The Psychopathological Influence of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in Korean Male : An Analysis of Multiphasic Personal Inventory Test Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Guro Teun Teun Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Inha University Hospital, College of Medicine, Inha University, Incheon, Korea. nsyoon@gmail.com
- 3Department of Radiology, Seoul Regional Military Manpower Administration, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2066979
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.1.13
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
There are few published studies which have documented psychopathological abnormalities in patients with of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) The aim of this study was to evaluate the psychopathological influence of AIS in Korean 19-year-old males.
METHODS
The authors compared the Korean military multiphasic personal inventory (KMPI) military profiles of 105 AIS cases (more than 10 degrees of Cobb's angle without surgical treatment) with the KMPI profiles of 108 normal controls. The AIS group was split depending on Cobb's angle to further evaluate this relation by the severity of AIS.
RESULTS
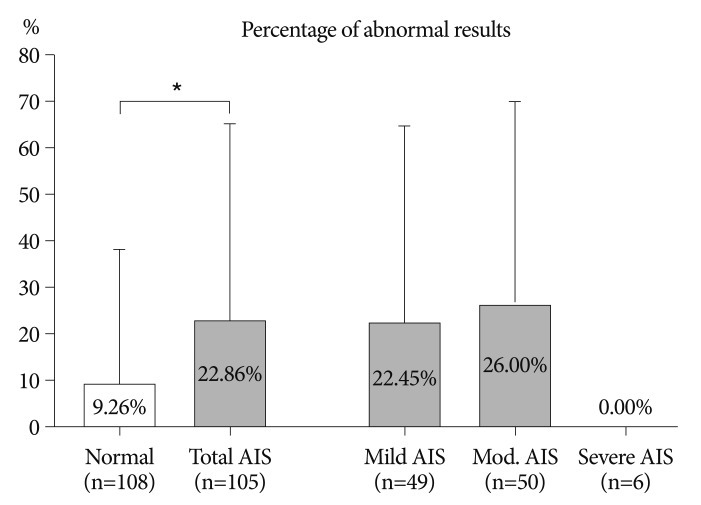
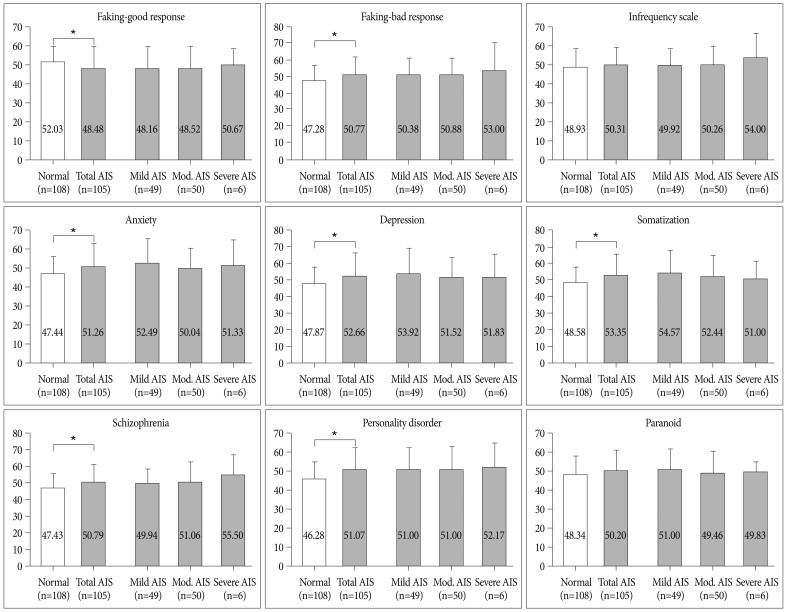
A significantly decreased result on the faking-good response scale and an significantly increased result on the faking-bad response were observed in the AIS group compared to the control (p<0.012). The neurosis scale results, including anxiety, depression and somatization symptoms, were significantly increased in the AIS group compared to the control (p<0.010). The severity level of personality disorder and schizophrenia were also significantly increased in the AIS group (p<0.010). Differences in KMPI scale scores were not related to the severity of AIS.
CONCLUSION
Young males with AIS tend to have abnormal results on the multiphasic personal inventory test compared to normal volunteers, suggesting that AIS may be related to psychopathology in the young male group in Korea. Although these psychopathology in AIS were differently observed compared to normal controls, but not interfered with military life. Clinicians are recommended to pay attention the psychopathological traits of patients with AIS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Result of Multiphasic Personality Inventory among People with Scoliosis: Retrospective Cross-Sectional Analysis of Military Candidate in Korea
Seung Keun Kim, Taehyun Kim, Jeong Seok Seo, Seok Woo Moon, Tae Ho Kim, Jonggook Lee, Beomwoo Nam
J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2017;56(4):181-185. doi: 10.4306/jknpa.2017.56.4.181.Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Treatment by a Korean Neurosurgeon: The Changing Role for Neurosurgeons
Seung-Jae Hyun, Woong-Beom Kim, Young-Seop Park, Ki-Jeong Kim, Tae-Ahn Jahng, Yongjung J. Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(1):50-53. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.50.Can Breast Asymmetry Following the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Scoliosis with Growing Rod Be Prevented? : A Preliminary Analysis
Yunus Atici, Barış Polat, Sinan Erdogan, Tahsin Gürpınar, Serdar Demiröz
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2020;63(2):228-236. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2019.0192.
Reference
-
1. Bridwell KH, Shufflebarger HL, Lenke LG, Lowe TG, Betz RR, Bassett GS. Parents' and patients' preferences and concerns in idiopathic adolescent scoliosis : a cross-sectional preoperative analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:2392–2399. PMID: 10984794.
Article2. Bunch WH, Chapman RG. Patient preferences in surgery for scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67:794–799. PMID: 3997933.
Article3. Bunge EM, Juttmann RE, de Kleuver M, van Biezen FC, de Koning HJ. Health-related quality of life in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis after treatment : short-term effects after brace or surgical treatment. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16:83–89. PMID: 16609857.
Article4. Danielsson AJ, Hasserius R, Ohlin A, Nachemson AL. Health-related quality of life in untreated versus brace-treated patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis : a long-term follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:199–205. PMID: 20038869.
Article5. Danielsson AJ, Wiklund I, Pehrsson K, Nachemson AL. Health-related quality of life in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis : a matched follow-up at least 20 years after treatment with brace or surgery. Eur Spine J. 2001; 10:278–288. PMID: 11563612.
Article6. Fiedler ER, Oltmanns TF, Turkheimer E. Traits associated with personality disorders and adjustment to military life : predictive validity of self and peer reports. Mil Med. 2004; 169:207–211. PMID: 15080240.
Article7. Haefeli M, Elfering A, Kilian R, Min K, Boos N. Nonoperative treatment for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis : a 10- to 60-year follow-up with special reference to health-related quality of life. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:355–366. discussion 367. PMID: 16449911.8. Haher TR, Merola A, Zipnick RI, Gorup J, Mannor D, Orchowski J. Meta-analysis of surgical outcome in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. A 35-year English literature review of 11,000 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:1575–1584. PMID: 7570172.9. Imanzadeh M, Asghari A, Malaei M, Jalili M. Relationship between scoliosis and depression anxiety in athlete and non athlete male students in selected universities of Tehran. Aust J Basic Appl Sci. 2011; 5:307–311.10. Kasai Y, Morishita K, Kawakita E, Kondo T, Uchida A. Pre-and postoperative psychological characteristics in mothers of patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2006; 15:1103–1107. PMID: 16308723.
Article11. Kasai Y, Takegami K, Uchida A. A study of patients with spinal disease using Maudsley Personality Inventory. Int Orthop. 2004; 28:56–59. PMID: 12851787.
Article12. Matsunaga S, Hayashi K, Naruo T, Nozoe S, Komiya S. Psychologic management of brace therapy for patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:547–550. PMID: 15738788.
Article13. Matsunaga S, Sakou T, Nozoe S. Psychological effects of brace therapy on patients with idiopathic scoliosis. J Orthop Sci. 1997; 2:391–395.
Article14. Misterska E, Glowacki M, Harasymczuk J. Personality characteristics of females with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis after brace or surgical treatment compared to healthy controls. Med Sci Monit. 2010; 16:CR606–CR615. PMID: 21119579.15. Noonan KJ, Dolan LA, Jacobson WC, Weinstein SL. Long-term psychosocial characteristics of patients treated for idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997; 17:712–717. PMID: 9591971.
Article16. Paik HK, Oh CH, Choi K, Kim CE, Yoon SH, Chung J. Influence of history of brain disease or brain trauma on psychopathological abnormality in young male in Korea : analysis of multiphasic personal inventory test. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 50:114–118. PMID: 22053230.
Article17. Reitan RM, Wolfson D. Emotional disturbances and their interaction with neuropsychological deficits. Neuropsychol Rev. 1997; 7:3–19. PMID: 9243528.
Article18. Rinella A, Lenke L, Peelle M, Edwards C, Bridwell KH, Sides B. Comparison of SRS questionnaire results submitted by both parents and patients in the operative treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:303–310. PMID: 14752354.
Article19. van Balen HG, de Mey HR, van Limbeek J. A neurocorrective approach for MMPI-2 use with brain-damaged patients. Int J Rehabil Res. 1999; 22:249–259. PMID: 10669974.
Article20. Weiss HR, Cherdron J. [Effects of Schroth's rehabilitation program on the self concept of scoliosis patients]. Rehabilitation (Stuttg). 1994; 33:31–34. PMID: 8165360.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Psychopathological Influence of Congenital Heart Disease in Korean Male Adolescents: An Analysis of Multiphasic Personal Inventory Test Results
- Psychopathological Influence of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Male Adolescent
- The Impact of Primary Spontaneous Pneumothorax on Multiphasic Personal Inventory Test Results in Young South Korean Males
- Influence of History of Brain Disease or Brain Trauma on Psychopathological Abnormality in Young Male in Korea : Analysis of Multiphasic Personal Inventory Test
- Result of Multiphasic Personality Inventory among People with Scoliosis: Retrospective Cross-Sectional Analysis of Military Candidate in Korea