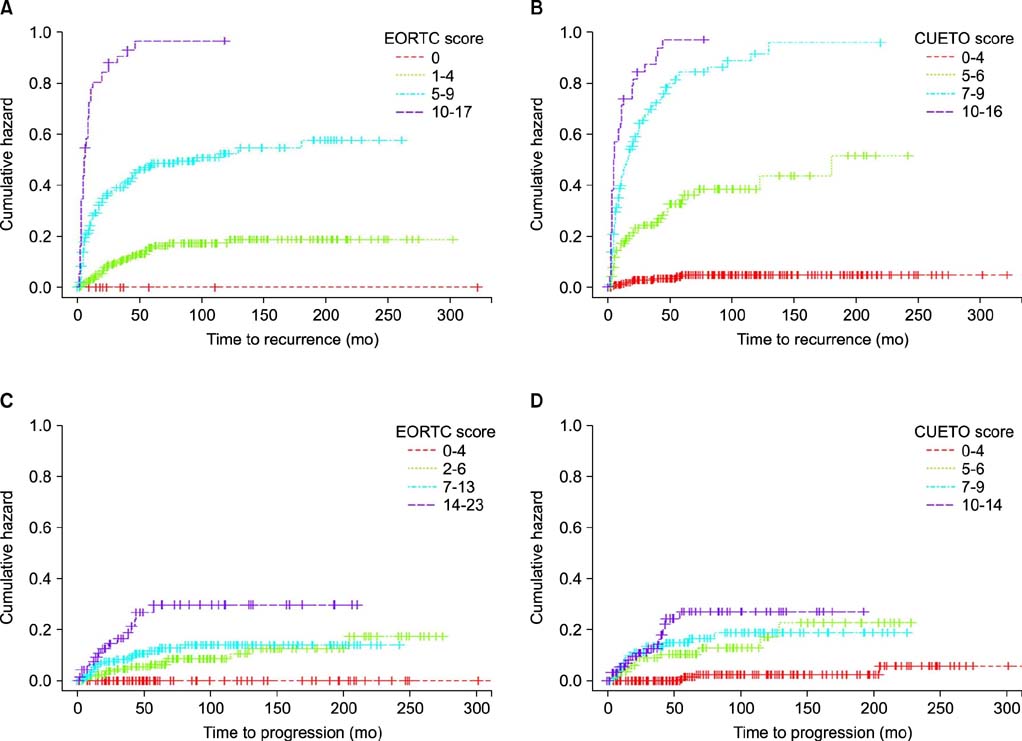
For risk of recurrence, with the use of the EORTC model, all groups had statistically significant differences except between the group with a score of 0 and the group with a score of 1-4. With the use of the CUETO model, all groups differed significantly. For risk of progression, with the use of the EORTC model, significant differences were observed between all groups except between the group with a score of 2-6 and the group with a score of 7-13. With the use of the CUETO model, a significant difference was observed between the group with a score of 0 and the other groups. The concordance index of the EORTC and CUETO models was 0.759 and 0.836 for recurrence and 0.704 and 0.745 for progression, respectively. The area under the ROC curve for the EORTC and CUETO models was 0.832 and 0.894 for recurrence and 0.722 and 0.724 for progression, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Both scoring systems, especially the CUETO model, showed value in predicting recurrence and progression in Korean patients, which will help in individualizing treatment and follow-up schedules.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Disease Progression
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Middle Aged
Models, Statistical
Neoplasm Invasiveness
Neoplasm Recurrence, Local/pathology
Retrospective Studies
Risk Assessment/methods
*Severity of Illness Index
Urinary Bladder Neoplasms/*pathology/surgery
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.2. Donat SM. Evaluation and follow-up strategies for superficial bladder cancer. Urol Clin North Am. 2003; 30:765–776.3. Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol. 2006; 49:466–465. discussion 475-7.4. Fernandez-Gomez J, Madero R, Solsona E, Unda M, Martinez-Pineiro L, Gonzalez M, et al. Predicting nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer recurrence and progression in patients treated with bacillus Calmette-Guerin: the CUETO scoring model. J Urol. 2009; 182:2195–2203.5. Murta-Nascimento C, Schmitz-Drager BJ, Zeegers MP, Steineck G, Kogevinas M, Real FX, et al. Epidemiology of urinary bladder cancer: from tumor development to patient's death. World J Urol. 2007; 25:285–295.6. Hayat MJ, Howlader N, Reichman ME, Edwards BK. Cancer statistics, trends, and multiple primary cancer analyses from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Oncologist. 2007; 12:20–37.7. Yee DS, Ishill NM, Lowrance WT, Herr HW, Elkin EB. Ethnic differences in bladder cancer survival. Urology. 2011; 78:544–549.8. Chamie K, Litwin MS, Bassett JC, Daskivich TJ, Lai J, Hanley JM, et al. Recurrence of high-risk bladder cancer: a population-based analysis. Cancer. 2013; 119:3219–3227.9. Seo KW, Kim BH, Park CH, Kim CI, Chang HS. The efficacy of the EORTC scoring system and risk tables for the prediction of recurrence and progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer after intravesical bacillus calmette-guerin instillation. Korean J Urol. 2010; 51:165–170.10. Hernandez V, De La Pena E, Martin MD, Blazquez C, Diaz FJ, Llorente C. External validation and applicability of the EORTC risk tables for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. World J Urol. 2011; 29:409–414.11. Xu T, Zhu Z, Zhang X, Wang X, Zhong S, Zhang M, et al. Predicting recurrence and progression in Chinese patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer using EORTC and CUETO scoring models. Urology. 2013; 82:387–393.12. Xylinas E, Kent M, Kluth L, Pycha A, Comploj E, Svatek RS, et al. Accuracy of the EORTC risk tables and of the CUETO scoring model to predict outcomes in non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109:1460–1466.13. Han RF, Pan JG. Can intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin reduce recurrence in patients with superficial bladder cancer? A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Urology. 2006; 67:1216–1223.14. Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Lamm DL. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin reduces the risk of progression in patients with superficial bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of the published results of randomized clinical trials. J Urol. 2002; 168:1964–1970.15. Sylvester RJ. Natural history, recurrence, and progression in superficial bladder cancer. ScientificWorldJournal. 2006; 6:2617–2625.16. Ojea A, Nogueira JL, Solsona E, Flores N, Gomez JM, Molina JR, et al. A multicentre, randomised prospective trial comparing three intravesical adjuvant therapies for intermediate-risk superficial bladder cancer: low-dose bacillus Calmette-Guerin (27 mg) versus very low-dose bacillus Calmette-Guerin (13.5 mg) versus mitomycin C. Eur Urol. 2007; 52:1398–1406.17. Kanagawa Urological Research Group (KURG). A 2-week maintenance regimen of intravesical instillation of bacillus Calmette-Guerin is safe, adherent and effective in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a prospective, multicenter phase II clinical trial. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012; 42:813–819.18. MacLennan GT, Kirkali Z, Cheng L. Histologic grading of non-invasive papillary urothelial neoplasms. Eur Urol. 2007; 51:889–897.19. Chen Z, Ding W, Xu K, Tan J, Sun C, Gou Y, et al. The 1973 WHO Classification is more suitable than the 2004 WHO Classification for predicting prognosis in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e47199.20. Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat SF, van Rhijn BW, Comperat E, et al. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol. 2013; 64:639–653.21. Oderda M, Ricceri F, Pisano F, Fiorito C, Gurioli A, Casetta G, et al. Prognostic factors including Ki-67 and p53 in Bacillus Calmette-Guérin-treated non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a prospective study. Urol Int. 2013; 90:184–190.22. Shariat SF, Zippe C, Ludecke G, Boman H, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Casella R, et al. Nomograms including nuclear matrix protein 22 for prediction of disease recurrence and progression in patients with Ta, T1 or CIS transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol. 2005; 173:1518–1525.23. Ke HL, Chen M, Ye Y, Hildebrandt MA, Wu WJ, Wei H, et al. Genetic variations in micro-RNA biogenesis genes and clinical outcomes in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2013; 34:1006–1011.24. Faba OR, Palou J, Breda A, Villavicencio H. High-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: update for a better identification and treatment. World J Urol. 2012; 30:833–840.25. Huguet J, Crego M, Sabate S, Salvador J, Palou J, Villavicencio H. Cystectomy in patients with high risk superficial bladder tumors who fail intravesical BCG therapy: pre-cystectomy prostate involvement as a prognostic factor. Eur Urol. 2005; 48:53–59.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Efficacy of the EORTC Scoring System and Risk Tables for the Prediction of Recurrence and Progression of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer after Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Instillation
- Predicting Progression and Survival in Korean Patients with High Grade T1 Bladder Cancer Using EORTC Risk Tables
- Effects of Simultaneous Transurethral Resection of Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- New and contemporary markers of prognosis in nonmuscle invasive urothelial cancer
- Autophagy and urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: A review