Prog Med Phys.
2015 Sep;26(3):185-191. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.3.185.
The Results of the Survey about Present Situation of Quality Assurance for Radiotherapy Machine of Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Bio-convergence Engineering, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. radioyoon@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2069482
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.3.185
Abstract
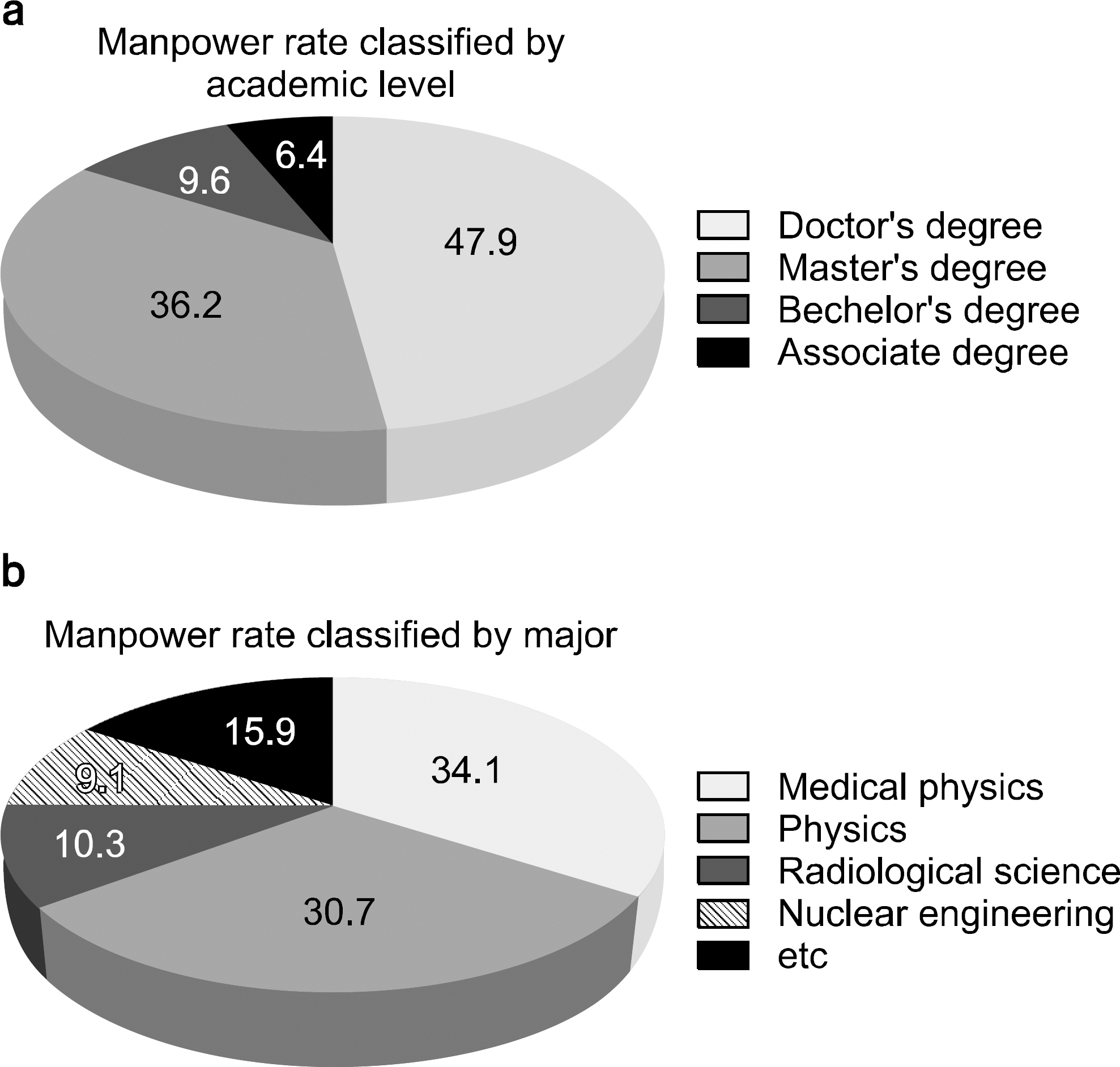
- As radiation therapy is one of three major cancer treatment methods, many cancer patients get radiation therapy. Because of the invisible and scattering characteristics of radiation, it is impossible to identify the quality and the amount of radiation and secondary cancer could be induced by scattered radiation. Because of advanced technique of radiation therapy and the reasons mentioned above, quality assurance of radiotherapy machine should be performed completely. International organizations such as International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) suggest report of quality assurance to recommend united method of radiotherapy machine quality assurance. Domestic society of medical physics, however, is too small to make such a report, domestic hospitals selectively choose some of contents in global suggestions. As there are no suggestions for domestic hospitals and global suggestions are being updated, we did a survey about quality assurance for radiotherapy machine. The questionnaire is composed of possession of radiotherapy machine, items performed for quality assurance and manpower, etc. 37 of 72 hospitals answered to survey. These results could be used for making domestic standard quality assurance procedure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Suggestion for Comprehensive Quality Assurance of Medical Linear Accelerator in Korea
Sang Hyoun Choi, Dong-wook Park, Kum Bae Kim, Dong Wook Kim, Jaiki Lee, Dong Oh Shin
Prog Med Phys. 2015;26(4):294-303. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.294.
Reference
-
References
1. Hall EJ, Wuu CS. Radiation-induced second cancers: the impact of 3D-CRT and IMRT. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. 56(1):83–88. 2003.
Article2. Kim S, Min BJ, Yoon M, et al. Secondary radiation doses of intensitymodulated radiotherapy and proton beam therapy in patients with lung and liver cancer. Radiotherapy and oncology: Journal of the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. 98(3):335–339. 2011.
Article3. AAPM TG No. 35: Medical Accelerator Safety considerations. American Association of Physicist in Medicine (. 1993.4. IAEA-TECDOC-989: Quality Assurance in Radiotherapy. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna (. 1997.5. AAPM TG No. 142: Quality assurance of medical acce lerators. American Association of Physicist in Medicine (. 2009.6. ECRP Radiation Protection No. 149: Medical Overexposures. European Commission Radiation Protection (. 2003.7. Lee SH, Kim JR, Cho SJ, et al. Analysis and Investigation for the Status of Radiation Therapy QA in Korea. Korean Journal of Medical Physics. 21(2):223–231. 2010.8. AAPM TG No. 41: Remote afterloading technology. American Association of Physicists in Medicine (. 1993.9. AAPM TG No. 43: Dosimetry of interstitial Brachytherapy Source. American Association of Physicists in Medicine (. 1995.10. AAPM TG No. 56: Code of particle for for brachytherapy physics. American Association of Physicists in medicine (. 1997.11. AAPM TG No. 40: Comprehensive QA for Radiation Oncology. American Association of Physicist in Medicine (. 1994.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Pilot Study of the Scanning Beam Quality Assurance Using Machine Log Files in Proton Beam Therapy
- Evolving Clinical Cancer Radiotherapy: Concerns Regarding Normal Tissue Protection and Quality Assurance
- Quality Assurance of Gastric Cancer Surgery
- Suggestion for Comprehensive Quality Assurance of Medical Linear Accelerator in Korea
- Use of Statistical Process Control for Quality Assurance in Radiation Therapy