Transcranial Direct Middle Meningeal Artery Puncture for the Onyx Embolization of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Involving the Superior Sagittal Sinus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea. smyoon@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2067092
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.57.1.54
Abstract
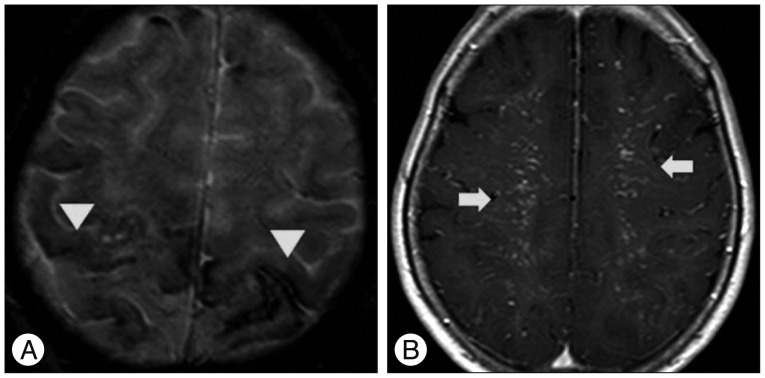
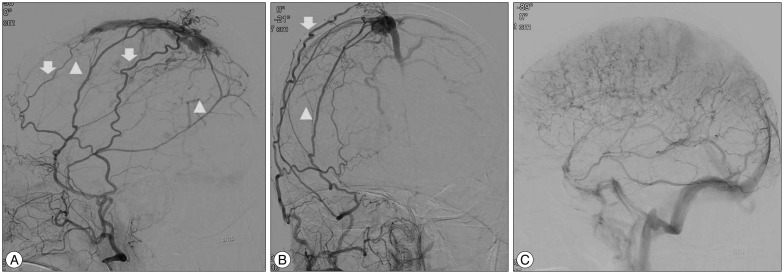
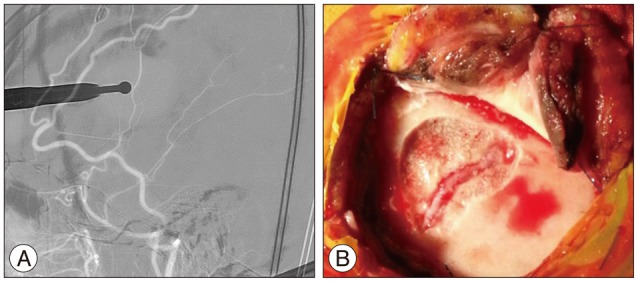
- A 66-year-old woman presented with intermittent paraparesis and generalized tonic-clonic seizure. Cerebral angiography demonstrated dural arteriovenous fistula (AVF) involving superior sagittal sinus (SSS), which was associated with SSS occlusion on the posterior one third. The dural AVF was fed by bilateral middle meningeal arteries (MMAs), superficial temporal arteries (STAs) and occipital arteries with marked retrograde cortical venous reflux. Transfemoral arterial Onyx embolization was performed through right MMA and STA, but it was not successful, which resulted in partial obliteration of dural AVF because of tortuous MMA preventing the microcatheter from reaching the fistula closely enough. Second procedure was performed through left MMA accessed by direct MMA puncture following small decortications of cranium overlying the MMA using diamond drill one week later. Microcatheter could be located far distally to the fistula through 5 F sheath placed into the MMA and complete obliteration of dural AVF was achieved using 3.9 cc of Onyx.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Direct Puncture of the Superficial Temporal Artery in Embolization of a Scalp Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
Gregory B. Walker, Alick P. Wang, Jeremiah Hadwen, Undrakh-Erdene Erdenebold, Razmik Bebedjian, Patrick Sullivan, Marlise P. Santos, Chad Chenier, Stephen Karwaski, Katie Caron, Gabriella Varga, Jennifer Lyon, Howard J. Lesiuk, Navraj Heran, Manraj Heran, Aiman Quateen, Brian J. Drake, Eduardo Portela De Oliveira, Mario Kontolemos, Robert Fahed
Neurointervention. 2023;18(1):67-71. doi: 10.5469/neuroint.2022.00465.Role of surgery in management of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
Young Sill Kang, Won-Sang Cho, Sung Ho Lee, Kangmin Kim, Hyun-Seung Kang, Jeong Eun Kim
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2023;25(2):117-131. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2023.E2022.10.006.
Reference
-
1. Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, et al. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas : clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology. 1995; 194:671–680. PMID: 7862961.
Article2. Fukai J, Terada T, Kuwata T, Hyotani G, Raimura M, Nakagawa M, et al. Transarterial intravenous coil embolization of dural arteriovenous fistula involving the superior sagittal sinus. Surg Neurol. 2001; 55:353–358. PMID: 11483194.
Article3. Gross BA, Ropper AE, Popp AJ, Du R. Stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Focus. 2012; 32:E18. PMID: 22537127.
Article4. Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Rosenblum M, Cahan L. Treatment of dural arteriovenous malformations involving the superior sagittal sinus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 9:337–343. PMID: 3128082.5. Houdart E, Saint-Maurice JP, Chapot R, Ditchfield A, Blanquet A, Lot G, et al. Transcranial approach for venous embolization of dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:280–286. PMID: 12186454.
Article6. Ihn YK, Kim MJ, Shin YS, Kim BS. Dural arteriovenous fistula involving an isolated sinus treated using transarterial onyx embolization. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 52:480–483. PMID: 23323170.
Article7. Kakarla UK, Deshmukh VR, Zabramski JM, Albuquerque FC, McDougall CG, Spetzler RF. Surgical treatment of high-risk intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae : clinical outcomes and avoidance of complications. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:447–457. discussion 457-459. PMID: 17881955.8. Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Okahara M, Tanoue S, Sagara Y, Matsumoto S, et al. Treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas : current strategies based on location and hemodynamics, and alternative techniques of transcatheter embolization. Radiographics. 2004; 24:1637–1653. PMID: 15537974.
Article9. Koh JS, Ryu CW, Bang JS, Lee SW. Transcranial Approach for Arterial Embolization of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Within the Wall of the Superior Sagittal Sinus. A Case Report. Neurointervention. 2007; 2:117–121.10. Kurl S, Saari T, Vanninen R, Hernesniemi J. Dural arteriovenous fistulas of superior sagittal sinus : case report and review of literature. Surg Neurol. 1996; 45:250–255. PMID: 8638222.11. Luo CB, Chang FC, Wu HM, Chung WY. Transcranial embolization of a transverse-sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous fistula carried out through a decompressive craniectomy. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007; 149:197–200. discussion 200. PMID: 17091209.
Article12. Oh JT, Chung SY, Lanzino G, Park KS, Kim SM, Park MS, et al. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas : clinical characteristics and management based on location and hemodynamics. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2012; 14:192–202. PMID: 23210047.
Article13. Ohara N, Toyota S, Kobayashi M, Wakayama A. Superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas treated by stent placement for an occluded sinus and transarterial embolization. A case report. Interv Neuroradiol. 2012; 18:333–340. PMID: 22958774.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Transcranial Approach for Arterial Embolization of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Within the Wall of the Superior Sagittal Sinus : A Case Report
- Onyx Embolization of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula, using Scepter C Balloon Catheter: a Case Report
- Endovascular Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Single Center Experience
- Feasibility and Effectiveness of Direct Puncture and Onyx Embolization for Transverse Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
- A Case of Intraosseous Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Involving Diploic Vein Treated with Transarterial Onyx Embolization