J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2015 Sep;22(3):75-81. 10.4184/jkss.2015.22.3.75.
Analysis of Treatment Methods for Subsequent Vertebral Fractures Following Osteoporotic Compression Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University, College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. sskim@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University, College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2068924
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2015.22.3.75
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A multicenter retrospective study.
OBJECTIVES
To compare the incidence and pattern of subsequent vertebral fractures following conservative treatment versus vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: Previous studies suggest that new vertebral fractures may increase following vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty because bony cement inserted into the vertebral body of a fractured bone can elevate its strength and stiffness, which in turn, may increase the probability of the compression fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From three hospitals, we recruited 135 patients who had been treated for acute osteoporotic compression fractures and had available spine images taken at their 1-year follow-up. The patients were divided into two groups according to treatment methods. Group C had been managed conservatively, and Group VK had undergone vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. The two groups were compared for subsequent vertebral fractures.
RESULTS
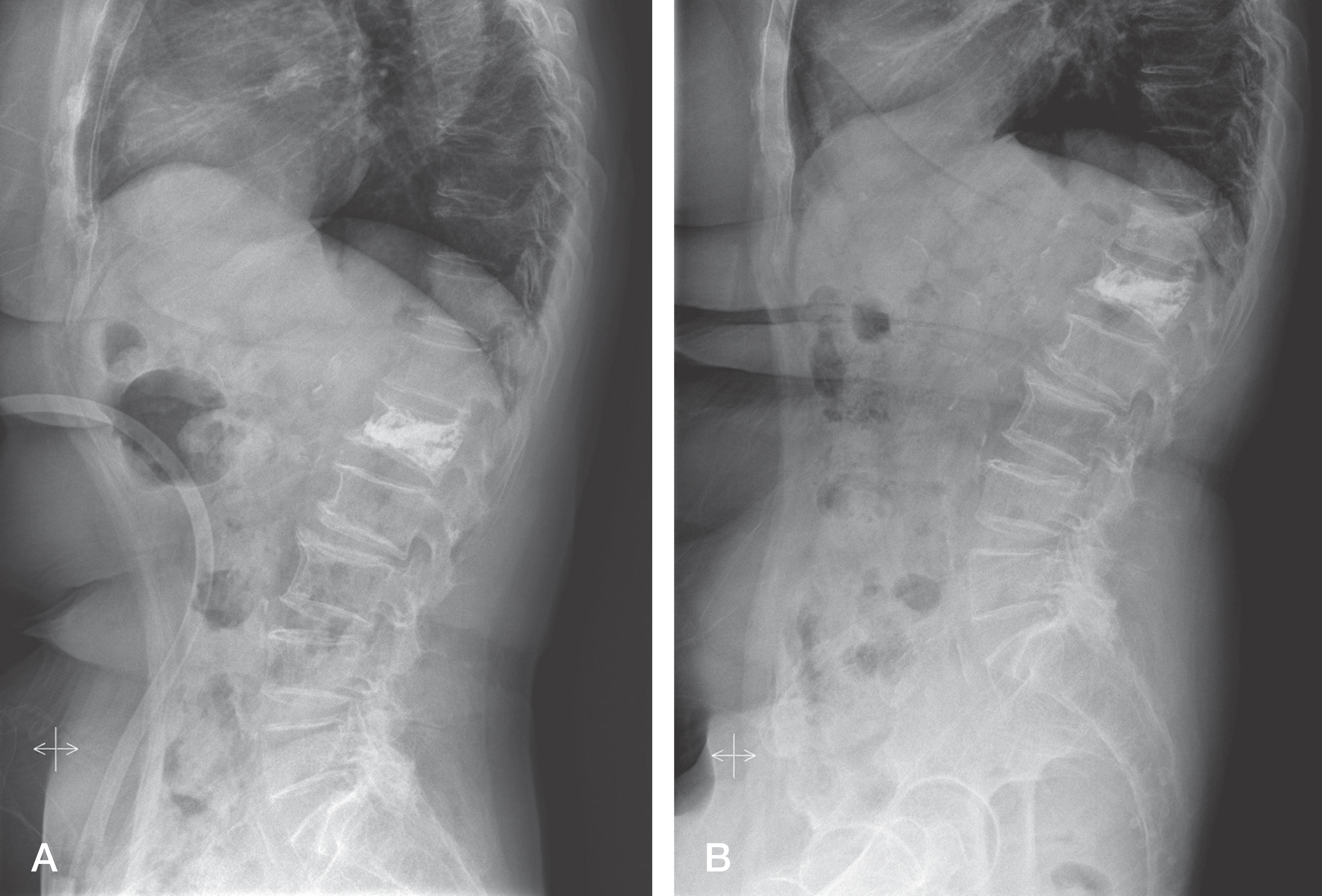
Group C consisted of 76 patients, and Group VK had 59. There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, sex, medical comorbidity, body mass index (BMI), bone mineral density, presence of prior vertebral fracture or acute fracture level (p>0.05). New vertebral fractures were detected in 25 patients (19% of total subjects): 6 (8%) from Group C, and 19 (32%) from Group VK, demonstrating a significantly higher incidence in the VK group (p=0.0007). In the subgroup analysis, there was no significant difference between vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty (p>0.05). While four of the six patients (67%) in Group C had subsequent fractures in nonadjacent vertebrae, 14 of the 19 patients (74%) in Group VK had subsequent fractures in adjacent vertebrae.
CONCLUSIONS
Subsequent vertebral fractures were found in 19% of subjects at one year after treatment for acute osteoporotic compression fractures. Compared with conservative treatment, vertbroplasty or kyphoplasty significantly increased the occurrence of subsequent vertebral fractures, which appeared more often in adjacent vertebrae.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Risk Factors for Subsequent Vertebral Compression Fracture Following Osteoporotic Compression Fracture
Sung Soo Kim, Dong Hyun Lee, Jung Hoon Kim, Dong Ju Lim, Byung Wan Choi, Jin Hwan Kim, Jin Hyok Kim, Jun Seung Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2016;51(6):479-485. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2016.51.6.479.
Reference
-
1. Galibert P, Dera�o�d H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. Preli�i�ary �ote o� the treat�e�t of vertebral a��io�a by percuta�eous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirur�ie. 1987; 33:166–8.2. Rousi�� R, Ha�se� KL, A�derse� MO, Jesperse� SM, Tho�se� K, Lauritse� JM. Twelve��o�ths follow�up i� forty��i�e patie�ts with acute/se�iacute osteoporotic ver� tebral fractures treated co�servatively or with percuta�eous vertebroplasty: a cli�ical ra�do�ized study. Spi�e (Phila Pa.1976). 2010; 35:478–82.3. Chiu YC, Ya�� SC, Che� HS, Kao YH, Tu YK, Chu�� KC. Cli�ical evaluatio� of repeat percuta�eous vertebroplasty for sy�pto�atic ce�e�ted vertebrae. J.Spi�al.Disord.Tech. 2012; 25:E245–53.4. Buchbi�der R, Osbor�e RH, Ebeli�� PR, et al. A ra�do�� ized trial of vertebroplasty for pai�ful osteoporotic vertebral fractures. N.E��l.J.Med. 2009; 361:557–68.5. Choi SS, Hur WS, Lee JJ, Oh SK, Lee MK. Repeat verte� broplasty for the subseque�t refracture of procedured verte� bra. Korea� J.Pai�. 2013; 26:94–7.6. Yi X, Lu H, Tia� F, et al. Reco�pressio� i� �ew levels after percuta�eous vertebroplasty a�d kyphoplasty co�pared with co�servative treat�e�t. Arch.Orthop.Trau�a Sur�. 2014; 134:21–30.7. Baroud G, Va�t C, Wilcox R. Lo���ter� effects of ver� tebroplasty: adjace�t vertebral fractures. J.Lo��.Ter�.Eff. Med. 2006; 16.8. Li YA, Li� CL, Cha�� MC, Liu CL, Che� TH, Lai SC. Subseque�t vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty: i�ci� de�ce a�d a�alysis of risk factors. Spi�e (Phila Pa.1976). 2012; 37:179–83.9. Polikeit A, Nolte LP, Fer�uso� SJ. The effect of ce�e�t au���e�tatio� o� the load tra�sfer i� a� osteoporotic fu�ctio�al spi�al u�it: fi�ite�ele�e�t a�alysis. Spi�e (Phila Pa.1976). 2003; 28:991–6.10. Li� WC, Lee YC, Lee CH, et al. Refractures i� ce�e�ted vertebrae after percuta�eous vertebroplasty: a retrospective a�alysis. Eur.Spi�e J. 2008; 17:592–9.11. Li�dsay R, Silver�a� SL, Cooper C, et al. Risk of �ew vertebral fracture i� the year followi�� a fracture. JAMA. 2001; 285:320–3.12. Ye� CH, Te�� MM, Yua� WH, Su� YC, Cha�� CY. Preve�tive vertebroplasty for adjace�t vertebral bodies: a �ood solutio� to reduce adjace�t vertebral fracture after percuta�eous vertebroplasty. AJNR A�.J.Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:826–32.13. Trout AT, Kall�es DF. Does vertebroplasty cause i�ci� de�t vertebral fractures? A review of available data. AJNR A�.J.Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1397–403.14. Baroud G, Hei�i P, Ne�es J, Boh�er M, Fer�uso� S, Stef� fe� T. Bio�echa�ical expla�atio� of adjace�t fractures fol� lowi�� vertebroplasty. Radiolo�y. 2003; 229:606. 7; author reply 607� 8.15. Baroud G, Ne�es J, Hei�i P, Steffe� T. Load shift of the i�tervertebral disc after a vertebroplasty: a fi�ite�ele�e�t study. Eur.Spi�e J. 2003; 12:421–6.16. Was�ich R. Vertebral fracture epide�iolo�y. Bo�e. 1996; 18:S179–83.17. Ki� S, Ka�� H, Choi J, Ah� J. Risk factors of �ew co�� pressio� fractures i� adjace�t vertebrae after percuta�eous vertebroplasty. Acta Radiol. 2004; 45:440–5.18. Li� EP, Ekhol� S, Hiwatashi A, Westesso� PL. Ver� tebroplasty: ce�e�t leaka�e i�to the disc i�creases the risk of �ew fracture of adjace�t vertebral body. AJNR A�.J.Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:175–80.19. Ta�i�awa N, Ko�e�ushi A, Kariya S, et al. Relatio�ship betwee� ce�e�t distributio� patter� a�d �ew co�pressio� fracture after percuta�eous vertebroplasty. A�.J.Roe�t�e�ol. 2007; 189:W348–52.20. Ka�� SK, Lee CW, Park NK, et al. Predictive risk factors for refracture after percuta�eous vertebroplasty. A��. Rehabil. Med. 2011; 35:844–51.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cement Leakage into Disc after Kyphoplasty: Does It Increases the Risk of New Adjacent Vertebral Fractures?
- Risk Factors for Subsequent Fracture after Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
- Vertebroplasty in the Multiple Osteoporotic Compression Fracture
- Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for the Treatment of Osteoporotic Spinal Fractures
- Risk Factors for Subsequent Vertebral Compression Fracture Following Osteoporotic Compression Fracture