Yonsei Med J.
2014 May;55(3):766-772. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.766.
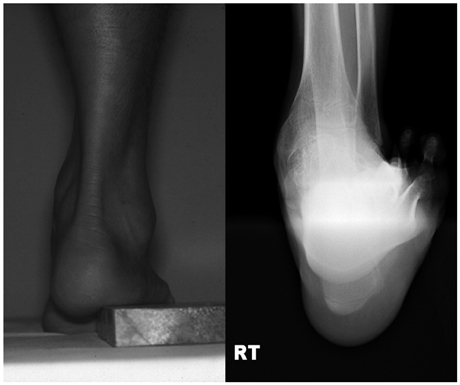
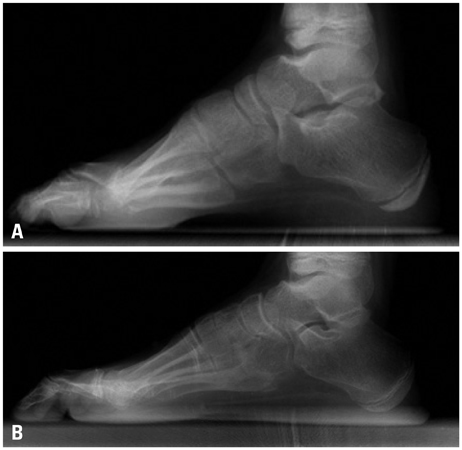
Changes in Dynamic Pedobarography after Extensive Plantarmedial Release for Paralytic Pes Cavovarus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Severance Children's Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, International St. Mary's Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kunbopark@gmail.com
- KMID: 2068689
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.766
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Plantarmedial release and first ray extension osteotomy are often combined to treat paralytic cavovarus foot deformity. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of additional first ray extension osteotomy in terms of dynamic pedobarography.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We reviewed findings of pre- and postoperative plain radiography and dynamic pedobarography for 25 patients in whom the flexibility of the hindfoot was confirmed by the Coleman block test. The results of treatment by extensive plantar medial release with first ray osteotomy (group I) were compared with the results of treatment by extensive plantar medial release alone (group II).
RESULTS
Plain radiographs obtained pre- and postoperatively showed no statistically significant improvement in each group. Only in group I, peak forces at the 1st metatarsal head, 2nd metatarsal head and medial calcaneus were increased after operation.
CONCLUSION
In paralytic hindfoot flexible cavovarus, extensive plantarmedial release with first ray osteotomy improve foot pressure distribution more than extensive plantarmedial release alone.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holmes JR, Hansen ST Jr. Foot and ankle manifestations of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Foot Ankle. 1993; 14:476–486.
Article2. McCluskey WP, Lovell WW, Cummings RJ. The cavovarus foot deformity. Etiology and management. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; 27–37.3. Schwend RM, Drennan JC. Cavus foot deformity in children. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003; 11:201–211.
Article4. Mubarak SJ, Van Valin SE. Osteotomies of the foot for cavus deformities in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009; 29:294–299.
Article5. Paulos L, Coleman SS, Samuelson KM. Pes cavovarus. Review of a surgical approach using selective soft-tissue procedures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980; 62:942–953.
Article6. Samilson RL, Dillin W. Cavus, cavovarus, and calcaneocavus. An update. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 125–132.7. Sherman FC, Westin GW. Plantar release in the correction of deformities of the foot in childhood. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:1382–1389.
Article8. Jahss MH. Evaluation of the cavus foot for orthopedic treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 52–63.
Article9. Coleman SS, Chesnut WJ. A simple test for hindfoot flexibility in the cavovarus foot. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977; 60–62.
Article10. Drennan JC. Current concepts in myelomeningocele. Instr Course Lect. 1999; 48:543–550.11. Herring JA. Tachdjian's pediatric orthopaedics. 4th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;2008. p. 1139–1186.12. Bradley GW, Coleman SS. Treatment of the calcaneocavus foot deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:1159–1166.
Article13. Azmaipairashvili Z, Riddle EC, Scavina M, Kumar SJ. Correction of cavovarus foot deformity in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005; 25:360–365.
Article14. Chang CH, Miller F, Schuyler J. Dynamic pedobarograph in evaluation of varus and valgus foot deformities. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002; 22:813–818.
Article15. Chan G, Sampath J, Miller F, Riddle EC, Nagai MK, Kumar SJ. The role of the dynamic pedobarograph in assessing treatment of cavovarus feet in children with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007; 27:510–516.
Article16. Metaxiotis D, Accles W, Pappas A, Doederlein L. Dynamic pedobarography (DPB) in operative management of cavovarus foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int. 2000; 21:935–947.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Snapping Pes Anserinus Caused By Gracilis Tendon: A New Mechanism Proposed by Dynamic Knee Ultrasonography
- Evaluation of the Outcomes according to Etiology in the Pediatric Pes Planovalgus after Lateral Column Lengthening: By Radiologic and Pedobarographic Measurements
- Radiologic Measurement of Pes Cavus
- Surgical Correction of Paralytic deformity of the Lips in Hansen's Disease
- Sonoanatomic Variation of Pes Anserine Bursa